Implementation of an electronic document management system at the enterprise. Electronic document flow in an enterprise Electronic document flow in an enterprise example
We study the basics of building an optimal document flow system, provide examples and step-by-step algorithm building a document turnover schedule.
From the article you will learn:
Document flow diagram at the enterprise
Centralized
This form is suitable for organizations with a strict hierarchical management structure that adheres to the principle of linear distribution of functions (unity of command). A centralized form of paper circulation presupposes the presence of organizational structure a company with a specialized division responsible for working with all documentation.
Decentralized
This form is suitable for organizations in which the powers of departments are clearly divided according to the principle of operational autonomy.
The decentralized form of document circulation assumes that each structural unit has its own department responsible for working with documentation.
Mixed
With this form of turnover, the leading role in working with documentation is given to the central service of the preschool educational institution, but some of the procedures are delegated special services created within each structural division of the company.
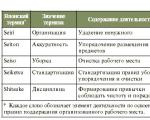
Example of a document flow diagram
The route scheme for the movement of documents is the basic principle of the business paper circulation system. In this scheme, each document flow is assigned common characteristics, instances are prescribed, and mandatory procedures are defined.
This diagram indicates:
- executors (i.e. departments taking part in the processing of this stream);
- route (i.e. the order of the performers);
- the presence of reverse movements (does the document go to the same executor several times);
- the nature of the operations carried out by each specific performer).
An example of an organization's document flow diagram is presented in Fig. 1:

Figure 1. Document flow diagram of the enterprise
Read also:
Types of document flows
The movement of data in a certain direction, organized within a closed system of document circulation, is called document flow. The source and receiver of the data remain the same.
The classification of document flows is carried out on the basis of their relationship to the control object and in the direction of movement.
First classification
- horizontal flows (occur between departments of the same level);
- vertical flows (occur between departments different levels);
- ascending (papers from subordinate structures move to management ones);
- downward (documents from management structures move to subordinates).
Second classification
- the incoming flow is formed by papers coming from external sources;
- the outgoing flow consists of documents sent from the organization;
- internal flow is formed by papers circulating within the organization.
Stages of document flow in an organization
Development and implementation of the scheme document flow of the organization involves combining the entire variety of procedures into a number of basic stages:
Forwarding processing. At this stage, incoming correspondence is received, checked, distributed to addresses and submitted to the manager for review.
Preliminary review. At this stage, the DOU service reviews and classifies papers by type, importance, complexity, author status, etc.
Direction to management. At this stage, resolutions are made and administrative decisions are made.
Processing. At this stage, the documents are executed and sent for storage.
The basic principle of all stages is rational movement, i.e. stream optimization, merging and reduction. For this purpose, special technological instructions, the main purpose of which is to determine the most effective order of procedures and develop optimal route schemes.
How to create a document flow chart
The best option for graphically displaying all stages of document processing is a diagram. Each type of work is carefully analyzed, and the result of this analysis is the development of a flowchart that visualizes the entire process.
The sequence of actions necessary to solve the problem is presented graphically.
There is no unified schedule scheme. Each enterprise needs to develop it independently. How more enterprise, the more activities he has, the more detailed the schedule should be.
Stage two.
We appoint those responsible for paperwork
It’s quite easy to do this with primary documentation - the one who compiles it is responsible for the execution. For other papers, such a person will have to be appointed. If this is not done, then if the document is lost or the deadline for its submission is missed, there will be no one to ask.
Stage three.
We set deadlines.
The deadline within which the responsible employee must submit the document is the most important part of the entire schedule. The deadline can be set in months or days elapsed from the date of execution of the paper.
Stage four.
Choosing a design
As mentioned above, a convenient way to design a graph is a flowchart. But it can be formatted both as text and as a table. The text form is suitable for a small organization; for a larger organization, a table will be more convenient. The main principle is that your diagram should be easy to read for employees responsible for document circulation.
With the proliferation of computers, 100% of documents are created in electronic form. However, more than half of them are still printed for review and approval.
As for the exchange of documents and the signing of agreements between business entities, paper media are almost always used.
There are three submission methods:
- Through the System of Guaranteed Message Delivery to personal account taxpayer;
- On magnetic media with digital signature
- Through the “Taxpayer Terminal” program at the tax office.
Increasing operational efficiency and reducing costs is the goal facing any enterprise that plans to remain in business for many years to come. And it can be achieved with the introduction of electronic document management, especially since this is provided for in Russian legislation.
At the same time, it is important to pay attention to those documents that must be printed in paper form according to the law and to ensure that paper and electronic document flow do not duplicate each other, because in this case nothing will be saved.
If everything is organized correctly, then electronic document management is the key to the efficiency of a modern enterprise.
The work of the EDMS is built around one basic concept - document. It is the document that is the “unit of information” in the EDMS. The document flow system provides fundamental operations with documents:
- storage
- audit
- movement of documents among performers in the organization
- execution of business processes to which these documents relate
In an organization where EDI has been implemented and a document management system is used, the document is also a basic management tool. There are no just decisions, instructions or orders here - there are documents containing these same orders, decisions, instructions, etc., that is, all management in the organization is carried out through documents. As a result, many tasks performed by employees are also tied to documents.
- Any document in the document management system is supplied with a “card”, similar, for example, to a library card. The composition of information about a document (document attributes, card fields) is determined by the type and type of document, their availability for viewing and editing is determined by access rights to the document and its state within the business process.
- Any document can have one or more attached files - these can be either drafts of new documents or scanned images of existing ones.
- Any document can be linked to other documents, which ensures the integrity of the organization’s information field.
- Any document can be found by its attributes or, if such functionality is available, by the occurrence of text in attached files (full-text search).
Thus, organizing document flow in an enterprise using an EDMS provides everything necessary for timely decision-making, response to situations and orderly stable work:
- categorization of documents by types and types
- supplying each type or type of document with any necessary attributes
- specified business processes for document processing
- mechanisms for managing tasks and monitoring their implementation
- reliable document storage with attribute and full-text search capabilities
It is worth noting that various EDMS interact with each other within the framework unified system interdepartmental electronic document management (EDF) and a unified system of interdepartmental electronic interaction (SMEI). The participants of the MEDO are the Administration of the President of the Russian Federation, the Office of the Government of the Russian Federation, Federal authorities executive power, as well as other government bodies. The main principle of MEDO is the integration of participants and the transport system, providing secure exchange of electronic messages.
Introduction of electronic document management. Why the development and implementation of an EDMS is needed. If we approach the idea of implementing electronic document management (EDF) in an organization from the usual perspective, then the following questions arise:
- What will we get from implementing EDI?
- What's wrong with working with paper?
- What economic effect implementation of EDI?
- How soon will this investment pay off?
Let's try to answer these questions. First, we’ll simply describe what changes the implementation of an EDMS will bring to an enterprise:
- document processing processes may partially change and become more stringent
- the number of paper documents will be reduced
- completing tasks will become clearer and more manageable
- reports on work with documents and performance discipline can be received promptly at any time
- employees working with documents will have to be trained to perform all actions electronically
Looking at this list, you might think that this is not a list of changes, but a list of benefits. Yes, in this case, these things are certainly close (otherwise what’s the point of implementing such an implementation?), but upon careful consideration, each of the points also contains some limitation or new requirement. You just need to be prepared for this when planning to implement EDI, and in addition, adapting the EDMS to the needs of the customer allows you to automate document flow with minimal restrictions.
Now about the benefits. The main benefit of implementing EDI is an increase in the efficiency of the organization (here by efficiency we mean the ratio of the achieved result to the costs of achieving it - the formula in this context is more speculative than mathematical). Based on this understanding, there are two ways to increase the efficiency of an organization: by reducing costs and/or increasing results. As a rule, EDMS allows you to implement both options. Figuratively speaking, the implementation of electronic document management using a suitable EDMS gives the organization the opportunity to spend less and earn more. As a rule, EDMS allows you to implement both options. Figuratively speaking, the implementation of electronic document management using a suitable EDMS gives the organization the opportunity to spend less and earn more.
Let's look at the possibilities first cost reduction:
- Reduce paper costs
- Reducing unproductive costs of employee working time
- Accelerating information flows
Now about results:
- Increasing the manageability of the organization due to the orderliness and transparency of document flows
- Increasing the speed and quality of decision making
- Increasing the level of executive discipline and performance efficiency of employees, work groups, and the organization as a whole
And finally, here are examples of questions that are not so obvious, but must definitely be considered within the framework of the topic of organizing electronic document management:
- How much can a draft contract not agreed upon on time cost your organization?
- What damage can a late invoice cause?
- How many documents could not have been revised several times if there had been greater transparency in setting and executing tasks?
Organization of electronic document flow with various points vision
- Leaders:
- promptly obtaining the information necessary to make a decision
- operational control of performance discipline
- Secretaries, assistants and assistants:
- quick document search
- high accuracy of document search
- facilitating control of performance discipline
- simplifying the preparation of all kinds of events and activities
- acceleration of preparation, coordination and approval of final documents
- Financial and accounting services:
- increasing the speed of document movement, for example, from branches to the parent organization
- reducing the risk of document loss
- saving time when selecting documents for reconciliation of calculations or inspections by supervisory authorities
- Legal service:
- reducing the labor intensity of document preparation
- effective control of deadlines
- quick search for what you need regulatory documents
Problems solved by automation of document flow.
Corporate document flow
- Registration of incoming correspondence (primary, repeated documents, responses to requests from legal entities, orders, instructions, letters from higher organizations, memos addressed to the manager from structural divisions)
- Registration of outgoing correspondence (responses to incoming documents, requests, notifications, outgoing memos from structural units addressed to the manager)
- Working with such types of documents as: orders, instructions, contracts, internal regulations, financial documents, memos, statements, protocols and applications, etc. the management of which is automated from the moment of initiation and creation of a draft document to the moment of execution, including the process of coordination and approval
- Up-to-date information on the progress of work with the document (document statuses, event history)
- Control of performance discipline
- Formation, presentation on the screen and printing of output forms in the form of cards, certificates, reports, protocols
- Searching for documents based on the values of the corresponding attributes
- A set of functions to support work with organizational and administrative documents
- Various types statistical reporting
- Transparent mechanism of substituents
- Working with document templates
- "Subscription" to documents
- Differentiation of access rights to documents
- The ability to build an access matrix to documents and system functions based on staffing structure organizations
- Secure document storage in structured storage
- Possibility of integration with a similar electronic document management system, thanks to the use of the Alfresco EDMS platform when developing software, or with electronic document management systems of third-party organizations, which allows you to create a single information and documentation space in the organization and automate business processes covering all divisions of the organization.
The well-established organization of document flow raises the activity of an enterprise to a qualitatively different level, and for some enterprises, the development of an EDMS is the only opportunity to successfully function in a competitive environment. Thus, document flow acquires such a concept as “corporate” EDI.
The most significant issues for the domestic EDMS community:
·Current needs of customers: what they expect from EDMS today and tomorrow, what IT offers now.
·The state as a regulator of the development of electronic document management: where the Russian information society is heading.
·Automation of business processes: new capabilities of ECM systems.
· Current trends development of ECM systems: mobility, BYOD, virtualization, electronic signature, data centers, cloud technologies, portal solutions and other technological innovations.
·Risks when working with electronic documents: ensuring safety.
· Electronic document management and working with personal data: how to comply with legal requirements.
Enterprise employees spend a lot of time searching for the necessary data (according to statistics, this takes up to 40% of working time) or recreating documents that already exist (this happens in approximately 70% of cases). A typical situation is when the original texts of contracts are stored by lawyers in electronic form (often without a history of changes); accounting entries for documents accompanying the execution of contracts are carried out in accounting system; records of contracts and accompanying documents are kept in a spreadsheet; accounts and acts are stored in paper form in finance department, and current correspondence regarding contractual work is in the employees’ electronic mailboxes. With such “scattered” data and documents, it is difficult to ensure their integrity, consistency and security.
Information resource management is of particular importance for the activities of any organization. Regardless legal status or organizational forms activities, institutions are called upon to actively interact with executive and legislative authorities, structures involved in regulating the economy. All this, in turn, gives rise to a specific workflow.
Thus, Met-Info LLC acutely feels the need to organize effective management information resources and take active steps to use computer technology in the field of document flow management (and information in a broad sense).
Unfortunately, the application computer programs in Met-Info LLC with documentation in a number of cases is not accompanied by a structural restructuring of the work with documentation, i.e. documents are compiled manually by some of the information users.
Therefore, it is recommended to provide access to the general accounting database of Met-Info LLC for all users of accounting documentation, that is, to ensure direct entry of information at the point of receipt of external documents, such as receipt of materials, transfer of products to the warehouse - in the workshop of the enterprise, the HR department will organize entering data on employment and dismissal directly into the accounting system.
All this will provide the following benefits: increasing the reliability of information; reduction of manual labor.
An electronic document management system (EDMS) or EDMS (Electronic Document Management Systems) is a system for automating work with documents throughout their entire life cycle(creation, modification, storage, search, classification, etc.), as well as processes of interaction between employees. In this case, documents primarily mean unstructured documents (Word, Excel files, etc.). As a rule, EDMS includes electronic archive documents and business process automation system.
Effective document management based on EDMS is based on three components of the system:
- - technology (based on modern computer systems).
- - corporate rules for creation and use information resources(and their consolidation in administrative documents).
- - psychology of users and their training (individual if necessary).
In document management systems, registration of normative documents, administrative documents (orders, instructions), correspondence with authorities, institutions, credit organizations, other institutions and enterprises, as well as citizens. In addition, the EDMS works with internal official correspondence and draft organizational and administrative documents created by structural institutions.
The EDMS provides control over the movement and execution of documents, contains complete information about the instructions given by management and the actions of performers. An important element of the EDMS is a system of formal and semantic links to interrelated documents and instructions. A search in the EDMS, in addition to traditional office details, is based on a system of classifiers (including thematic ones) that allow contextual selection of documents.
The procedure for maintaining classifiers is strictly regulated. Some directories are compiled by specialists conducting registration (for example, a classifier of correspondent organizations). Making changes to the rest is the prerogative of the administrator; in addition, the administrator constantly monitors new classifier positions and, if necessary, adjusts them. Thus, possible duplication of directory positions is eliminated, and errors in document registration are eliminated. The efficiency of the system can only be ensured by regular training of users and “soft” control over their actions in the system (correction of errors, compliance with the requirements for filling out mandatory information details, etc.).
The creation of an EDMS is also associated with a change in the role of the service documentation support: uniform technological requirements for organizing document flow using EDMS are determined, establishes a system of “administrative frameworks” for working with documents, which in fact is the methodological basis for organizing work with information.
In general, the establishment of a clear procedure for using the system and rules for working with information is one of the main factors that ensured the successful implementation of the EDMS and its full use.
The goals of implementing an electronic document management system are: automation of office work, automation of document flows, automation of control over the execution of documents and orders, increasing executive discipline, putting things in order in working with documents, reducing time for operations with documents, transition to paperless technologies.
Thus, it is possible to determine the effectiveness of using an electronic document management system (EDMS) in the narrow sense for individual industries and users.
Let's take a closer look at cost savings on labor costs for EDMS users.
Calculation of conditional annual savings labor costs j-th qualification With j, when the complexity of the processes of preparing and processing information changes as a result of the introduction of EDMS, is determined by the formula:
C j = C zpj (Q 1 - Q 2) A 2 / Ф j,
where C salary is the annual fund wages employee j qualifications involved in data preparation and processing, rub.; Q 1, Q 2 - labor intensity of preparing and processing a data unit in the basic and new versions software product, person/hour; A 2 - annual volume of work on preparing and processing data in a new version of the software product, natural units; F j is the annual working time of one employee of the jth qualification, engaged in the preparation and processing of data, hours.
Let's calculate labor cost savings personnel worker having a salary of 5787 rubles. Consequently, the manager’s annual salary fund is RUB 69,444. Considering that with a five-day working week, the number of working days is 249, the annual working time fund will be 1992 hours.
The complexity of preparing and processing documents with the previous method of work and in EDMS system is 25 [person/hour] and 20 [person/hour] respectively. The annual volume of work on preparing and processing data in the EDMS (in physical units) is? 80 documents.
Thus, we get savings in managerial labor costs:
C = 69,444 · (25 - 20) · 80 / 1992 = 13,944.58 rubles,
which is 20% of the annual wage fund of a personnel employee engaged in the preparation and processing of documents in automated system document flow.