Municipal unitary enterprises with the right of economic management. Municipal unitary enterprise. Programs of activity of unitary enterprises
State and municipal unitary enterprises? In Russian legislation, in particular in the Civil Code, there is a definition of this term. In accordance with it, state and municipal unitary enterprises are organizations created for the purpose of solving basic problems and making a profit, but at the same time not being the owners of the property assigned to them.
Only the founder directly has the right to dispose of it. They are called unitary because property cannot be divided into shares, shares, deposits and other parts. The name of this entity must necessarily contain an indication of the owner.
State and municipal unitary enterprises are divided into 2 types. The first is organizations based on It should be noted that this includes unitary enterprises such as municipal ones. They are created after the relevant decision is made by the authorized government agency or municipality.
The second type is organizations based on the right of operational management. They can be founded only by decision of the government of the country. State and municipal unitary enterprises in this case have a rather specific position in legal aspect. Thus, they are created for the purpose of providing certain services, performing work or producing any products, which is typical for commercial organizations. At the same time, all activities of the enterprise can be based on financing from the budget.
State (municipal) unitary enterprises. Peculiarities

First of all, this type of business entity has special legal capacity. That is, they were created for the purpose of performing certain works, providing services or producing some products, which is characteristic feature commercial organizations. However, state and municipal unitary enterprises are not at all limited in their rights to carry out certain transactions. For example, they can rent out vacant premises (unless otherwise provided by the charter and other regulations).
Another feature is that such business entities are individual enterprises.
The third specific feature of this type of enterprise is related to the Civil Code. Special attention paid to terminology. In relation to such organizations, the definition of “enterprise” acts as a subject in other cases - it is only an object of legal relations.
Among other things, they can apply for (this includes subsidies, subsidies, and subventions). It is carried out to execute a variety of programs. Preference is given to those with a social orientation.

This leads to the fourth feature. The charter of unitary type business entities must include information about the direct owner of the property, sources of formation authorized capital and the order of its formation. It should be noted that the enterprise is not responsible for the obligations of the owner, but he is responsible for the activities of the organization.
Management of unitary enterprises
Here there is a sole manager, and not a collegial body, as happens in other cases. As a rule, this is the director. Person on this position appointed by the owner or a special body with appropriate powers.
Advantages and disadvantages of this form of business entities
Let's consider first positive aspects unitary enterprises. Firstly, they are designed to solve those issues that are relevant in society at a given moment in time. Secondly, they are more stable (compared to other commercial enterprises). This is due to the fact that they, as a rule, operate in industries whose level of profitability is not of interest to them; therefore, there is no competition. In addition, support from the state protects these entities from ruin. Another advantage is timely payment wages, predictability.
Now, a few words about the shortcomings.
First of all, unitary enterprises have less efficiency with economic point vision. Also, a constant level of remuneration leads to a decrease in productivity and loss of interest on the part of employees, since there is no competent motivational component. It is also important that at these facilities property is often used for personal gain, theft, and there is a high degree of bureaucracy.
Thus, we can say that it is advisable to create unitary enterprises only in those areas where the use of other forms is less effective.
Unitary enterprise
Unitary enterprise- a special organizational and legal form of a legal entity. A commercial organization that is not vested with the right of ownership of the property assigned to it by the owner. The property is indivisible and is not distributed among deposits (shares, shares), incl. between employees of the enterprise. In addition to the information specified in paragraph 2 of Art. 52 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the legal status of state and municipal unitary enterprises is determined by the Civil Code and the law on state and municipal enterprises.
Russian Federation
IN Russian Federation The main law regulating the activities of unitary enterprises is the Federal Law of November 14, 2002 No. 161-FZ “On State and Municipal Unitary Enterprises.”
Unitary enterprises can be of three types:
- Federal State Unitary Enterprise - FSUE
- State unitary enterprise - SUE (subject of the federation)
- Municipal unitary enterprise - MUP (Municipal entity)
Constituent document of a unitary enterprise is the charter.
A unitary enterprise does not have the right to create as legal entity another unitary enterprise by transferring part of its property to it (subsidiary enterprise). This restriction was introduced by Federal Law No. 161-FZ of November 14, 2002, whereas previously Russian legislation allowed unitary enterprises based on the right of economic management to create subsidiary unitary enterprises. With the adoption of this law, existing subsidiaries of unitary enterprises were subject to merger with the enterprises that founded them within six months, that is, until June 3, 2003.
Unitary enterprises are obliged, in cases determined by the owner of the property, to conduct an annual mandatory audit. In this case, an agreement to conduct a mandatory audit of the reporting of unitary enterprises must be concluded based on the results of placing an order through bidding in the form open competition, in the manner prescribed by Federal Law No. 94-FZ of July 21, 2005 “On placing orders for the supply of goods, performance of work, provision of services for state and municipal needs.”
Typically, unitary enterprises are regarded as a less transparent form compared to joint stock companies, since in latest law establishes corporate governance procedures. However, one advantage of unitary enterprises is that the property remains in state (municipal) ownership.
Unlike joint stock companies and other commercial organizations, unitary enterprises are required to disclose information about their procurement on official websites at the level of their subordination. For Federal State Unitary Enterprise - on the official website public procurement Russian Federation (federal government order), for state unitary enterprises on the regional procurement websites and for municipal unitary enterprises on the official websites of municipalities or, in their absence, on the official regional procurement websites.
Since, in accordance with paragraph 2 of Art. 50 and art. 113 Civil Code In the Russian Federation, unitary enterprises are commercial legal entities, their activities are aimed at generating profit in favor of the owner of the property - the state or municipality as well as to cover your own expenses. In addition, of course, the purpose of the activity is not to make a profit, but to satisfy the public interests of the state and provide for state needs.
At the same time, depending on the method of securing property, two types of unitary enterprises are distinguished (clause 2 of Article 113 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation):
- unitary enterprises based on the right of economic management (Article 114 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation);
- unitary enterprises based on the right of operational management (state-owned enterprises) (Article 115 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
CIS
In most CIS countries, there are also private unitary enterprises that are not vested with ownership rights to the property assigned to them. The property is indivisible and cannot be distributed among deposits, shares, interests, shares and is the common joint property of its members, individuals, one individual or one legal entity. These include peasant (farm) enterprises, individual, family and subsidiary enterprises. In the Russian Federation as independent organizations, with the exception of subsidiaries, they are not recognized as such, and the heads of such organizations are individual entrepreneurs, which creates property and organizational difficulties for individual entrepreneur(actually enterprises). For example, there is no right of private ownership of an enterprise, as in property complex, since the enterprise involves additional economic relations, which is not the case with individual entrepreneurship, there are no clear regulations for the position of members in the enterprise, the distribution of profits and responsibilities between them and many other aspects.
Examples
- FSUE Design Bureau "Arsenal" named after M.V. Frunze »
- FSUE "Space Communications"
- FSUE "NPP VNIIEM"
- FSUE "Scientific and Production Center for Gas Turbine Engineering "Salyut""
- FSUE Russian Post
- Federal State Unitary Enterprise "Russian Television and Radio Broadcasting Network"
- FSUE ""
- Federal State Unitary Enterprise "Housing and Communal Administration of the Russian Academy of Sciences"
See also
Notes
Links
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
See what a “Unitary enterprise” is in other dictionaries:
See Enterprise unitary Dictionary business terms. Akademik.ru. 2001 ... Dictionary of business terms
Unitary enterprise- (English Unitarian/unitary enterprise) in the civil law of the Russian Federation commercial organization not endowed with the right of ownership to the property assigned to it by the owner... Encyclopedia of Law
Legal Dictionary
Unitary enterprise- (unitary enterprise) a commercial organization that is not vested with the right of ownership of the property assigned to it by the owner (state, municipality): it belongs to it by the right of economic management or operational management. IN… … Economic and mathematical dictionary
unitary enterprise- A commercial organization that is not vested with the right of ownership of the property assigned to it by the owner (state, municipality): it belongs to it by the right of economic management or operational management. In the form of unitary... ... Technical Translator's Guide
UNITARY ENTERPRISE- according to the civil legislation of the Russian Federation, a commercial organization that is not vested with the right of ownership of the property assigned to it. Property U.p. is indivisible and cannot be distributed among deposits (shares, shares), incl. between employees... ... Legal encyclopedia
UNITARY ENTERPRISE- in accordance with Art. 46 of the Civil Code, a unitary enterprise is one of the forms of commercial organizations in which legal entities can be created. According to Art. 113 of the Civil Code, a unitary enterprise is a commercial organization that is not... ... Legal Dictionary of Modern Civil Law
Unitary enterprise- a commercial organization that is not vested with the right of ownership to the property assigned to it by the owner. The property of a unitary enterprise is indivisible and cannot be distributed among contributions (shares, shares), including between... ... Administrative law. Dictionary-reference book
Unitary enterprise- A unitary enterprise is a commercial organization that is not endowed with the right of ownership to the property assigned to it by the owner. The property of a unitary enterprise is indivisible and cannot be distributed among contributions (shares,... ... Vocabulary: accounting, taxes, business law
unitary enterprise- according to the civil legislation of the Russian Federation, a commercial organization that is not vested with the right of ownership of the property assigned to it. In the form of U.p. only state and municipal enterprises. Property U.p. located… … Large legal dictionary
Many frequently encountered and already familiar abbreviations are not fully understood by everyone. For example, what is a federal state unitary enterprise? Reply to this question we will dedicate today's material.
FSUE - unitary enterprise
FSUE stands for Federal State Unitary Enterprise. Please note that this is a somewhat outdated version of the abbreviation. After the adoption of Federal Law No. 161, the abbreviation FGP - Federal State Enterprise - began to be used. In general, both abbreviations are equivalent.
To understand what a federal state unitary enterprise is, we need to turn to the definition of a unitary enterprise and its characteristics. UP is a specific organizational and legal form of a commercial institution. Its main difference is that it does not have ownership rights to the property assigned to it. The latter is owned by the state, in the case of a federal state unitary enterprise - at the federal level. This property is indivisible - it cannot be divided into deposits, shares, shares.
Unitary enterprises will be divided into three large groups:
- FGP (FSUE).
- State-owned enterprise of a constituent entity of the Russian Federation - region (OGUP), territory (KSUP), republic (RGUP).
- State enterprise of the municipality - MGUP.
It follows that only state or municipal enterprises can be unitary. The real right to their property belongs only to their founder - the state. The organization itself disposes of this property only within the framework of operational management or economic management.
The purpose of the FGP is to solve state problems on a commercial basis.
Regulation by law
Federal state unitary enterprises in Russia are regulated by the following legislative acts:
- Civil code. In particular, paragraph 2 of Article 52 of this act.
- Law on municipal and state-owned enterprises - Federal Law No. 161.
- Federal Law No. 131 “On the general principles of self-government in the Russian Federation” (in particular, paragraph 3 of Article 17 of the mentioned law).
Characteristic features of a unitary enterprise
FSUE in Russia is characterized by the following:
- Lack of any membership.
- Indivisibility of property.
- The right to property is assigned only to the founder.
- Property is assigned to a legal entity only on a limited right - in rem.
- The creation of a legal entity here, in essence, is not the unification of the property of a number of citizens or organizations, but the allocation of a certain share of the property mass by the founding state.
- The management of federal state unitary enterprises and other unitary enterprises is a sole body.

Creation of UE
The creation of federal state unitary enterprises and other unitary entities is determined by three main reasons:
- In activities it is necessary to use property, the privatization of which is prohibited.
- It is required to conduct a somewhat unprofitable production or a subsidized type of activity.
- As a result of the work of the UP, it is necessary to solve some state social objectives- for example, the sale of services and goods to the population at a minimum cost.

When establishing a FSUE, the following is taken as a basis:
- The property allocated to the UE remains in state ownership - the institution has the right only to use it, but not to dispose of it.
- The corporate name of the UE must transparently indicate the owner of the provided property.
- The charter must clearly indicate the owner of the property allocated to the unitary enterprise - the state, municipal entity.
- FSUE is liable, like many other organizations, for its obligations only with its personal property. But he is not subject to the obligations of the owner who provided the institution with his property for use.
- The head of a unitary enterprise is appointed either by the founder or his authorized representative. The management body of the UE is accountable to this person.
Ways to use the property
There are only two directions for the use of the property provided to him by the UE:
- Operational management. A unitary institution disposes of both the provided property and its profits and products produced only with the consent of the founder.
- Economic management. The UE can freely dispose of the property given for use, its income, and its products, but subject to the restrictions imposed by law.

Main types of unitary enterprises
There are two main forms of unitary enterprises. This:
- Operating under the right of economic management - state and municipal.
- Those operating with the right of operational management are state-owned.
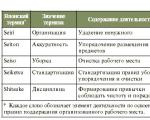
Let's present their features in the form of a table.
| Economic management | Operational management | |
| Regulatory legislation (Civil Code of the Russian Federation) | Art. 114. | Art. 115. |
| Creation | By decision of the authorized body - state or municipal. | They are formed on the basis of a share of property that is in federal, regional or municipal ownership. |
| Constituent documentation | Charter approved by the authorized body - ministry, department, etc. | The charter, which is approved by the Government of the Russian Federation, a subject or an authorized institution of local government. |
| Key Features | The charter, among other things, contains information about the purpose and subject of the work, and the amount of the authorized capital. The amount of authorized capital for a state unitary enterprise is not lower than 5000 minimum wages, for a municipal unitary enterprise it is not lower than 1000 minimum wages. The owner of the provided property is not liable for the obligations of this UP, unless the bankruptcy of this institution occurred on his order. | The owner of the property provided to this UE has the right to withdraw from the institution unused, redundant, or improperly operated property. The UP does not have the right to dispose of property without the permission of the owner. The corporate name of this unitary enterprise must necessarily contain information that it is government-owned. The owner of the provided property bears subsidiary liability for the obligations of the UE - in case of insufficiency of the latter's property. By decision of the government of the state, subject or municipality, the unitary enterprise may be liquidated or reorganized. |
MGUP, OGUP, FSUE are the only commercial organizations whose civic duties and the rights are directly related to the activities prescribed in their charter.
Activities of a unitary enterprise
Let's talk a little about the features of the activities of Federal State Unitary Enterprises and other unitary institutions:
- The unitary enterprise does not have the right to act as a founder or create subsidiaries.
- The right to dispose of the active share of its fixed assets: to sell owned raw materials, equipment, vehicles, inventory and other material assets.
- Sale real estate prohibited for a unitary enterprise.
- Transactions with property valued at more than 150 million rubles are approved by the regulatory authority - the Federal Agency for State Property Management.
- The sale of federal real estate assigned to a federal state unitary enterprise (operating within the framework of economic management) is carried out only at auction. Proceeds from the sale must reach the state treasury no later than 25 days from the date of sale.

Specific examples of federal state unitary enterprises
Let's consider the well-known FGPs:
- FSUE "Russian Post".
- "Space Communication".
- "Russian radio and television network".
- "Mosfilm Film Association".
- "Arsenal Design Bureau".
- "Central Research Institute of Mechanical Engineering".
- "Housing and Communal Management of the Russian Academy of Sciences."
- "Communication-Security".
- FSUE "Security" of the Ministry of Internal Affairs of Russia.
Examples of municipal - city unitary institutions (SUE) in Moscow are given below. This:
- "NIIMostroy".
- "Moscow Metro".
- "Mosgotrans".

A unitary enterprise is a special form of commercial organization. Legal protection Federal state unitary enterprises and other unitary enterprises are provided current legislation RF.
A municipal unitary enterprise is a commercial organization that is not vested with the right of ownership to the property assigned to it by the owner. The property of a unitary enterprise is indivisible and cannot be distributed among contributions (shares, shares), including among employees of the enterprise. Only state and municipal enterprises can be created in the form of unitary enterprises. See State unitary enterprise.
The property of a municipal unitary enterprise is in municipal ownership and belongs to such an enterprise with the right of economic management. A municipal unitary enterprise is liable for its obligations with all its property and is not liable for the obligations of the owner of its property.
The charter of a municipal unitary enterprise must contain, in addition to information, the indication of which, in accordance with the provisions of Article 52 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, is mandatory in the constituent documents of any legal entity (name of the legal entity, its location, the procedure for managing the activities of the legal entity), also information about the subject and goals of the enterprise’s activities , as well as the size authorized capital enterprise, the procedure and sources of its formation. The corporate name of a municipal unitary enterprise must contain an indication of the owner of its property.
The body of a municipal unitary enterprise is the head, who is appointed by the owner or a body authorized by the owner and is accountable to him.
The legal status of municipal unitary enterprises is determined by the Civil Code of the Russian Federation and the law on state and municipal unitary enterprises.
Russian electoral law: dictionary-reference book. 2013 .
See what a “Municipal Unitary Enterprise” is in other dictionaries:
Municipal unitary enterprise
Unitary enterprise- Unitary enterprise with special organizational structure legal form legal entity. A commercial organization that is not vested with the right of ownership of the property assigned to it by the owner. Property is indivisible and is not distributed among... ... Wikipedia
UNITARY ENTERPRISE- according to the civil legislation of the Russian Federation, a commercial organization that is not endowed with the right of ownership to the property assigned to it by the owner. Property U.p. is indivisible and cannot be distributed among deposits (shares, shares), including... ... Encyclopedia of Lawyer
State unitary enterprise- Unitary enterprise (usual abbreviations: State Unitary Enterprise GUP, Municipal Unitary Enterprise MUP, Federal State Unitary Enterprise FSUE) is a commercial organization not vested with ownership rights to ... Wikipedia
Encyclopedia of Law
Agricultural unitary enterprise- (English: agricultural Unitarian enterprise) in the Russian Federation, a state or municipal unitary enterprise operating in the field agriculture. S.u.p. status as subjects economic activity determined by the norms of civil legislation of the Russian Federation... Large legal dictionary
Federal State Unitary Enterprise- Unitary enterprise (usual abbreviations: State Unitary Enterprise GUP, Municipal Unitary Enterprise MUP, Federal State Unitary Enterprise FSUE) is a commercial organization not vested with ownership rights to ... Wikipedia
Enterprise- a type of organization, an independent economic entity created to produce products, perform work and provide services in order to satisfy public needs and make a profit. Enterprises can be created in... ... Administrative law. Dictionary-reference book
A commercial organization that is not vested with the right of ownership of the property assigned to it by the owner. Property is indivisible and is not distributed among deposits (shares, shares), including among employees of the enterprise. In addition to the information specified in paragraph 2 of Art. 52 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the legal status of state and municipal unitary enterprises is determined by the Civil Code and the law on state and municipal enterprises.
Encyclopedic YouTube
-
1 / 5
In the Russian Federation, the main law regulating the activities of unitary enterprises is the Federal Law of November 14, 2002 (as amended on May 23, 2016) No. 161-FZ “On State and Municipal Unitary Enterprises.”
Unitary enterprises can be of three types:
A unitary enterprise is a commercial organization that is not vested with the right of ownership to the property assigned to it by the owner. Such enterprises are called unitary, since their property is indivisible and cannot be distributed among deposits, shares, interests, shares.
Only state and municipal enterprises can be created in this form. Property (state or municipal, respectively) belongs to a unitary enterprise with the right of economic management or operational management. The real right to the property of unitary enterprises (as well as institutions) belongs to their founders.
A unitary enterprise is liable for its obligations with all the property it owns, but is not liable for the obligations of the owner of its property.
The size of the authorized capital of a state unitary enterprise must be no less than 5000 minimum wages, and of a municipal enterprise - no less than 1000 minimum wages.
The constituent document of a unitary enterprise is the charter.
A unitary enterprise does not have the right to create another unitary enterprise as a legal entity by transferring part of its property to it (a subsidiary). This restriction was introduced by Federal Law No. 161-FZ of November 14, 2002, whereas previously Russian legislation allowed unitary enterprises based on the right of economic management to create subsidiary unitary enterprises. With the adoption of this law, existing subsidiaries of unitary enterprises were subject to merger with the enterprises that founded them within six months, that is, until June 3, 2003.
Unitary enterprises are obliged, in cases determined by the owner of the property, to conduct an annual mandatory audit. At the same time, in accordance with clause 16, part 1, article 20 Federal Law“On state and municipal unitary enterprises” 161-FZ of November 14, 2002, the owner of the property of a unitary enterprise approves the auditor and determines the amount of payment for his services.
Typically, unitary enterprises are regarded as a less transparent form compared to joint stock companies, since in the latter the law establishes corporate governance procedures. However, as an advantage [ ] unitary enterprises can be distinguished by the fact that the property remains in state (municipal) ownership.
Conducting procurement by State Unitary Enterprises for own funds regulated by the Federal Law of the Russian Federation “On the procurement of goods, works, services certain types legal entities" No. 223-FZ dated July 18, 2011. In terms of spending the provided budget funds, starting from 01/01/2017, - Federal Law dated 04/05/2013 No. 44-FZ “On contract system in the field of procurement of goods, works, services to meet state and municipal needs" (came into force on January 1, 2014). Before this, the Federal Law of the Russian Federation dated July 21, 2005 No. 94-FZ was in force.
Since, in accordance with paragraph 2 of Art. 50 and art. 113 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, unitary enterprises are commercial legal entities, their activities are aimed at generating profit in favor of the owner of the property - the state or municipality, as well as to cover their own expenses. In addition, of course, the purpose of the activity is not to make a profit, but to satisfy the public interests of the state and provide for state needs.
At the same time, depending on the method of securing property, two types of unitary enterprises are distinguished (clause 2 of Article 113 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation):
- unitary enterprises based on the right of economic management (Article 114 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation);
- unitary enterprises based on the right of operational management (state-owned enterprises) (Article 115 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
Federal State Unitary Enterprises, unlike non-state legal entities, are not only large taxpayers, but also annually contribute 25% of profits to the federal budget in accordance with Art. 17 of the Federal Law “On State and Municipal Unitary Enterprises”. For example, for the Federal State Unitary Enterprise "COMMUNICATION - Security" in 2016, the transfer of 8 million 530 thousand rubles was approved (25% of net profit enterprises for 2015). Accordingly, after the privatization of federal state unitary enterprises, the state ceases to receive additional income.
CIS
In most CIS countries there are also private unitary enterprises (ChUP), not vested with the right of ownership of the property assigned to him. The property is indivisible and cannot be distributed among deposits, shares, shares, shares and is in the common joint ownership of its members: individuals, one individual or one legal entity. These include peasant (farm) enterprises, individual, family and subsidiary enterprises. In the Russian Federation, they are not recognized as independent organizations, with the exception of subsidiaries, and the heads of such organizations are individual entrepreneurs, which creates property and organizational difficulties for the individual entrepreneur (in fact, an enterprise). So, for example, there is no right of private ownership of an enterprise as a property complex, since the enterprise involves additional economic relations, which does not exist in individual entrepreneurship, there are no clear regulations for the position of members in the enterprise, the distribution of profits and responsibilities between them, and many other aspects.