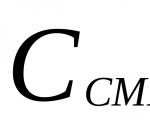Business reputation analysis. Assessment of the company's business reputation. Methods for assessing business reputation using the goodwill method
"The market value of goodwill is perhaps the most exotic valuation object in Russian business practice"
Ella Tomilina, deputy general director LLC "Energocapital-Consult", Ph.D. n.
You can have a company's business reputation or goodwill assessed at our valuation company.
Valuation of goodwill from an appraiser's point of view
On the one hand, this is due to the relative novelty of such an asset for Russian companies in their modern “market status”, on the other hand, with the features and essence of goodwill itself as such.
In everyday understanding, any company has one or another business reputation, enshrined in Article 150 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation "Intangible benefits", the object of assessment can only be business reputation placed on the balance sheet of the enterprise. In the balance sheet, such a value appears only if the enterprise has made a purchase of another enterprise. The value of your own business reputation is not reflected in the balance sheet! Moreover, this intangible asset does not exist separately from the enterprise - it is inalienable property. It cannot be disposed of separately from the enterprise. This feature distinguishes this type assets from all other accounting objects, including other types of intangible assets (IMA).
Has no business reputation certain period life. Domestic practice proceeds from the fact that most of the possible factors that make up its positive side, bring economic benefits for 20 years from the date of acquisition. During this time, this intangible asset must be amortized. However, it is necessary to be aware that the adopted depreciation period is conditional and may affect the accuracy of calculating the financial result of the enterprise. Some countries have introduced a maximum depreciation period: Japan - 5 years, the Netherlands, Sweden - 10, Australia - 20, Canada - 40.
Until recently, goodwill was amortized in the USA, but now at the request of the SEC American companies, whose shares are listed on open market, are obliged to annually re-evaluate this intangible asset. Perhaps Russia, which is on the eve of the transition to IFRS, will take this experience into service.
IN regulatory documents, scientific and methodological literature There is no unambiguous interpretation of the concept of “business reputation”. According to Russian accounting (PBU 14/2000 “Accounting for intangible assets”), business reputation is taken into account as part of intangible assets and is defined as the difference between the purchase price of the organization (the cost of the acquired property complex as a whole) and the carrying amount of all its assets and liabilities. This definition differs significantly from the definition in International Accounting Standard No. 22, according to which goodwill is defined as the difference between the purchase price and the fair, that is, market value of the firm's assets.
In this case, it is essentially implied that the specified excess of the enterprise value is associated with the possibility of obtaining a higher level of profit (compared to the average market level of investment efficiency) through the use of more effective system management, dominant positions on commodity market, application of new technologies, etc.
By the way, goodwill is not necessarily a positive value. If the market value operating enterprise below book value net assets, then goodwill will be negative. Of course, this does not necessarily indicate a “bad reputation” in the common sense. A positive reputation means that the value of an enterprise exceeds the total value of its assets and liabilities, that the enterprise has something inherent in it that is not determined by the value of its assets and liabilities, that is, more in simple language business reputation is a set of assets that encourage customers to use the goods and services of a particular company.
Division of goodwill during valuation
Conventionally, these assets that make up business reputation can be divided into:
- Intangible assets (IMA), inseparable from the company as a whole (availability of trained personnel, management system, constant customer base, a niche in the market, a stable and positive reputation of goods, awareness of customers, creditors, suppliers, the public about reliability, quality of service, financial stability).
- Intangible assets inseparable from specific employees of the company ( professional qualities and the reputation of both its owners and employees).
- Intangible assets that can be separated from the company (the presence of a recognizable and proven trademark, copyrights, licenses, patents, long-term or unique contracts, customer database).
Methods for assessing the value of business reputation
There are two main approaches to determining the value of business reputation.
- The first involves assessing reputation as a source of additional income and uses methods of isolating economic effect from goodwill in business (the “excess profit” method, the method of advantage in price or in the volume of product sales).
- The second approach is based on taking into account the results of specific transactions. The amount of acquired business reputation is taken as the difference between the amount actually paid for the enterprise and the total value of individual assets and liabilities of this enterprise recorded in the most recent balance sheet. There are known attempts to use “advanced” valuation methods - option valuation (ROV): knowing the value of the business (company capitalization), the market value of assets is determined using the Black-Scholes formula, and then goodwill is calculated as the difference between the market price of assets and their book value.
The importance of a correct assessment of business reputation for some areas of business is very great. In particular, this applies to the trade and services sector, where the value of goodwill is a significant value along with the valuation of tangible assets in determining the value of a business. Most beautiful examples So far from foreign practice. Thus, Philip Morris Corporation bought Kraft Foods for almost $13 billion, which was four times its book value, only because its goodwill was valued accordingly.
If you need to assess the business reputation of a company, contact us using the contact information. Call us, we will help!
"Head of a construction organization", 2010, N 9
A company's reputation is an intangible asset that can, however, bring quite tangible dividends. It can influence all aspects of a business, attracting or, conversely, repelling customers, suppliers, partners... How to assess the reputation of an organization and in what cases should this be done?
What is goodwill?
Recently, more and more managers of Russian companies are thinking about value based management (VBM). Many questions that until recently were of interest only professional appraisers business are included in the daily affairs of top managers and owners. A modern manager, in addition to ideas about how certain decisions affect the value of the company, must know exactly which assets - tangible and intangible - contain its value. Hence the interest in such a relatively new concept for Russian economic relations as intangible assets, the most important of which is business reputation.
In world practice, it is customary to determine the value of an organization’s business reputation using the concept of “goodwill” (from the English good will). One of the most accurate definitions of goodwill is given by G. Desmond and R. Kelly in the book “A Guide to Business Valuation.” Goodwill is defined “as the sum of those business or personal attributes that encourage customers to continue to use the services of a given enterprise or of this person and which bring the company a profit in excess of that required to generate a reasonable return on all other assets of the enterprise, including all those intangible assets that can be separated and separately valued"<1>.
<1>Desmond G., Kelly R. Business Valuation Guide. M.: Russian Society of Appraisers, 1996.
The value of goodwill can be either positive or negative. A positive business reputation is formed due to the fact that the value of an enterprise exceeds the value of its assets and liabilities. This means that the company has a certain quality that motivates customers to purchase its products and services. According to Lev Baruch, reputation is a guarantee for which people pay money.<2>.
<2>Baruch L. Intangible assets. Management, measurement, reporting. M., 2003.
In most cases, business owners overvalue their existing intangible assets, which causes the realizable value of the business to increase significantly. It is important to consider that intangible (intangible) capital must be converted into income and the indicator of this income must significantly exceed the market average.
Goodwill will be negative (in this case it is sometimes called badwill) if the market value of the enterprise is lower than the book value of net assets: for example, if the brand does not win the competition and does not allow the product to be sold at a higher price than that of a competitor. In this case, reputation negatively affects the final value of the company, since with comparable tangible assets it will be more difficult to sell products than with a positive reputation.
The issue of assessing the goodwill of a Russian investment and construction company is not so simple. Firstly, it is very difficult to determine the market value of a developer’s business - the shares of almost all construction companies are not quoted on the market, and there are no active mergers and acquisitions that could give an idea of the price of a particular company. Secondly, today developers in Russia do not always receive competitive advantage due to having a good and objective business reputation. In conditions of shortage of space for development great value has the proximity of the company's top officials to the authorities local authorities. That is, a developer can have a reputation for “having access to the body”, receive the most attractive sites for development - and he is already winning.
Despite the obvious difficulty objective assessment business reputation in Russian conditions, construction companies Nevertheless, such attempts were made. So, in 2005 construction group LSR was the first in the St. Petersburg market to value its business reputation at almost $50 million and included this figure in its balance sheet. At that time this exotic by standards Russian business reception, according to experts, indicated ambitious plans company, including its preparation for IPO. Leaders of others construction companies assessed LSR's step as progressive: Western companies have long understood that brand and reputation are valuable assets, against which the company, for example, can attract financing.
We can recall another illustrative example. In 2003, the Social Initiative Corporation, as a result of calculations carried out using the IBRD methodology, estimated its reputation at 70% of its capitalization. That is, with a paid-in share capital equal to $270 million, the value of the Social Initiative's goodwill amounted to $190 million. At that time, company representative Nikolai Deryabin stated in the media: the reputation assessment indicates that his organization thinks not only about the present, but also about the future. Today, knowing the sad history of the Social Initiative for seven thousand domestic shareholders, these facts can only be perceived as a curiosity.
When is an assessment needed?
One of the most important reasons why it is necessary to estimate the value of goodwill is the preparation of a sale or purchase transaction or a merger or acquisition of a company. If the acquired entity generates revenues in excess of the rate of return on its tangible and identifiable intangible assets, then the owner of the company has the right to demand a premium over the cost of the identified assets equal to the present value of these additional revenues. In this case, goodwill acts as compensation for future additional income.
Note. Russian courts are increasingly considering claims for damage to the business reputation of a company. But if the reputation has not been reliably assessed in advance, it is impossible to correctly determine the amount of damage.
Another important reason for assessing goodwill is the preparation of financial statements in accordance with international standards financial statements. IFRS requires an annual impairment test for goodwill. If this happens, adjustments must be made to the reporting. The growing interest of domestic organizations in IFRS and the transition of many of them to this reporting system are among the reasons for the growing interest in methods for measuring the value of such an intangible asset as goodwill.
An assessment of business reputation is also required in cases where it is necessary to assess the damage caused to it. This can happen, for example, if the media publishes materials discrediting the business reputation of the company (such publications may be ordered by competitors). The most famous example of causing damage in Russian practice- litigation between the Kommersant Publishing House and Alfa Bank OJSC in the summer of 2004. The reason for the litigation was an article published in the Kommersant newspaper, “The banking crisis has hit the streets,” which spoke about Alfa Bank’s difficulties with liquidity. The note caused panic among customers, as a result of which an increased number of demands for the return of deposits brought the bank to the brink of collapse. Intangible damage to the bank’s business reputation was assessed and satisfied by the court in the amount of 270 million rubles.
Another category of cases when the injured party can go to court to claim compensation for damage to business reputation are situations with illegal production of products and use of brands, brands etc., belonging to another company or similar to them. Similar situations are typical for the construction sector, when an unscrupulous developer assigns a name that is confusingly similar to the name of a bona fide company, and thus misleads consumers.
While the Russian practice of litigation in cases of damage to business reputation is represented by only isolated precedents, in the West such cases are very common, and the amount of damage often amounts to tens of millions of dollars. However, as the example of the litigation between Alfa Bank OJSC and Kommersant Publishing House shows, the amount of payments in Russian practice is already approaching Western standards.
Quantitative assessment methods
There are two main approaches to determining the value of business reputation.
Excess Profit Method involves assessing goodwill as a source of additional income. According to this methodology, there is a direct contrast between the profitability levels of the company being valued and its competitors (or similar companies in the industry) with the subsequent capitalization of that part that cannot be explained by “material” influence (assets).
Balance sheet method is based on taking into account the results of specific trading operations. The amount of goodwill acquired is reported as the difference between the amount paid for the entity and the total value of the entity's assets and liabilities as recorded in the most recent accounting report or balance sheet.
Considering the balance method, one cannot help but note its cumbersomeness and inconvenience. The comparative method is more reliable because the measurement of goodwill in a business must be tangible. After all, it is she who explains why, for example, clients buy apartments in houses under construction by this particular developer at prices higher than the market average.
There are known attempts to use “advanced” option methods valuations (ROV): knowing the value of the business (company capitalization), using the Black-Scholes formula, the market value of assets is determined, and then business reputation is calculated as the difference between the market price of assets and their book value.
To assess goodwill, the following documents are required:
- financial statements for the last three years, as well as balance sheet and income statement;
- audit reports on financial statements companies (if any);
- a list of the company's fixed assets as of the date of assessment;
- information about all existing assets of the enterprise (real estate, shares of third-party organizations, bills, inventories, patents, licenses, etc.) with a transcript and explanations;
- deciphering the company's accounts receivable;
- availability information subsidiaries And financial statements on them.
Qualitative assessment methods
A qualitative approach to assessing reputation is based on the statement that reputation is the image of a company in the eyes of certain target groups, which is not amenable to exact quantification. A variation of the qualitative approach method is the expert approach, which, in turn, is divided into rating and recommendation. The first includes the compilation of business reputation ratings by independent organizations. Thus, a rating study of the reputation of developers in Krasnodar, conducted by the Villan company in 2008, showed that the importance of non-price factors of a developer’s reputation varies greatly for purchases for residential purposes and for investment purposes. Buyers of apartments for residential purposes are sensitive to factors such as the developer’s work on Federal law dated December 30, 2004 N 214-FZ, brand recognition, quality of construction. For investment purchases, these factors are much less important. At the same time, such a factor as whether the developer currently has other ongoing projects (houses under construction at the same time) is decisive for buyer-investors and is practically unimportant for buyers - future residents.
The recommendation method involves experts discussing the company’s goodwill and making recommendations. Analysis of documents and interviews with experts usually touch on a block of issues related to the reputation of the company’s owners and top managers, its corporate strategy, financial situation, the composition and quality of the management team, the reputation of the product or service, as well as the social responsibility of the organization. It must be borne in mind that the contribution of all these parameters to the creation of reputation is not the same. The peculiarities of reputation as a social phenomenon lie in its continuous development, are supplemented by new criteria, and change the degree of significance in the definition of the concept of “good business reputation.”
The value of an expert interview lies in the possibility of moving from the level of simply recording opinions to explaining the source of their formation. This circumstance is fundamental for further work on developing effective strategies reputation management in the organization. When conducting repeated studies, parameters such as the completeness and adequacy of experts’ ideas about the organization’s business, its strategy, projects, achievements, and the frequency of reproduction of certain assessments can be measured and compared.
Note. The practice of conducting reputation research shows that for a geographically localized company it is optimal to conduct 35 - 37 interviews. Increasing the number of respondents significantly delays and increases the cost of the study, while practically not improving its quality.
Experts in the field of reputation audit believe that it is optimal to use both quantitative and qualitative methods of business reputation research. They can be carried out in-house by the company (accounting, marketing and PR departments) or with the help of invited consultants.
The importance of correctly assessing reputation for some areas of business is very great. In particular, this applies to the trade and services sector, where the value of goodwill is a significant value along with the valuation of tangible assets. The most illustrative examples so far are from foreign practice. Thus, Philip Morris Corporation bought Kraft Foods for almost $13 billion, which was four times its book value.
O.S.Paramonova
Journal expert
"Supervisor
construction organization"
The business reputation of the enterprise is qualified Civil Code as an intangible asset. This indicator has a significant impact on the market value of the organization. Read the article on how to evaluate a company's business reputation.
From the article you will learn:
Download documents on the topic:
Why is it necessary to analyze the business reputation of an enterprise: an example
The administration of a large city confiscated land from the owners for municipal needs for the reconstruction of the highway. The building in which a popular restaurant had been operating for several years was being demolished. He had a constant circle of visitors and an established positive business reputation.
The city offered to pay compensation to the restaurant owner in the amount of the book value of the company's assets. The businessman was not happy with this. He turned to independent appraiser. The company's business reputation was assessed. Goodwill was calculated and included in the cost of the restaurant as ready-made business. The amount of compensation paid to the building owner was eventually increased by almost 20%.
What is the difference between the image and business reputation of an organization?
The concepts of image and business reputation of an organization correspond to the same thing legal entity and are interconnected with each other. But the sources of formation of these intangible assets are different.
Organizational business reputation management
Analysis and assessment of the experience and business reputation of organizations allows us to find existing problems and outline ways to solve them.
The answer to the question of how to assess a company's business reputation depends on the choice of assessment methods. For this we use:
- Qualitative assessment methods. Sociological surveys and ratings that do not allow one to calculate the exact value of goodwill, but record its change in a positive or negative direction.
- Quantitative assessment methods. Their use makes it possible to obtain quantitative indicators of intangible assets that form business reputation.
Evaluation criteria business reputation of the company, which can be quantified:
- number regular customers;
- profitability;
- number of sales;
- amounts of funds raised as investments, etc.
The following quantitative methods for assessing the business reputation of an enterprise are used abroad:
- excess profitability;
- treasury;
- discounting financial flows;
- residual.
In Russia, the only approved method for accounting for intangible assets is the “residual” method (PBU 14/2007). In accordance with it, the company's business reputation is determined for inclusion on the balance sheet as the difference between the price of its acquisition and the value of its assets. The disadvantage of this approach is that the assessment result cannot be used in managing the business reputation of the organization.
In practice for business reputation assessments Companies often use the excess profitability method. In this case, goodwill is measured as brand, helping to improve profitability.
A company's positive business reputation allows it to increase its book value. It is an appraised intangible asset and is an object accounting. The purpose of management influence is to increase the business reputation of the organization.
Methods for assessing business reputation (goodwill)
In assessing the business reputation of an enterprise, this is the amount by which the value of the business exceeds the market value of the financial, material and part of the intangible assets of the enterprise reflected in the financial statements.
In other words, an enterprise's goodwill represents that part of the value of an enterprise that exists only with that enterprise and cannot be attributed to any specific asset.
The value of a business's goodwill arises when a business earns a return on assets or equity that is typically above the industry average.
There are methods for assessing the business reputation of an enterprise (goodwill):
- o accounting method;
- o excess profits;
- o formulaic.
Accounting method. The business reputation of an enterprise, calculated by the accounting method, is the difference between the purchase price (acquisition costs) of the company (enterprise) and the total value of all its identifiable assets and debt obligations (in liabilities).
The sequence of determining the value of an enterprise's business reputation (goodwill) using the accounting method:
- o the price (costs) of acquiring the enterprise (Zp) is determined;
- o the book value of tangible assets is determined on the date of sale (acquisition) of the enterprise (BStma);
- o the book value of assets is adjusted so that their market value (RStma) is determined;
- o the value of separately identified intangible assets (separable from the enterprise) is determined from the balance sheet as of the date of sale (acquisition) of the enterprise (Stna);
- o all liabilities, all accounts payable of the enterprise are determined (Ab);
- o the value of an enterprise's business reputation (goodwill) is determined as the difference between the purchase price and the market value of all tangible assets and separately identifiable intangible assets, minus the accounts payable (liabilities) of the enterprise:
St 6m = Zp - (RStma + Sleep) - Vol. (9.16)
Example. Company "A" paid company "B" 1,090,000 thousand rubles. for 6,000,000 ordinary shares. There are a total of 10,000,000 shares of Company B's common stock outstanding. Therefore, the investor's share is 60% (6000: 10,000 x 100%).
Direct expenses of company "A" for the acquisition of company "B" amounted to 2,000 thousand rubles. The consolidated balance sheet of company "B" at the time of purchase is presented in table. 9.7. Determine the value of the goodwill of company B, which was acquired by company A.
Table 9.7
Balance sheet (consolidated) of company B (at the time of purchase)
|
Negotiable |
Authorized capital |
||
|
Cash funds |
Additional |
||
|
Basic |
Total own funds |
||
|
including: |
Short term obligations |
||
|
Bond |
|||
|
buildings (rest station) |
|||
|
equipment (remaining station) |
|||
|
Other assets |
|||
|
Total assets |
Total liabilities |
||
- 1. The market value of assets and the bond issue is determined.
- 1.1. Calculation market value bond loan with a coupon yield of 6% at a discount rate of 8% and a maturity date of 4 years.
Calculation procedure.
Coupon interest (payments) on bonds: 200,000 x 0.06 = 12,000 thousand rubles.
Total amount of payments on bonds:
Sob = 200,000 x (1 + 4 x 0.06) = 200,000 + 48,000 = 248,000 thousand rubles.
Current value of the total amount of payments on bonds:
And purchase price = 12,000 x = 39,745.52 thousand rubles.
And the main amount = 200,000 x (1 + 0.08) -4 = 147,006 thousand rubles.
The present value of the entire bond issue is equal to 39,745.52 + 147,006 = 186,751.5 thousand rubles.
Market value of the bond loan as of the valuation date: RUB 186,751.5 thousand.
- 1.2. The market value of assets and liabilities of company B, identified as a result of revaluation as of the valuation date, was:
- - reserves: 95,000 thousand rubles;
- - land: 420,000 thousand rubles;
- - buildings: 550,000 thousand rubles;
- - equipment: 80,000 thousand rubles;
- - bond loan: 186,751.5 thousand rubles.
Discount rate 8% (interest rate on the market at the time of purchase), repayment period: 4 years.
- 2. Procedure for calculating business reputation (goodwill).
- 2.1. Investment costs: 1,090,000 + 2000 = 1,092,000 thousand rubles.
- 2.2. A normalized balance sheet (not an accounting balance sheet) is drawn up for the purpose of evaluating company “B”, taking into account the market value of assets and liabilities identified as a result of revaluation (Table 9.8).
Table 9.8
|
Negotiable |
Authorized capital |
||
|
Cash |
Additional |
||
|
Retained net profit |
|||
|
Fixed Assets |
Total equity |
||
|
including: |
Short-term obligations |
||
|
buildings (rest station) |
Bond |
||
|
equipment (remaining station) |
|||
|
Other assets |
|||
|
Total assets |
Total liabilities |
||
2.3. The value of net assets (equivalent to the company’s equity capital) is calculated:
Net assets = Equity = Assets - (Short-term liabilities + Bond debt) = 1,590,000 - (155,000 + 186,751.5) = 1,248,248.5 thousand rubles.
2.4. Investor's share in the net assets of company B at book value:
Investor's share = Net assets x Investor's share = 1,248,248.5 x 0.60 = 748,949.1 thousand rubles.
2.5. The difference between investment (purchase) costs and the value of net assets is 1,092,000 - 748,949.1 = 343,050.9 thousand rubles.
Thus, the value of the business reputation of company “B” acquired by company “A” is 343,050.9 thousand rubles.
Excess Profit Method proceeds from the fact that all intellectual property objects, including unidentified (non-allocated) NML enterprises, participate in the formation of the enterprise’s total profit. The value of an enterprise's business reputation (goodwill) using the excess profit method is considered as the value of part of the intangible assets that create profit above the market average.
The sequence of determining the value of an enterprise's business reputation (goodwill) using the excess profit method:
The average industry profitability (Ro) is calculated as the ratio of annual net profit(NPR) to the average annual cost of equity capital of the industry (Sko):
Rho = ChPr/Sko;
The profitability (Рп) of an operating enterprise is determined as the ratio of the annual net profit (NPr) to the average annual cost of the enterprise's equity (Skp):
Rp = ChPr/Skp;
Excess profit (EP) is determined, for which the difference between the industry average profitability and the profitability of the enterprise is multiplied by the average annual cost of equity (ACC) of the enterprise:
DPri = (Pn - Po) x Sqp;
- - capitalization ratio (Kk) is calculated;
- - the value of intangible assets is calculated as the quotient of dividing the amount of excess profit by the capitalization ratio:
Sleep = DPri / Kk;
The part of the value of intangible assets attributable to the assessed goodwill is determined.
This method is used when the difference between the industry average profitability and the enterprise profitability is positive. This difference determines the degree of excess profit in a given business.
Example. Based on the analysis results financial condition The enterprise has compiled a normalized balance sheet (Table 9.9).
Table 9.9
Normalized balance sheet of company "B"
|
Negotiable |
Authorized capital |
||
|
Cash funds |
Additional |
||
|
Retained net profit |
|||
|
Basic |
Total equity |
1 248 248,5 |
|
|
including: |
Short term obligations |
||
|
buildings (rest station) |
Bond |
||
|
equipment (remaining station) |
|||
|
Other assets |
|||
|
Total assets |
Total liabilities |
||
Normalized (average annual) net profit 240,000 thousand rubles. Average return on equity by industry (profitability by equity) 15%. Capitalization rate 20%.
We calculate the amount of equity capital (SC):
SK = Assets - Liabilities = 1,590,000 - (155,000 + 186,751.5) = 1,248,248.5 thousand rubles.
The industry average return on equity (return on equity) is 15%, so the return (average profit) on equity is:
ChPro(sk) = 1,248,248.5 x 0.15 = 187,237.28 thousand rubles.
Then the excess profit is:
240,000 - 187,237.28 = 52,762.725 thousand rubles.
The value of goodwill is determined as the quotient of excess profit divided by the capitalization ratio:
St good = 52,762.725: 0.2 = 263,813.63 thousand rubles.
If the data about industry average profitability are insufficient or absent, and excess profit has to be determined based only on enterprise data, then use formula method. Its essence lies in the fact that instead of the industry average profitability, retrospective data on the enterprise’s profit are used.
Calculation sequence:
- 1) determined average income(net profit) for the retrospective period;
- 2) the average annual market (not book value) value of tangible assets for the same retrospective period is determined (RStma);
- 3) from the average annual market value of tangible assets, the average annual values of separately identified intangible assets, but not included in the balance sheet, and all liabilities are subtracted.
The result obtained is the value of assets for the formula (RStma - IMA - Ob);
- 4) the profit of material assets is determined according to industry indicators of the rate of return ( i pr.neg 1tp): RStmasr - NMA - Ob) x i np. from p;
- 5) from the amount of net profit received, the profit from tangible assets is subtracted: ChPsr - (RStmasr - NML - Ob) x i pr .neg ;
- 6) if there is excess income, then this income is capitalized:
Sfm = [ChPsr - (Stmasr - NMA - Ob) x i pr.neg ] / i To
Example. Determine the value of goodwill if, but the results of the balance sheet analysis and financial results the following was revealed:
- - industry rate of profit indicator: i ave.neg = 15%:
- - profitability of company i k = 20%;
- - financial indicators are presented in table. 9.10.
Based on retrospective data of the enterprise's profit, a table is compiled. 9.10:
Table 9.10
Determination of net profit on average tangible assets, thousand rubles.
Excess profit: 240,000 - 128,486 = 111,514 thousand rubles. The cost of business reputation (inseparable intangible assets) when i k - = 20%:
St good - 111,514: 0.2 - 557,570 thousand rubles.
Salvage value when determining the value of an enterprise (business) using the cost approach, it represents the value that the owner of the enterprise can receive upon liquidation of the enterprise and the separate sale of its assets.
The assessment work includes several stages.
- 1. The latest balance sheet is taken.
- 2. A calendar schedule for the liquidation of assets is being developed, since the sale various types assets of the enterprise requires different time periods.
- 3. The gross proceeds from the liquidation of assets are determined.
- 4. The estimated value of assets is reduced by the amount of direct costs. Direct costs associated with the liquidation of an enterprise include commissions for appraisal and law firms, taxes and fees that are paid upon sale, taking into account calendar schedule liquidation at the valuation date at a discount rate that takes into account the risk associated with the sale.
- 5. The liquidation value of assets is reduced by the costs associated with holding the assets until they are sold, including the costs of maintaining inventories finished products and work in progress, preservation of equipment, machinery, mechanisms, real estate, as well as administrative expenses to maintain the operation of the enterprise until its liquidation.
- 6. Operating profit (loss) of the liquidation period is added (or subtracted).
- 7. Subtracted preemptive rights for severance pay and payments to employees of the enterprise, claims of creditors for obligations secured by a pledge of the property of the liquidated enterprise, debt on mandatory payments to the budget and extra-budgetary funds, settlements with other creditors.
Thus, salvage value of an enterprise is calculated by subtracting from the adjusted value of all assets on the balance sheet the amount of current costs associated with the liquidation of the enterprise, as well as the amount of all liabilities.
Determining the final value of the business value assessment
After reading this chapter, you will be able to determine the final value of the enterprise valuation.
International Business Valuation Standards recommend, and Russian standards establish as mandatory three assessment approaches - costly, comparative and profitable, which necessitates harmonization of the results obtained, since these approaches are applied to the same object within the same assessment procedure.
To derive the final value of cost calculated by three approaches and valuation methods, we use various ways determining the weighting coefficients necessary to derive the value of a business based on the weighted average formula. In addition to the methods of mathematical and subjective weighing described in the monographs of S. Pratt, the method of expert qualimetry, the probabilistic approach and the method of hierarchy analysis (MAI) are also used. The method uses a criteria tree in which general criteria are divided into specific ones. For each group of criteria, importance coefficients are determined. A means of determining the coefficients of importance of criteria or the criterion value of alternatives is pairwise comparison. The comparison result is assessed on a point scale. Based on such comparisons, criteria importance coefficients are determined, alternatives are evaluated, and overall rating as a weighted sum of criteria scores.
The proposed methods for harmonizing assessment results are heuristic in nature, i.e. do not have strict scientific evidence. However, these methods have found widespread practical application V appraisal activities because of its simplicity and clarity.
Rice. 10.1.
Empirically, a weighted average was determined to determine the final cost:
o when using two methods, use the following formula:
where C min - min the calculated value of the cost, determined by any method; C max - max is the calculated value of the cost, determined by some method.
o when using three methods, use the following formula:
![]() (10.3)
(10.3)
where C min - min the calculated value of the cost, determined by any method; C max - ptah the calculated value of the cost, determined by some method; C av - the average calculated value of the cost, determined by some method.
The final value of the cost, calculated by three approaches and valuation methods, and the justification for this value are included in the report.
Cost assessment acts as a performance criterion management decisions, which can lead to a decrease or increase in the value of the enterprise.
The value of an enterprise (business) is reflected in the value of securities.