What professions do people need to know geography? Start in science. Useful video: profession geographer
Every year our school hosts subject weeks to introduce students to the natural sciences. At my events, I try to attract children’s attention to geography, to show the role of their favorite subject in the life of every person. My main goal is to help students with career guidance, the opportunity to expand the range of ideas about professions through the school subject “geography”.
Download:
Preview:
Lesson topic: “Professions related to geography”
Objective of the lesson:
- help students with career guidance, expand the range of ideas about professions through the school subject “geography”.
- formation of skills and qualities necessary for a person of the 21st century: responsibility and adaptability, communication skills, creativity and curiosity, critical and systematic thinking, the ability to work with information, the ability to pose and solve problems.
- fostering cooperation and respect for all group members, social activity
Equipment: PC, multimedia, political, administrative and physical map of Russia, atlas maps, computer presentation, portraits of travelers.
Lesson progress:
1. The song “Globe” performed by Vladimir Troshin is played
(music by M. Svetlov, lyrics by M. Lvovsky).
I don't know where to meet
We'll have to go with you.
The globe is spinning, spinning,
Like a blue ball
And cities and countries flash by,
Parallels and meridians,
But there are no such dotted lines anywhere,
By which we can wander around the world.
I know there is an unknown
Latitude of latitudes,
Where is our wonderful friendship?
It will definitely bring you together.
And then we will know what is brave
Everyone took on a big deal
And the places we've been
People marked on world maps.
We will hear each other
Beyond the mountain tops
Behind the February blizzards,
Through the snowy expanse
And even though we wandered hundreds of miles,
Let there be kilometers between us,
But behind thousands of miles of separation
Songs of friendship distinguished sounds.
1.1.Teacher's opening speech
If you are a romantic at heart, want to travel a lot, explore Nature in all its manifestations, contemplate and enjoy the beauty of the earth’s landscapes, cultivate fortitude and physically strengthen yourself, then the science of geography will help you.
Presenter 1: Guys! What professions do you know related to geography?
(the kids list, the teacher invites the kids to look at the table, which contains a list of professions related to the subject, and express their opinion about the material in the table).
Geography is the only one of all the sciences, the object of study of which is our entire planet, and recently other bodies of the solar system (cosmic geography, planetology) and the science most closely related to nature. At its core, geography is a science at the intersection of the natural and human sciences. Geography is a science both old and young.
Presenter 2: When did the science of geography appear? Who is the founder of science?
Well done guys, that's right. Geography, as a fundamental science, originated in ancient times more than 2500 years ago (Eratosthenes).
Presenter 3: What does the word "Geography" mean?
What is she studying? (teacher summarizes student answers)
There are many definitions of what “geography” is, that geography studies nature, human society and economy in the spatial aspect and their interrelations in the form of geographical complexes. At the same time, a professional geographer must find answers to questions such as: WHAT, WHERE, HOW MUCH, HOW, WHY, what could happen next to this object (WHAT WILL HAPPEN and WHERE). Modern geography is no longer a descriptive science and not even just an explanatory one, revealing the mechanisms of nature, population and economy of a certain territory, but an explanatory - predictive and constructive science, aimed at solving specific practical problems. Therefore, a geographer, in addition to his subject, must know the basics of all fundamental sciences. “From geology to ideology N. N. Baransky is a classic of Russian geography. Possess a wide range of means and methods to achieve your goal. As one famous geographer said: “A geographer must be able to handle both a shovel (field practices and expeditions) and a computer.”
Presenter 1: Among the professional geographers there were and are famous generals, admirals, seafarers, statesmen, diplomats and even heads of state, writers and actors. Several world and Russian stars have received higher geographical education: musicians, producers, composers, prose writers and poets, TV presenters, journalists, media editors. Here is a far from complete list of famous personalities of our time (last quarter of the 20th, early 21st centuries) who studied to become a professional geographer and (or) defended a scientific degree in geography:
Artur Chilingarov (world-famous polar explorer);
Nikolai Drozdov (host of the TV program “In the Animal World”, world-famous ecologist)
Alexander Belyaev (“chief teleforecaster” on Russian television (NTV)
Ivan Zatevakhin (TV and radio host of programs about animals);
Fyodor Konyukhov (world-famous navigator and traveler);
Yuri Loza (musician, composer (remember the hit “On a Small Raft”)
Among the foreign stars we can note:
Jacques-Yves Cousteau (scuba inventor, world-famous oceanographer);
Thor Heyerdahl (world-famous traveler and ethnographer (“Kon-Tiki”, “Ra”);
Crown Prince Harry of England is the son of Princess Diana and Prince Charles.
Teacher: So, guys, I think that we have interested you in the science of Geography. And now I give the floor to the guys who will introduce you to the profession of a meteorologist, because soon you will be faced with the task of choosing a profession that would be interesting to you, would correspond to your abilities and would be popular in the labor market.
Presenter 2: In the near future, you are faced with the task of creating a professional plan for yourself. Let's try to compose it right now. There are leaves on your tables. Try to describe your future profession:
“I WANT” - I like it, I’m interested, I’m attracted to it.
“I CAN” - I am capable, I am able, I have skills.
“MUST” - demand for a profession in the labor market
Presenter 3: Well, before moving on to the main topic of our lesson, please answer the question: “How do we know whatWill it be rain or wind, colder or warmer? (on radio, television, newspapers)
What profession studies and gives us this information? (Meteorologist)
Today we will tell you about the profession of a meteorologist. This is a very important profession because meteorologists help people in different professions. But how? And with what?
Presenter 1: This is the definition of a meteorologist given in the Big Encyclopedic Dictionary.
Presenter 2: Even though the hot sun is shining,
Even if it's twenty degrees below zero,
The meteorologist is watching
The weather forecaster writes his forecast.
Are there cyclones, or menacing storms?
No matter the flood, no matter the heat
Nothing can stop them
Issue forecasts for Mt.
So let people be glorious,
Those who carry out this brave work,
Descendants will not forget them
And they will give what they deserve
Presenter 3: Every now and then a bag of jokes spills onto the heads of weather forecasters - meteorologists.
Meteorology (Meteora - in Greek - an atmospheric celestial phenomenon, "Logos" - teaching) ... And all together... this is the science of the earth's atmosphere, its structure, properties and phenomena occurring in it.
Presenter 1: There are thousands of weather scout posts scattered around the world. There are weather stations everywhere: on land and at sea, in the Pamir Mountains and the Sahara Desert, in the ice of the North Pole and in the vastness of Antarctica. Meteorologists monitor the weather in any weather. They have an anemometer, weather vane, barometer, and moisture meter in their service. They determine temperature with thermometers and thermographs, and air humidity with a barometer. Anemometer - wind speed and strength, rain gauge - amount of precipitation
Presenter 2: From time to time, meteorologists send balloons into the air. Equipped with a radio transmitter and all kinds of measuring instruments, heavenly messengers report by radio what the weather is like at an altitude of 20-30, or even 300 kilometers from the earth. Meteorological satellites of the Earth send from above photographs of clouds enveloping our planet
Presenter 3: Reports from a large army of scouts come to weather headquarters, the Institute of Forecasts. Here scientists compile a synoptic map (“weather forecaster” - “joint observer”). Meteorologists study this map, compare information, take into account the movements of warm and cold air masses, computer programs make complex calculations and then give a weather forecast.
Presenter 1 : Meteorologists warn farmers about possible frosts, hot winds and hail (take care of the harvest!), sailors about the approaching storm (quickly take shelter!), pilots - about poor visibility, the possibility of icing on the plane, about a thunderstorm (fly away from the thundercloud!), railway workers - about blizzards (wouldn’t have skidded along the path!) Each of us, having connected the weather forecast on our phone, knows whether to take an umbrella or not, and what to wear!
Presenter 2: Previously, meteorologists only knew how to predict the weather, now they know how to change it: with the help of airplanes and rockets they disperse thunderclouds. The tasks that meteorologists solve are very diverse. Specialists work in the field of designing new devices, and participate in expeditions, working with the most complex instruments. A person who has dedicated his life to such a difficult task must be very accurate when collecting information and observant when analyzing weather conditions. Making forecasts requires the development of memory and creative imagination, and the ability to work on a computer. It is necessary to remember conventional signs and symbols in order to depict them on special maps, and then translate them in the mind into visual pictures so that a “portrait” of the weather appears and it is clear how it will change after certain periods of time.
Presenter 3: When working at drifting stations in the Arctic, on weather ships, and in high mountain areas, a meteorologist needs endurance and the ability to overcome difficulties. When you finish school, maybe one of you will decide to devote yourself to this work. Technical schools and institutes train meteorological specialists.
Presenter 1: Another interesting profession in geography is an oceanologist.
Presenter 2: Oceanologists study waters, seas and oceans, the state of the bottom and shelf, and monitor the development of aquatic flora and fauna. Analysis of the physical, chemical and biological processes occurring in deep waters allows scientists to predict the further development of ecosystems. The main task of oceanographers is environmental: saving the natural resources of the sea, preventing conditions for the extinction of one or another species of underwater flora and fauna. The research of oceanographers is also used in fisheries, hydraulic engineering and military fields, paleontology and biology. Most of the research is carried out from specially equipped ships, submarines, bathyscaphes and other technical devices. To initially collect information or material, oceanographers have to descend to depth.
Presenter 3: Oceanologist is a fascinating, but very rare profession. I think few people could boast of knowing an oceanologist. This is due primarily to the fact that this profession requires deep knowledge in various fields of natural and mathematical sciences. Oceanologists are usually trained by departments working at the intersection of the study of geography, geology and physics. In Russia, only the best universities raise future ocean researchers: Moscow State University, Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology, St. Petersburg State University, RGGMU, specialized universities in Rostov-on-Don and Vladivostok, institutes of the Russian Navy
Presenter 1: Places of work:
- research institutes,
- underwater and onshore laboratories,
- hydrographic services,
- oceanographic vessels.
Presenter 2:
Professional skills:
- knowledge of general biological laws and processes
- knowledge of the laws of physics and chemistry
- understanding of geographical and climatic processes
- possession of special equipment for diving and water research
- carrying out analyses, measurements and experiments on collected materials
3. Reflection.
The teacher asks questions:
What was the purpose of our lesson? Do you think we accomplished it? What would you do differently? Why? What other professions would you like to know about?
Teacher: In conclusion I would like to tell a parable.
During the construction of the cathedral, a traveler comes up and asks the workers what they are doing. One answered: “I carry stones.” Another said: “I earn money so that I have something to live on.” And a third exclaimed enthusiastically: “We are building a cathedral!”
Let your work be the joy of serving a great goal. “A person only achieves something where he believes in himself.” I wish you to believe in yourself and achieve your goals, and choose your professional path. I will be very glad if the science of Geography helps you with this.
Preview:
To use presentation previews, create a Google account and log in to it: https://accounts.google.com
Slide captions:
Professions related to geography
What professions do you know related to geography?
Geologist - a person who studies the earth's interior and searches for minerals
An oceanologist is a specialist who studies the physical, chemical and biological processes occurring in the seas and oceans.
Cartographers - develop ways to display three-dimensional relief on a plane, methods for creating thematic maps and atlases, and the development of digital cartography.
A meteorologist is a scientist who studies the earth's atmosphere and the processes occurring in it.
A land surveyor is involved in the allocation of land for construction and ensures that the land is used rationally.
Slide captions:
Professions related to geography (Part 2)
Nikolai Drozdov, host of the TV program “In the Animal World”, world-famous ecologist
Alexander Belyaev “chief teleforecaster” on Russian television (NTV)
Ivan Zatevakhin TV and radio presenter of programs about animals
Fyodor Konyukhov, world-famous navigator and solo traveler
Yuri Loza musician, composer
Jacques-Yves Cousteau, inventor of scuba gear, world-famous oceanographer
Thor Heyerdahl, world-famous traveler and ethnographer (“Kon-Tiki”, “Ra”)
Crown Prince Harry of England is the son of Princess Diana and Prince Charles
Professional plan: “I WANT” - I like it, I’m interested, I’m attracted “CAN” - I am capable, I know how, I have the skills “MUST” - the demand for the profession in the labor market
I want to become an oceanologist - let them teach me!
Places of work: -research institutes; - underwater and onshore laboratories; - hydrographic services; - oceanographic vessels.
Thank you for your attention!
One of the poets said that all professions are important and all professions are needed. But professions related to the earth have always been and will be in demand and useful: geologists, miners, agronomists, ecologists, surveyors, builders. Let's look at them in more detail.
Professions related to the study of the lithosphere
Geologists and miners - romance with a risk to life (professions related to the study of the lithosphere) Geologists have always been associated with the romance of travel, life in tents. But this is only one side of the coin. The heroic work of people in this profession is the study of the composition of the earth, the lithosphere (hard shell of the Earth), the search for minerals, and their development.
Scientific work
Seismologists, scientists. Representatives of this profession are collected, responsible, observant, know how to work in a team, and are not afraid of extreme conditions.
Miners can rightfully be considered the bravest and most courageous people. After all, every million tons of coal mined costs approximately four human lives. It is the miners who have to work deep underground and risk their lives almost every time. One of the highest paid professions, one that develops endurance and requires good physical fitness, is also the most risky and dangerous.
The oldest professions on earth
Agronomist is rightfully one of the most widespread and most ancient. Already several thousand years ago, people knew how to cultivate the land and grow certain crops. It is impossible to imagine agriculture without this profession: agronomists not only grow crops, but also select new varieties of wheat, apple trees, and rapeseed that are so useful and necessary for humanity.
To some extent, construction professions can also be classified as professions related to land, since houses are built on the ground. It is also one of the oldest professions, which can safely be called the most peaceful. The secrets of the construction craft have been passed down from generation to generation, some, unfortunately, have been lost forever, but palaces built many centuries ago still stand.
The builder is always in good physical shape, resistant to stress, and knows how to finish what he starts. In addition, builders will be in demand at any time.
Taking care of the ground and a little about convex-concave surfaces
Ecologists make sure that the harm caused by humanity to the earth is minimal, they take care of environmental protection, and study flora and fauna in interaction with human activity.
A land cadastre specialist takes into account the quantity and quality of land, its fertility and location.
And the surveyor, who in Tsarist Russia was called a land surveyor, studies all the convexities and concavities of the earth’s surface in order to correctly design and arrange buildings.
Professions related to the earth and the study of the lithosphere are quite earthly, sometimes risky and difficult. But the one who chose these professions is truly always needed and important.
Professions related to geography are distinguished by their diversity. You can master them in different educational institutions. Right now in the Russian Federation, students are studying at 24 faculties with a geographical focus. These are just university departments. In addition, there are 41 geographical departments of pedagogical institutes.
All this means that professions that require knowledge of the designated science are in demand, and there are not as few of them as it might seem.
What are the specialties in this area?
Not all professions are listed below in the text, but the most relevant and in demand of them in our time are touched upon. So the list looks like this:
- biogeography;
- landscape science;
- land hydrology;
- soil science.
Based on this list, you can form an opinion about what profession a student studying at the Faculty of Geography needs.
Biogeography
It implies the study of the fauna and flora of the entire Earth. In biogeography, two more promising “branches” can be distinguished: medical geography, as well as the ecological direction of the subject. In turn, the first involves studying the centers of spread of various diseases, and, most importantly, their primary sources. Also, the medical industry does not ignore hotbeds of disease.
If we define the area where biogeographers work, then their workplace most often becomes various reserves, parks and arboretums. The most common activity of these people is the search for wild animals and various kinds of plants for their further domestication. They are also hired to select the most favorable places for the future construction of cities and other settlements.
Landscape science is a classic specialty for all people who want to study geography. Representatives of this field of science deal with all factors that in one way or another relate to the subject, analyze the relationship of all natural components: from the smallest elements (forest, park, meadow, river, field, pond) to the largest of them - the geographical envelopes of the planet.
People in this profession have the goal of learning absolutely the entire history of a particular landscape. They need to try to predict the development of the soil, not forgetting to include in their field of view a huge number of various factors. Concurrently, landscape scientists should understand not just one area of geography, but absolutely all scientific fields, even biology.
Of course, this profession is divided into various areas, among which the most popular are:
- geochemistry;
- geophysics;
- ethnocultural landscape studies;
- environmental assessment of the territory;
Experts in geochemistry study various chemical processes that in one way or another affect the soil of a certain area. In turn, geophysics analyzes physical phenomena. Ethnocultural landscape science studies how people and plants influence the soil and, by extension, how the land influences them.

It is important to note that the profession requires mobility from people, because the field of study of its workers is the entire globe. Most often, of course, they can be observed on the territory of Russia, but knowledge of a foreign language allows you to go on business trips around the world. It is noteworthy that the Russian school of landscape design is known throughout the world as the best. And it was founded back in the nineteenth century by the famous geographer Dokuchaev.
Land hydrology
Unfortunately, in the twenty-first century, humanity is faced with a huge shortage of fresh water. It gets to the point where entire wars are broken out between individual states over its possession. Currently, a project is even being developed that involves various ways of transporting glaciers from the poles to the arid places of the Earth. It is people who have chosen the profession of “Terrestrial Hydrology” who undertake to rationalize the balance of water throughout the world, thereby providing fresh liquid to all corners of the planet.
Ever since school, everyone has heard about the water cycle in nature. This is precisely the phenomenon that hydrologists study. They also touch upon the influence of man himself on this cycle and analyze various regimes of water flows in various places. In addition, hydrologists try to forecast and assess the optimal consumption of all resources and are directly involved in projects for the construction of canals, reservoirs, dams, dams, hydroelectric power stations and even beaches.
If the question arises, which branch of geography is best to delve into in order to study land hydrology, then it is worth asking:
- biology;
- ichthyology.
- hydraulic engineering;
- chemistry.
Lake Baikal is also considered by hydrologists to be a promising object for research. Based on some forecasts, it will become a real ocean in the future.

Soil science first began to emerge in Russia. This is due to the fact that it is here that the largest tracts of the most fertile land in the whole world are located. This science includes knowledge not only of geography, but also of biology. She is engaged in the objective use of land resources, studying:
- dynamics;
- origin;
- development;
- soil condition.
Soil science is taught not only in the departments of geography, but also in biological areas. But people who finished first spend additional time:
- spatial analyses;
- soil assessments;
- mapping.
All notes of these specialists are entered directly into the databases of the Unified Land Cadastre of the Russian Federation.

The task of soil scientists is to study such phenomena as:
- soil geography;
- geochemistry;
- biogeochemistry;
- hydrology;
- genesis;
- hydrogeology.
Indeed, there are a lot of professions related to geography. Based on the descriptions of this or that specialty, you can form your own point of view on the question of which one people need most now.
Material overview
How healthy and right this is,
What among the many sciences
We study geography
So that the world around you becomes clear!
Geography- science about everyone and for everyone. What is beyond the horizon, what kind of people live behind the high mountains, are there other countries beyond the mountains, is there an end of the Earth, and if so, where is it? These questions have always excited and excite people's imagination. Why does a modern young man need geography? I believe that it is generally impossible to do without the knowledge that we gain in geography lessons. Any person should have a correct idea in his head about which country, region, city, village he lives in. Without this, true patriotism - love for one's Fatherland - is impossible.
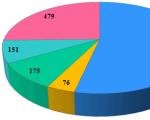
Relevance of the chosen topic. I like the subject of geography, and I would like to study it in more detail in the future, but I don’t know whether it will be in demand for me? I heard that only a few take the Unified State Exam in Geography, and only those who are going to enter the Voronezh Military School to become a military meteorologist. I became interested in this question, because I will soon have to make a choice of profile. I decided to conduct a small sociological survey of 9th grade students, since they are more knowledgeable about this issue. The results surprised me and encouraged me to take further action. It turns out that out of 35 respondents, 25 people (71%) chose geography to take the OGE form, because they consider it an interesting and most understandable subject, but more than half of them do not know where knowledge in geography is needed in ordinary professions. 20 ninth-graders (57%) do not know professions that are closely related to geography, except for a geography teacher, but 31 people (almost 89%) wanted to find out.
I wondered what the profession of a modern geographer is associated with? Asking this question to my friends and acquaintances, people far from geography, I received a set of similar answers: a geographer is a traveler, a geographer draws maps and talks about the weather, a geographer teaches geography at school. That's all! This is such meager knowledge about the profession of a geographer. Do the general public know who, for example, geomorphologists, ekists (a specialist in population geography) or glaciologists are? Many people have a primitive idea of geography as a purely speculative science, without any practical orientation, so it is relegated to the background, and this subject is far from a priority in schools. So what do professional geographers do, what geographical specialties exist, and how does geography contribute to solving practical problems? Most modern schoolchildren cannot answer these questions.
Conclusion: many do not understand why they need geography and what professions and specialties exist that are closely related to geography.
Hypothesis: Geography- the basis of many professions. She is able to form an opinion about self-determination in a future profession and the requirements that society places on the quality of labor resources. To raise the prestige of geography, it is necessary to cultivate the profession of geographer, to help society achieve an understanding that, indeed, “without geography you are nowhere!”
Target: introduce professions closely related to geography and show the need to study geography at school for further self-determination in society.
Tasks:
1. Study the relationship between geography and people’s professions and draw up a table “Application of knowledge and laws of geography in various professions.”
2. Find out what qualities a professional in a particular profession related to geography should have and where to get an education in this specialty.
3. Analyze the labor market for the demand for geographical professions (specialties).
4.Identify the attitude of schoolchildren to the subject “geography” and their future, including in terms of employment.
5. Compose a booklet “You are nowhere without geography!”
Practical significance: the results of this study can be used in geography lessons, in extracurricular activities, in career guidance work with students, and work with parents.
Research methods:
· collection of information
· analysis of collected information
· synthesis of collected information
· sociological survey (questionnaire method)
· analysis of personal data
comparison, generalization
graphic method
Chapter 1. Geography and profession.
1.1. The role of geography in human life.
Geography as a science originated a very long time ago, during the formation of human society. She helped landowners choose a place for a field, sailors - navigate their ships across the seas and oceans, discover new lands, merchants - successfully trade with other countries. It was sailors and merchants who were the first discoverers of new lands. But it was not only the desire to acquire important practical knowledge or the thirst for profit that forced people to hit the road to unknown distant lands and risk their lives. Often it was ordinary human curiosity - the desire to learn something new, unknown, interesting. So what is the science of geography? Modern geography as a science studies the environment, its spatial features and relationships with society, the territorial organization of society. Today, geography has two very important and interconnected wings - natural history and socio-economic, and both of them are equally its essence and content. Nowadays, it is impossible to imagine geography without a person, without an attitude towards a person, without caring for a person, and, of course, without human activity. Is the role of geography becoming important and changing rapidly in modern times? Why? Yes, because the world is changing so rapidly, so significantly, that it is sometimes difficult to imagine what it was like in the recent past. In our time, geography is not the former “romantic” science, but a science experiencing its rebirth. Having become a constructive science, setting itself the task of solving the contradictions “man – nature – economy – environment”, enriching itself with new knowledge, it began to serve as a bridge between the natural and social sciences. Now, having such a huge amount of knowledge, she solves problems of a different nature and at different levels, from local to global. Geography has very close connections with many sciences, because today there are a lot of methods for studying and understanding the modern world: historical, physical, chemical, mathematical, biological, etc. (Appendix 1)
Geography is an essential component of any profession and specialty. Its most important aspect is the formation of a worldview, intellectual and professional outlook as leading principles in the formation of professional self-awareness of the personality of a future specialist. The relevance of this problem is represented by the tasks set by the state for the transition at the senior level of general education to specialized ones, the recent emergence of new ways of accumulating and processing information, and a large number of new professions and specialties. Geographical knowledge is necessary for every person in order to understand their role and place in life and in the transformation of reality, and to determine an active life position. Many classmates and my acquaintances believe that in a profession, earnings are the main thing, but we also need to think about the meaning of the work, its social usefulness. A good specialty for me is one that gives me the opportunity to realize, first of all, my personal interests and plans, where I can bring more benefit.
1.2. Main groups of “geographical” professions.
Having considered the classification of professions, I decided to find out which professions require knowledge of geography. This list is quite large. Here are some of them: agronomist, archaeologist, military man, geologist, geomorphologist, surveyor, hydrologist, mining engineer, demographer, diplomat, journalist, urban planner, ship captain, cartographer, climatologist, landscape architect, forester, logistician, medical geographer, marketer , tourism manager, meteorologist, oceanographer, pilot, sociologist, customs officer, trade analyst, travel agent, farmer, ecologist, agricultural economist, etc. (Appendix 2)
Despite the abundance of modern geographical specialties, they can all be grouped according to several criteria.
There are “old” ones, which arose at the end of the 19th century.- at the beginning of the 20th century, traditional geographical specialties (for example, geomorphology, geosciences, climatology), and there are “new” ones that have appeared relatively recently (for example, bioclimatology, tourism geography or geographical planetology).
There are the most and least popular geographical specialties. For example, the highest competition when choosing a specialization at the Faculty of Geography of Moscow State University is observed in the following departments: geography of the world economy, economic and social geography of foreign countries, geoinformatics, and environmental management. A new specialty is developing dynamically - tourist geography.
The aura of romanticism inherent in geography as such reaches its maximum strength in departments with which famous navigators and travelers were in one way or another connected (oceanology, biogeography).
We can distinguish a group of geographical specialties where methods of exact and natural sciences are widely used, especially mathematical calculations: meteorology and climatology, oceanology and hydrology, cartography and topography with geodesy, glaciology and cryolithology (permafrost science). Chemical methods and formulas should be known to geochemists-landscape scientists, geomorphologists, soil geographers, paleogeographers, geoecologists, geographers-volcanologists. Physical and geophysical methods are used by meteorologists, oceanologists, hydrologists, glaciologists, and landscape scientists. Biogeographers, medical geographers, limnologists (lake scientists), and landscape scientists are closely familiar with biology.
In the group of economic-geographical specialties, statistical methods and computer-mathematical modeling are widely used. An economic geographer must also understand the basics of industrial and agricultural production.
Representatives of all specialties without exception must have a high level of knowledge of computer and information technologies (especially cartographers, meteorologists and weather forecasters) and be able to apply the cartographic method and methods of aerospace sensing of the Earth in their work.
Male graduates of most geographical faculties, in addition to their main civilian specialty, also acquire a military specialty, while simultaneously studying at the military department. As a rule, this is a “military weather forecaster, meteorologist”, “military cartographer-topographer” and “photogrammetrist-decipherer of aerospace intelligence materials”. Purely military geography is taught at the Academy of the General Staff.
There are geographical specialties that are closest to nature. They can be called office-field. These are mainly physical-geographical specialties that involve empirical testing of scientific hypotheses and theories. As a rule, the work of a physical geographer consists of two stages:
1) travel to nature, where field research of objects is carried out (expeditions, educational practices) and 2) detailed processing of the results of such research in office conditions (laboratories at departments of geographical faculties and in divisions of IGRAN and other natural science research institutes).
There are “male” and “female” geographical specialties. For example, glaciology, cryolithology and military geography are almost completely masculine. An increased proportion of men is observed in oceanology, geomorphology, geodesy, and topography. But among graduates of geographical faculties of pedagogical universities, among meteorologists, forecasters and cartographers, representatives of the fairer sex predominate. There is no doubt that the more field-based a geographic specialty is, the more “male” it is, and vice versa.
1.3. Features of some specialties.
Let's consider individual geographical specialties: their content, important qualities, pros and cons, and note the structures where graduates of geographical faculties who have received the corresponding specialty can work. (Appendix 3)
Geology. Geology is a complex of sciences about the composition, structure of the earth's crust and the history of the earth's development. Accordingly, a geologist is a specialist in studying the composition and structure of rocks for the purpose of searching and exploring mineral deposits. It solves the following tasks: carrying out geological surveying and prospecting work in promising areas; exploration and evaluation of identified deposits on land and offshore; providing geological services to mining enterprises; establishing the locations of mine workings and boreholes; development of mining plans; study of the geological structure of deposits; implementation of geological control over mining operations, the state of oil and gas development; generalization of geological material and results of field and geophysical studies. Advantages of the profession: unconventional, analytical and creative work; high wages. The profession of a geologist is one of those few professions that are considered romantic and has its own attractive sides for people of different interests. For travel lovers - the romance of working in taiga, polar, desert, high mountain conditions, the opportunity to visit different regions of Russia. For extreme sports enthusiasts - field work in difficult conditions on land, at sea and in the air: the unbearable heat of deserts or frosts of the north of tens of degrees, myriads of mosquitoes in the taiga and in swampy areas require heroic endurance. Living in a tent, daily multi-kilometer routes throughout the field season provide the opportunity to test your strength. Disadvantages of the profession: rotational work - geologists go on expeditions for several weeks, where they work very intensively without days off, lack of household amenities, difficulties of camp life. Place of work: Geological exploration expeditions; geophysical and drilling parties; geological research institutions; mining industrial organizations; oil and gas producing industrial organizations.
Important qualities: excellent health and physical endurance; ability to think globally; developed logical thinking; well developed memory; analytical thinking; the ability to withstand prolonged physical and mental stress in different weather conditions and in different terrain; the ability to quickly navigate the environment; high level of concentration; ability to work under irregular working hours; observation; emotional-volitional stability; forecasting ability; ability to work in a team.
Geodesy. The word geodesy comes from the Greek: “geo” - earth and “daizo” - to divide into parts, and, simply put, it means land division, that is, the study of the Earth using measurements on its surface. The difference between geodesy and other geosciences lies in the fact that this study is based on very accurate measurements of various parameters and quantities that characterize the Earth both as a whole and its individual parts. Geodetic work helps to draw up a map of the areas of their probable occurrence prior to the exploration of minerals, to conduct geological and geophysical exploration to determine the locations and quantities of their reserves, as well as to carry out ground and underground surveys, allowing for the correct and economical design of mining operations. The role of geodetic work in urban construction and the construction of various engineering structures is great.
Volcanology- the science of the causes of the formation of volcanoes, their development, structure, composition of eruption products and patterns of location on the Earth's surface. A volcanologist is a volcanologist who studies volcanoes. The profession of a volcanologist is steeped in the spirit of romance of long-distance expeditions and stands on a par with such interesting professions as geologist, geophysicist, and oceanographer. Modern volcanology is designed to study volcanoes not only with the aim of predicting their eruptions, but also using the energy of volcanic heat for the needs of the national economy. Monitoring of active volcanoes is carried out around the clock by seismic stations. The structures of ancient extinct volcanoes are studied for scientific and practical purposes. The help of volcanologists is invaluable at the time of a volcanic eruption: by monitoring the direction of the ash plume, studying its chemical composition, they issue forecasts to weather services and air traffic controllers who correct aircraft flight trajectories. Volcanologists also study geysers, which are usually located near volcanoes. Despite the rarity of the profession, volcanologists are constantly in demand and are in demand: more than 1,000 active volcanoes have been registered on earth. As MSU volcanologist professor P. Plechov noted: “A billion years of volcanic activity on earth is guaranteed.” International cooperation is well developed in this industry. Volcanologists around the world are working together to study volcanoes and improve research methods and technologies. As a rule, volcanoes are named after the volcanologists who studied them. There is a real opportunity to immortalize your name in the name of the next volcano or geyser! Among the disadvantages of the profession is a high degree of risk: the study of active volcanoes takes place in conditions of increased danger - surrounded by hot lava, suffocating gases and hot dust, constantly exposed to the danger of eruption. For protection, volcanologists use special clothing - heat-insulating clothing and shoes coated with a layer of aluminum or other metal that reflects heat. Protective helmets are put on the head. Gas masks and gas masks are designed to protect against poisonous gases. Place of work: Institute of Volcanology and Seismology, Far Eastern Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences in Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, Department of Petrography and Volcanology at Moscow State University and St. Petersburg State University. Important qualities: physical endurance; spatial imagination; analytical mind; observation; attention; logical thinking; emotional-volitional stability; good hearing and vision.
Geomorphology. The unofficial name of this science is engineering geography. She studies the history of the Earth's topography. The branch of geomorphology is paleogeography - the reconstruction of the prehistoric relief of the Earth. The most promising areas in geomorphology are space geomorphology (the study of the relief of the planets of the solar system) and aesthetic geomorphology (the creation of artificial landscapes). Geomorphology is a monetary specialty. Professionals participate in the design of settlements, roads, airports and seaports, dams, reservoirs, parks, beaches, oil and gas pipelines (including on the seabed), and work in geological teams. This is one of the most male-dominated geographical specialties. Much attention is paid to the physical training of the geomorphologist. Labor market: research institutes, manufacturing firms, various geological exploration services, engineering design organizations.
Biogeography. Biogeography studies the flora and fauna of the Earth. Promising directions are environmental geography and medical geography (the study of the sources of occurrence and spread of various diseases and their vectors). Biogeographers can be found in national parks and reserves, in arboretums; As part of expeditions, they look for wild plants and animals that are promising for domestication, and choose environmentally friendly places for the construction of new settlements (including country houses for the elite). TV presenters Nikolai Drozdov and Ivan Zatevakhin graduated from the Department of Biogeography, Faculty of Geography, Moscow State University.
Glaciology and cryolithology. Both sciences study the ice sphere of the Earth: glaciology - on the earth's surface (glaciers and snow cover), cryolithology - under the earth's surface (permafrost and seasonal permafrost). Promising directions - Antarctica as one of the future places on Earth for mining, the ice cover of Antarctica and Greenland as laboratories of the ancient climates of the Earth (mysterious Lake Vostok), oil and gas basins, communications and settlements in the permafrost zone in northern Russia, the impact of global warming to the polar regions of the Earth, the “ice planet” is Titan. Glaciology is currently in a boom phase. In Antarctica, the number of scientific stations is increasing, with their research preparing the basis for contenders for the Earth’s ice shell. These are the most male-dominated majors in geography: almost 100% of graduates are representatives of the stronger sex. Accordingly, students will need to intensively engage in sports (especially alpine skiing, swimming and mountaineering), gain skills in speleology, learn to drive all-terrain vehicles and snowmobiles, and drill ice and soil. The “domains” of glaciologists and cryolithologists in the Far North of Russia are extensive. They are interested in the cover glaciers of the islands of the Arctic Ocean and permafrost on the mainland in the areas of large cities, oil and gas pipelines, railways and roads. They monitor the Northern Sea Route. On the glaciers of the Caucasus, Urals, Altai, Kamchatka and other mountain systems, glaciologists monitor and predict the movement of ice, snow avalanches and mudflows. And the most prepared, seasoned and courageous specialists go for romance and the opportunity to make good money at Antarctic research stations. Labor market: relevant research institutes, permafrost stations in the North of Russia, avalanche and mudflow stations in the mountains, State Committee for Hydrometeorology, State Committee for Ecology, Hydrometeorological Center of the Russian Federation.
Meteorology and climatology. Promising areas here are paleoclimatology (ancient climates of the Earth), biometeorology (the impact of climatic conditions on living organisms, cycles of solar activity), medical climatology (the life and economic activities of people in different climatic zones of the Earth), weather forecasts based on satellite meteorology, military meteorology ( the development of so-called climate weapons), planetary meteorology (the study of the atmospheres of planets and their satellites), the problems of global warming and ozone holes on Earth. Specialists need to have a good knowledge of physics, mathematics, computer science and geography itself. Labor market: the bulk of climate meteorologists – and often women – work as weather forecasters at ground-based weather stations scattered throughout Russia. In the last 15 years, the number of these stations has decreased, especially in the Far North and Far East. Other possible places of employment are the Hydrometeorological Center of the Russian Federation, State Hydrometeorological Committee, Meteorological Bureau of Large Cities of Russia, meteorological services at airports and seaports, research institutes, marine weather stations, scientific oceanographic vessels, cosmodromes.
Landscape science. This is a geography classic. It is here that they deal not with just one aspect of nature or human society, one natural or anthropogenic component, but with the entire set of connections between different components of one natural or anthropogenic complex (landscape), starting from the smallest (river, pond, park, forest, meadow) , mountain, settlement, field) and ending with the geographical envelope of the Earth. The task of a landscape scientist is not only to describe this or that landscape of the Earth, but also to find out the history of its origin and give a forecast of its further development, taking into account the influence of many factors. And here you need to know the basics of almost all other geographical sciences. Promising directions - geophysics and geochemistry of the landscape (the influence of physical and chemical processes on the formation and dynamics of a particular territory), ethnocultural landscape studies (how different cultures and human settlements influenced different landscapes of the Earth and how nature influenced the mentality of different peoples), environmental assessment terrain, aerospace sensing methods in landscape science, construction of artificial aesthetic landscapes (parks, etc.). Landscape scientists are perhaps the most mobile people among geographers; After all, the subject of study for them is the entire surface of the Earth! Hence - numerous trips to different regions of Russia, and with good knowledge of a foreign language - abroad. The Russian landscape school, founded in the 19th century by V.V. Dokuchaev, is considered the strongest in the world. Labor market: research institutes, public and private firms engaged in environmental design and expertise, the State Committee for Nature, nature conservation committees of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation, natural science museums, botanical gardens, nature reserves and national parks, urban planning organizations and architectural and artistic workshops (design of aesthetic landscapes ).
Speleology. This is a frontier science at the intersection of geology and physical geography. She studies the internal cavities of the earth's crust (formation, dynamics, current state), in a simpler sense - the study of caves. The most interesting and promising direction in speleology is underwater speleology (studies cavities in the topography of the bottom of seas and oceans). Speleology is for strong romantics. Try climbing caves without physical training and theoretical knowledge! The scope of work for speleologists is wide: expedition teams, topographic and geodetic surveys of the internal cavities of the Earth, fulfilling orders from the military and special services regarding the suitability of certain caves as sites where military-industrial complex enterprises and secret facilities could be located. City halls of large cities attract speleologists to study the underground urban environment, where there are many voids of both natural (karst) and anthropogenic origin (mined out adits, bunkers, foundations of ancient buildings, rivers hidden in pipes, underground warehouses and communications). Speleologists can also work as instructors in sports and tourism organizations that specialize in organizing routes to different caves.
Oceanology. Oceanology includes ocean physics (it is interested in the interaction of the ocean and the atmosphere, acoustics, optics, radioactivity and the electromagnetic field of sea water), ocean chemistry (salinity, chemical composition of water), ocean geology (what rocks and minerals make up the seabed and seamounts) , minerals); ocean biology (study of aquatic fauna and flora, including identification of habitats of organisms of food importance); topography of the ocean floor (underwater relief mapping). The program for oceanographers includes a lot of mathematics, physics and chemistry. After the 2nd year, students go on practical training to a marine station or research vessel to conduct research. You will not only take a free ride on the seas and oceans and enjoy the beauty of the sea and the places where the ship will moor, but you will also harden yourself, turning into a real “sea wolf”. And if you're lucky, you'll find yourself on board the bathyscaphe! And oceanology itself is a promising geographical science. The planets of the solar system are better studied than the depths of the oceans. And oceanographers and submariners are deservedly compared to astronauts. Even a new term has arisen - aquanauts. Labor market: various hydrographic services, research institutes, underwater and coastal laboratories, marine hydrological and biological stations, oceanographic vessels, private diving training companies, travel agencies. With a high level of professionalism and good knowledge of English, Russian oceanographers can try to work in oceanographic institutes in the USA, Canada, Great Britain, France, Germany, Japan and in the Mecca of all oceanographers on Earth - the Oceanographic Museum of Monaco, created by Master Cousteau.
Hydrology of land. In the 21st century, fresh water has become such a valuable resource that military conflicts between countries even occur over the possession of its sources and projects are being developed to deliver icebergs to the arid regions of the Earth. People who have chosen terrestrial hydrology as their profession are called upon to optimize and rationalize the water flows and water balance of the country. Hydrologists study the water cycle in nature, analyze the regime of water bodies and the water regime of individual territories; provide an assessment and forecast of the state and rational use of water resources; participate in the design and monitoring of reservoirs, hydroelectric power stations, canals, sea dams, river dams and bridges, ports, beaches, water intakes for settlements and enterprises; compile catalogs of water bodies on land. Labor market: research institutes, lake and river stations, hydrological posts and hydroobservatories, hydroelectric power stations, water transport department of the Ministry of Transport of the Russian Federation, fish breeding companies, water parks, river canal departments, river ports, Hydrometeorological Center of the Russian Federation, Ministry of Emergency Situations of the Russian Federation. Soil science. The world's largest tracts of the most fertile soil lie in our country. And it is not for nothing that soil science appeared in Russia. It is a biological and geographical science about the origin, dynamics, current state, future development of soil and the rational use of soil resources. There are also departments of soil science in biology departments, but in geography departments they are mainly engaged in spatial analysis of soils, their mapping, quantitative and qualitative assessment of soil resources in different territories for entering this data into the Unified Land Cadastre of the Russian Federation. Graduates solve problems in agriculture of increasing soil fertility and using the necessary fertilizers, participate in land reclamation (irrigation, drainage, gypsum, soil liming) and in the fight against soil erosion, and draw up maps of soil and land resources for agronomic farms. A good soil scientist is the right hand of the manager of an agricultural enterprise. The role of the soil geographer has especially increased now that large-scale land reform is being carried out.
Economic and social geography. Economic geography studies the spatial distribution of productive forces (population and economy) and is at the intersection of geography and economics. And social geography lies in the plane of interaction between general geography and a number of humanities disciplines - history, ethnology, sociology, cultural studies, even psychology (studies the mentality of the population of a particular territory). Economic geographers consider the natural resource and economic potential of a territory; identify specific features and problems of the territory; assess the value of land; looking for the optimal location for the construction of national economic facilities; give recommendations for government and economic structures on the integrated development and solution of problems of the territory; determine the degree of environmental risk in the process of economic development of the territory; give a forecast for the development of the territory.
Sociogeographers participate in assessing the labor and intellectual potential of the territory; study the lifestyle, traditions, customs, behavior (mentality) of different groups of the population, social classes and ethnic groups; collect and systematize information about migrants; give government agencies recommendations on the optimal distribution of migration flows of the population; help in settling refugees; analyze population censuses; take part in ethnographic expeditions; help plan settlements and recreational areas; identify national problems and provide advice on how to resolve them; participate in determining the human development index (quality of life of the population). The results of economic and sociogeographical research are presented in various forms - from memos to computer presentations. But in any case, a map is attached to the report - so the specialist needs to have a good knowledge of the cartographic method. Here is an approximate labor market for economic and sociogeographers: work in research institutes, teaching economic geography in economic, financial and tourism universities, in high schools and colleges. Also, their place of work can be cartographic factories (editors of socio-economic maps), planning, land and socio-cultural departments of federal, regional and local authorities.
1.4. Where to get an education
Currently in Russia there are 24 geographical faculties and departments of classical universities and 41 geographical faculties of pedagogical universities and institutes. The study of geography in pedagogical universities is special. Here they train not research analysts, as in the geofaculties of classical universities, but, first of all, teachers who know how to teach both physical and social geography. These two branches of a single geography consist of many narrower disciplines, each of which corresponds to one or another geographical specialty (about fifty in the Russian register of such an academic discipline as “geography”). The nearest university is VSU. At Voronezh State University you can get an education at one of two faculties: Faculty of Geography, Geoecology and Tourism. Departments: geoecology and environmental monitoring; physical geography and landscape optimization; socio-economic geography and regional studies; environmental management; recreational geography, regional studies and tourism. The work is carried out in two main forms of education: higher vocational education (HPE) and secondary vocational education (SVE). At the Faculty of Geology there are departments: geophysical methods of prospecting and exploration of mineral deposits; hydrogeology, engineering geology and geoecology; historical geology and paleontology; mineralogy, petrography and geochemistry; general geology and geodynamics; mineral resources and subsoil use; ecological geology.
Today in Russia there are many educational institutions where it is possible to obtain a narrower specialization, for example, the profession of a surveyor. In the field of geodesy, at various levels of mastering this complex specialty, you can work after graduating from both a secondary educational institution - a technical school or college, and a higher one - a university, institute or academy. Volcanologists in Russia are specialists. In Moscow, the profession of volcanologist can be obtained at the Geological Faculty of Moscow State University. Lomonosov and St. Petersburg State University, Department of Petrology and Volcanology, are the main centers for the study of volcanoes in Russia. And also at the Department of Geomorphology and Paleogeography of the Faculty of Geography and at the Department of Mechanics of the Faculty of Mechanics and Mathematics. In other cities, the specialization of a volcanologist can be obtained at the geological exploration faculties of universities or technical universities. Most often, geologists and geophysicists become volcanologists. (Appendix 4).
Chapter 2. Research part.
2.1. Analysis of the labor market in Russia.
There is a special market for labor trade - the labor market. The labor market is the sphere of formation of demand and supply of labor (labor services). Through the labor market, the majority of the working population obtains work and income. In the labor market, entrepreneurs and labor sellers jointly negotiate, collectively and individually, over employment, working conditions and wages.
We analyzed what are the most in-demand professions on the labor market in Russia today? If 10 years ago specialists with economic and legal education were required, now the labor market is overcrowded with representatives of such professions, and many people have a question about which professions will be the most in demand in the future, and what kind of education to receive. It would seem very difficult to answer this question, since the labor market is an unpredictable area, but some research and forecasts can be made. So, according to research by sociologists, the ten most in-demand professions in the near future are:
1.Engineers. It is technical engineers who will take leading positions in the employment market. 2. Specialists in the field of IT technologies. Not a single modern company can do without computers; accordingly, the enterprise must have specialists who are responsible for the organization and coordinated operation of computer networks, setting up Internet use, servicing subscriber telephone lines, etc.
3. Specialists in the field of nanotechnology. Nanotechnologies are based on the atomic-molecular interaction of substances; these technologies make it possible to use the hidden, beneficial properties of substances. Nanotechnology is the technology of the future. Nanotechnology will soon cover all areas: the food industry, mechanical engineering, space technology, medicine, and the chemical industry. 4. Specialists in the field of biotechnology and bioengineering. The concept of biotechnology means a modern method that uses any biological structures, systems, and their parts to solve a particular problem within a given technological process. Biotechnologies are especially often used in modern agricultural enterprises, where the properties of cultivated products are changed using genetic engineering methods, for example, to increase yield or resistance to pests. Pharmacology also uses biotechnology methods to create drugs based on biological organisms.
5. Marketing specialists. The Russian market is constantly updated with a huge number of various goods and services.6. Service specialists. Gradually, the well-being of people in Russia and other countries of the world is improving, so there is an increasing need to provide high-quality services.
7. Specialist in the field of logistics - management of information flows and material assets during the production and sale of products. Russia is increasingly integrating into the global market system, and plans are underway to join the World Trade Organization and other organizations. In this regard, a profession that is already in demand is logistics. Communication skills, ability to quickly understand and evaluate daily work. At the same time, it is necessary to understand a little more about technology, transport, economic issues, and have geographical skills.
8. Environmental safety specialist. In our country, unfortunately, little attention has always been paid to environmental protection and human health due to environmental problems. However, currently the scale of anthropogenic impacts has reached such a level that it is impossible to do without competent specialists in the field of ecology.
9.Specialists in the field of medical research. Medicine is constantly evolving, new treatment methods, technologies, and medicines are appearing, so such specialists will always be in demand.
10.Specialists in the field of chemistry and chemical research. Energy is an area in which chemical specialties will be in greatest demand. It is estimated that the world's oil reserves will last only a few decades, and scientists are already looking for and researching alternative energy sources. Soon, humanity will begin to actively apply research to practice, and chemical professions will become one of the most in demand.
Conclusion: Based on these data, we see that almost all of the most in-demand professions in Russia are, to one degree or another, related to geography.
2.2. Student and career. While working on the research topic, we decided to find out:
1. Have the 9th grade students of our school decided on their choice of future profession?
2. What do they know about their future profession;
3. What school subjects are needed.
Students were offered a questionnaire (Appendix 5). After analyzing the results, we found that the majority of 9th grade students have not yet fully decided on their choice of profession or have a low level of awareness about their chosen profession. The data shows that in general there is a lack of knowledge about professions and their specifics. In terms of importance, the subject geography ranks 7-8 out of 10. The subject is not needed for 68% of respondents, although by naming the chosen professions they do not imply that in this profession one cannot do without geography, for example, a specialist in the Ministry of Emergency Situations. Only 2 people (5.7%) indicated that their future profession would be directly related to geography (geodesy and tourism). Among the professions related to geography, students name: geologist, meteorologist, truck driver, sailor, pilot, agronomist.(Appendix 6).
1. Modern geography- the basis of many professions. Two branches of a single geography, physical and social, consist of many narrower disciplines, each of which corresponds to one or another geographical specialty - there are about 50 of them in total: “old” and “young”, male and female, rare and common, “monetary” and not really. The choice is very large.
2. One of the main motives for the professional choice of graduates is the social prestige of the profession, i.e. assessment of the importance and usefulness of this profession from the media, parents, and the entire social environment surrounding schoolchildren. The demand for the profession in the labor market and, of course, material rewards play an important role. This work will help us decide on a professional field or navigate specialized training.
3. In the future, such “geographical” professions as engineers, technical specialists, geologists, and ecologists will be in demand. Every year the tourism sector of the economy is increasingly developing.
4. If you decide to connect your life with geography, then you need to develop professionally important qualities: curiosity; propensity for research activities; eye gauge; memory; I navigate the area; ability to analyze and think logically; physical endurance.
5.Ways to obtain a profession - universities and secondary vocational education.
6 . The geographer works not only indoors, but also in open areas; you need to be prepared for field trips (expeditions, field observations, field work).
7. The hypothesis put forward that geography is capable of forming an opinion regarding self-determination in a future profession and the requirements that society places on the quality of labor resources has been confirmed.
Conclusion.
Studying a geography course is very important for students’ professional self-determination. Geography can reveal the causes and consequences of unemployment, outline the requirements for a modern worker in the labor market, form an opinion about self-determination in a future profession and the requirements that society places on the quality of labor resources.
Download materialProfessions related to geography are very diverse. Specialists in various fields apply their knowledge in this area.
In their work, knowledge of geography is used by geologists, archaeologists, pilots, navigators, meteorologists, surveyors, guides, and tour operators.
Associated with the discovery of natural resource deposits. He studies the features of the occurrence and location of various rocks.
Geologists take part in research work and expeditions related to the study of the earth's interior.
Knowledge of geology is also used in construction to identify soil features before developing an area.
They study the culture of ancient civilizations with the help of remains and traces of their life activities. Basically the work consists of excavating and finding a place to carry out research.
Archaeological scientists devote entire years to their discovery and piece by piece recreate the life and culture of ancient civilizations. Excavations of archaeological monuments help to learn about peoples who lived thousands of years ago.
The pilot is the navigator. This is an ancient maritime profession. The safety of navigation depends on the pilot, or more precisely on his knowledge of coastal features, the fairway of a certain area and maritime geography.
The pilot studies maps of the seabed and guides the vessel along the optimal path, taking into account the depths and features of the sea relief.
The profession of a navigator is very similar to that of a pilot. The navigator controls air, land, water and underwater transport.
He studies the course, calculates the routes of transport, marks it on the map and monitors the operation of navigation devices. In addition, it takes into account the influence of weather conditions on movement and transport routes.
Meteorologists study the factors that influence weather. They constantly monitor changes in weather conditions, record, evaluate, process and take into account what such changes may affect. Meteorologists also make weather forecasts and study the climate of different geographical zones.
They study the territory using measurements, calculating coordinates and compile maps that are used by motorists, builders and geologists. Such specialists take part in various engineering and construction works, and also map the area.
A guide or tour guide must accompany tourists during hikes, excursions or cruises. The guide knows well the cities and countries in which he conducts the excursion, as well as cultural and historical monuments, and speaks foreign languages.
The work of translators is very diverse. They know many languages and translate texts, documents of various types, films and books.
They can also accompany delegations and interpret oral speech. While learning the language, the future translator also studies the customs, culture, history and geography of the country.
Tour operators are well versed in the geographical and climatic characteristics of different countries. They will help you choose the most suitable tour based on your preferences, interests and capabilities.