Modern methods of personnel motivation presentation. Presentation "motivation and stimulation of personnel." World experience in motivation research
To use presentation previews, create a Google account and log in to it: https://accounts.google.com
Slide captions:
Motivation Motivation as a management function
Once you have a staff of trained, skilled and energetic people, the next step is to stimulate their creativity. A. Morita
Creating staff interest in achieving the company's goals. Motivation is the process of encouraging oneself and other people to achieve personal and organizational goals.
Needs are the conscious absence of something that causes impulses to action. Needs Primary are physiological, they are genetically determined: the need for food, warmth, rest, etc. Secondary - by their nature they are psychological in nature, they arise in the course of cognition and gaining life experience.
Reward is what a person considers valuable to himself. Rewards External - they are given by the organization (monetary payments, promotion) Internal - received through the means of work (a feeling of success in achieving a goal, the content and significance of the work performed, self-esteem, friendship and communication that arise in the process of work)
Basic concepts Motive is what causes certain human actions. Incentives - act as levers of influence or carriers of “irritation” that cause the action of certain motives.
There are various theories of motivation based on satisfying needs and motivating people to take action. It is customary to highlight:
Maslow's hierarchy of needs theory Main ideas: unsatisfied needs motivate a person to action, satisfied needs do not motivate people; The higher the position of needs in the hierarchy, the fewer people they become motivators of behavior.
Hierarchy of needs according to A. Maslow The need for self-expression The need for recognition Physiological needs Social needs The need for security The need to feel a sense of self-worth and need for the enterprise, etc. The desire to discover one’s abilities and self-improvement, etc. The need to be accepted in a team, to receive support, etc. Satisfied with money. This is the preservation of life and health, confidence in the future, etc.
Disadvantages of Maslow's concept Ignoring the individual characteristics of people and the influence of situational factors; assumptions about the possibility of transition from one level of needs to another only in the direction from bottom to top; the assertion that satisfaction of the upper group weakens the effect on motivation.
Herzberg's two-factor theory The author showed that people's behavior is influenced by both satisfaction and dissatisfaction of needs. The manager must first relieve dissatisfaction among employees, and then achieve satisfaction.
Groups of needs Motivating (for recognition, success, promotion, etc.) “Hygienic” (amount of payment, working conditions, interpersonal relationships and the nature of control by the immediate superior)
Scales for assessing the degree of satisfaction of needs “Satisfaction - lack of satisfaction” (satisfaction of motivating needs stimulates work activity, dissatisfaction does not demotivate). “Dissatisfaction is the absence of dissatisfaction” (dissatisfaction with “hygienic” needs reduces incentives to work, but satisfaction does not completely activate it).
The influence of motivational factors on people’s attitudes towards work Factors that increase productivity Force them to work better, % Make work more attractive, % Both together, % Good chances for promotion 48 22 19 Good earnings 45 22 22 Work that forces you to develop abilities 40 22 20 Complex and difficult work 38 30 15 Work requiring independent thinking 32 33 17 Interesting work 36 35 18 Work requiring quality 35 31 20 Recognition and approval of good work 41 34 17
The influence of hygiene factors on people’s attitudes towards work Factors that make work more attractive Make work better, % Make work more attractive, % Both together, % Quiet work 13 61 15 Availability of information 21 49 16 Good management 19 52 12 Quiet and clean environment 12 56 2 Flexible work schedule 18 49 15 Convenient work location 12 56 12 Additional benefits 27 45 18 Fair distribution of tasks 21 45 8 Good team 17 54 13
Money Forms of monetary incentives can be different: - salary increases - bonuses - incentives
Perspective Many companies lose their best employees because they do not give them the opportunity to “grow.” the opportunity to occupy a higher position is a more complex and responsible job.
Better working conditions Their mood depends on what color the walls of the room where people work are painted, how the furniture is arranged, and whether there are flowers on the windows.
Recognition No matter how strong the material incentives are, the moral ones can be even stronger. There is no person who would remain indifferent to the recognition of his abilities and the high appreciation of his work.
Free time The manager can reward his subordinates for good work by increasing the duration of vacation, give the employee a task for the day and release him from work if it is completed earlier.
Interesting work It is intended for the best workers. If a person performs well, the manager can reward him by giving him interesting tasks and allowing him not to do what he does not like.
Ways to reward people for their work: Material rewards for more intensive work and its better quality, regardless of the employee’s length of service, in various forms. One-time monetary reward for performing scientific and engineering work upon their implementation in production (bonuses). Promotion to a position or rank that best matches the employee’s capabilities. Encouraging free time or providing the employee with the opportunity to independently plan their workday. Public and personal recognition of the employee’s merits through awards, thanks, certificates, press, provision of benefits and privileges for the best work.
Lecture.
STAFF MOTIVATION
AKHALAYA OLGA ANATOLIEVNA, C.E.N.,
ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR IPMEIT SPBPU 2
Work motivation
activity motivation of the employee or
groups of workers to
activities aimed at
achieving the goals of the organization,
by satisfying them
own needs.
World experience in motivation research
4World experience in motivation research
Classic
theories
"Human
economic"
act
economic
incentives
Theory
human
relations
Theory
human
resources
"Human
social"
"human
resources"
stimulation is not
only salary, but
and positive
attitude
to the employee
career growth,
satisfaction from
work, development
creative
abilities
employee
Motivational structure of personality
Human needs
A need is a conscious needhave something (need) to maintain
life activity and human development.
Every person has a set of needs
specific in quantitative, qualitative
composition, according to hierarchical relationships.
The first theories of motivation were based on
dividing needs into primary ones
(congenital, vital) and secondary
(purchased). This corresponds to modern
the idea of man as a unity
biological and social components.
Motive
Motive (lat. movere – bring toaction) – internal motivator
activity; what motivates a person to
activities.
The motive represents
defined need.
There is always material or
ideal object because of which
personal activity is activated.
Motivational sphere is a set of relatively stable
and dominant human motives,
components of the motivational core
personality.
Properties of the human motivational sphere
1. Multimotivation: the presence of a whole complexmotives regulating activity.
2. Hierarchical subordination: the same motives
occupy a leading position, others - a subordinate one.
3. Dynamism: in the process of personality development
its structure changes, differentiation occurs,
integration of motives, transformation of one into another,
strengthening, weakening, etc.
4. Interchangeability: some motives can be replaced
others. (For example, an employee’s need for
interesting work may be partially compensated
providing high wages with boring,
monotonous work).
Stimulus
Stimulus – (lat. stimulus – a pointed stick, withwith which they drove cattle) - a means
influences to motivate action;
motivating reason for action.
Comparing the concepts of “motives” and “stimuli”, it is clear that
that motive is inherent in human activity, and
stimulus - as a motivating reason for an action, comes from
external environment (in the context of work motivation - from
manuals).
Stimulation is a targeted impact on
employee behavior (behavior management) with
using the appropriate set of tools c.
Impact with a “+” sign and with a “-” sign
Main staff disincentives
Anti-stimulus- a method of influence that either does not
leads to the desired behavior or encourages
negative behavior (dismissal).
Is evidence of flaws in the system
stimulation.
Main staff disincentives
Lack of important information from staff.
Failure to use any employee skills,
which he himself values.
Violation of an unspoken contract.
Ignoring ideas and initiative.
Lack of feeling of belonging to the company.
No changes in employee status.
Lack of recognition of achievements and results from
management and colleagues.
Unfair punishment.
Purpose of activity
Taken together, the need, motive, incentive, determininghuman behavior is aimed at achieving
a specific goal.
A goal is a conscious result for which
At the moment, action related to
activities that satisfy
updated need.
When a goal is achieved, need satisfaction can
be complete, partial or negative.
In case of a positive result (satisfaction)
a person tends to repeat this behavior in a similar
situations in the future. Behavior leading to
negative result is avoided.
Emotions
Emotions are a subjective manifestation of need-motivational processes; they signal the progressrealization and satisfaction of needs.
Activity is always accompanied by emotions (there is no
“non-emotional motives”).
Particularly important for the study of work motivation
emotions of success and failure (joy, confidence, hope,
surprise, sadness, regret, despondency, anxiety).
Among all the elements of the motivational structure, it is
employees' emotions are most convenient for
observations. But in order for the manager to evaluate
degree of satisfaction of the subordinate in the process
work activity, he must have the skills
"reading" people.
Motivation and incentive system
Systemmotivation
System
stimulation
Attraction
Consolidation
Hold
Education
Monitoring
needs
Attracting employees
Salary size, availability of bonuses, participation inprofit.
Business reputation, company status on
market.
Job title.
Terms of reference.
Career growth.
Corporate infrastructure.
Office location.
Compliance with labor standards, etc.
Hold
Skill development programsand careers.
Lending, deferred payments.
Providing benefits taking into account
length of service.
Compensation for inflation
tax losses.
Personnel retention program
Analysissituations:
Questionnaire;
Reasons
layoffs
Loosen and
eliminate
Factors
leashes
auspicious
employees
Strengthen
and stabilize
Conversations;
Seminars;
Studying
image
enterprises
Results
fastenings:
-
Decrease
-
Reduction
number
passes and
absenteeism;
-
turnover
personnel;
Gain
attachment to
enterprise
Motivation for effective work of performers
Level adequate to market conditionsSalary, social package.
Clearly defined tasks.
manager
Lack of “equalization”
injustice in the wage system
Transparency of the remuneration system.
The relationship between employee performance evaluation and
activities of the department.
External management style
immediate superior.
Motivation for effective work of middle managers
Decent salary level, socialplastic bag.
Clearly defined tasks of the unit.
Delegation of authority from outside
top manager.
Compliance with the management hierarchy
(no “jumping” over them
heads).
Availability of leverage over
subordinates.
Motivation for effective work of top managers
Participation in business.Option.
Self-realization through business.
Responsibility for business.
Pension plans.
Partnerships with
owner.
Essence of an option
Agreement on the manager's right toa certain period (from one
years to several years) buy at
fixed price certain
number of company shares and
sell at market price
quotes.
5 types of motivation according to V.I. Gerchikov
Type of motivationMain motive
Instrumental
"I can make money"
Professional
"I can use my
knowledge and experience"
Patriotic
"I feel needed
to the team"
Master's
“I can decide for myself
what and when should I do"
Unattainable
(avoidant)
Usual work
stability
1. Instrumental type
Interested in the price of labor, not itcontent;
The validity of the price is important, not
wants handouts;
The ability to provide
your life on your own.
2. Professional type
Interested in the content of the work (notagrees to things that are uninteresting to him
work no matter how much they pay for it);
Interested in difficult tasks -
opportunity for self-expression;
Considers freedom in operational matters important
actions;
Professional recognition is important
the best in the profession.
3. Patriotic type
You need an idea thatwill move it;
Public is important
confession;
The main award is universal
recognition of indispensability in
company.
4. Master type
Voluntarilyaccepts on
myself
responsibility
b;
Characterized by
I'm heightened
requirement
5. Non-attentive (avoidant) type
It doesn't matter what kind of work to do, nopreferences;
I agree to low payment, provided
so that others do not receive more;
Doesn't strive to improve skills
counteracts this;
Low activity and opposition
activities of others;
Low responsibility, desire
transfer to others;
The desire to minimize effort.
Forms of incentives
1.NegativeFines, punishments, threat of job loss
2.Money
Salary, all types of bonuses and allowances
3.Natural
Car, telephone, provision
housing
4.Moral
Certificates, badges of honor, awards (20
thousand)
5.Paternalism
Additional social and
health insurance, conditions
rest
6.Organizational
Working conditions, its contents and
organization
7. Participation in co-ownership and management
Correspondence of motivational types and forms of stimulation
Formsstimulation
Types of Motivation
Instr.
Prof.
Patr.
Household
Unreached
0
-
+
–
Base
Base
+
0
+
0
Natural
(social package)
+
0
+
0
Base
Moral
-
+
Base
0
0
Paternalism
-
-
+
-
Base
Organizational
0
Base
0
+
–
Participation in
co-ownership and
management
0
+
+
Base
–
Negative
Cash
Difficulties in developing a motivation system
Lack of understanding of the meaning of motivationpersonnel;
The predominance of the “punitive” system
staff motivation;
Expectations and interests are not taken into account
employees;
Significant interval between receiving
results and encouragement;
No monitoring of the motivation system;
Lack of support for the motivation system;
Lack of information from staff
motivation factors;
Instability of the motivation system.
The relationship between the concepts of “motivation” and “stimulation”
Motivation(internal)
Inducement through
appeals to the exalted
needs, orientation
for personal reasons,
encouraging the employee
act. Source
motivations are
needs both internal
mental mechanism.
Stimulation
(external)
External influence on
workers for the purpose
direct influence
on labor results and
intensification of activities
workers. Appeal to
primary needs.
The stimulus is given from the outside.
5
Theories of motivation
Content theories of motivation:theory of motivation by A. Maslow,
theory of needs by D. McClelland,
two-factor theory of F. Herzberg,
needs theory ERG theory
(existence, connection and growth) K. Alderfer.
Process theories:
V. Vroom's theory of expectation,
S. Adams' theory of justice
Porter-Lawler model of motivation.
Structural elements of work motivation
Motive -Stimulus-
internal
motivation
Target-
external
motivation
desired
result
Reward-
Values-
what a person thinks
valuable
set of standards and
evaluation criteria
person
3
need need for something
Values
orientation a stable attitude towards
material and
spiritual benefits and
values
Definition of labor incentives in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
6Definition of labor incentives in
Labor Code of the Russian Federation
Stimulus
additional to the tariff wage
remuneration of employees for work, not
specified by job duties
(labor standards)
Stimulation
labor
establishment
specific
forms,
sizes,
conditions
receiving
rewards for the purpose of forming
certain
labor
behavior
employee
And
accruals
to him
a certain amount of money
subject to achieving target
installations supplied by the employer Punishment
7
Limitation of powers and satisfaction
employee needs, as well as positive
rewards.
Forms of punishment
- verbal punishment (condemnation, reprimand);
- material sanctions (fine, deprivation of privileges);
- social isolation (neglect, ignorance,
rejection by the group).
Flaws
Short-term influence, since punishment stimulates
activities (or restrain from unwanted actions)
only for the period of their validity.
Abraham Maslow's pyramid of needs (American psychologist)
8Needs
higher
level
Primary
needs
Theory of needs by David McClelland (American psychologist, researcher of successful individuals)
Need theoryDavid McClelland
9
(American psychologist, researcher of successful personalities)
Needs
top level
Need
in power
Need for
accessories
Need
in achieving
The scientist recommends relying on needs
top level
Two-factor theory by Frederick Herzberg (American psychologist)
Efficientmotivation
Motivational
factors
Hygiene factors
policy
companies and style
management;
control methods
staff;
relationships with colleagues
work;
wage level;
employee status in
organizations;
conditions and safety
labor.
achieving results;
success and recognition for
achievements;
interest in work;
responsibility;
professional
improvement and
career growth.
10ERG theory by Clayton Alderfer
11
(American psychologist)
Needs
ERG
Need
existence
(Existence)
Social
needs
(Relatedness)
Need
growth
(Growth)
Survival
(physiological
well-being)
Significance
interpersonal
and social
relationships
Internal
desire for
development
Motives for staff turnover
Motives for staff turnover are the immediate reasonsencouraging workers to quit.
Personal motives
character
(moving, changing
marital status)
Dissatisfaction
quality of life
(impossibility
self-realization,
dissatisfaction
needs)
Professional qualifications
motives
(inconsistency
position held)
Dissatisfaction
conditions inside
enterprises
(uncomfortable conditions on
workplace)
12
Methods of motivational influence on organizational personnel
Economic(wages)
Disciplinary
(remark, reprimand,
dismissal)
Psychological
promotions
(praise, blame)
Participation
(collective acceptance
decisions, work in
team)
Target
(clear statement
goals)
Groups
methods
Extension
and job enrichment
(new projects and technologies)
Eliminating Negatives
incentives
(positive motivation without
threats)
13
Non-material methods of motivation
OrganizationalSocio-psychological
Participation of employees in the affairs of the organization
Development programs and career growth
Enrichment of labor content
Creating favorable working conditions
Delegation of authority
Development of corporate culture principles
Public recognition of employees' merits
Congratulations on successes and anniversaries
Photo for the honor board, booklets, etc.
Respect, trust, approval and support
Negative reinforcement (blaming)
Visits by managers to workplaces
best employees
14
Types of non-material incentives
Non-material incentives(non-monetary reward)
Official
confession
merit
Participation in
management
Organizational culture
Psychological climate
Possibilities
For
creativity
Change
status
employee
Style
management
Improvement
working conditions
15
Material methods of motivation
Discounts ongoods
companies
Awards
and bonuses
Payment
labor
Provide
basic
needs and
assessment of the contribution
employee
Household
services
Payment for treatment
rest, rest
training
Material
help
Benefits and
social package
Surcharge to
salary
Percent
16
Ways to increase work motivation
17Ways to increase work motivation
Material
stimulation
Intangible
stimulation
Improvement
quality
labor force
Improvement
labor organization
Involvement in
control
Types of internal motivation according to V. Gerchikov
Commercial(focus on
earnings, not
content and
working conditions)
Lumpensky
Master's
(low self-esteem and
low level
performance)
(desire for
achieving
results,
independence)
Patriotic
Professional
(commitment to
team and place
work)
(value - content
work, difficult
tasks)
18
Structure of the personnel motivation system
19Structure of the personnel motivation system
Personnel motivation system
Material
stimulation
Remuneration
Social package
Constant
Part
(salary, tariff)
Incentives,
convertible
in money and
saving
funds
employee
(payment
rest, study
etc.)
Variable
Part
(awards, etc.
payments)
Intangible
stimulation
Formalized
incentives
Fastening
existing
position
(certificates, honorary
ranks, etc.)
Orienting
for changes
(increase in
positions,
training, etc.)
Unformalized
-y incentives
Informal
events,
raising
loyalty
(commitment)
to the organization
Management style
head
(relationships
with an employee) System development algorithm
staff motivation
2021
Methods for studying personnel motivation
Observation
Method
expert
ratings
Problem Analysis
organizations
Testing and
survey
Conversation and
survey
Methods
diagnostics
Speech analysis
and behavior
Experiment
Main sections of the staff motivation program
Purpose of the programEmployee categories
Duration of the program
Employee evaluation criteria
System of rewards and penalties
Calendar of events
Responsibility for implementation
Program budget
22
Types of personnel policies
23Types of personnel policies
Stimulating influence - the use of various incentives to
increasing employee interest in productive work.
American scientist Frederick Taylor to create workers
tried to ensure interest in high labor results
connection between labor results and wages.
Motivational management is a powerful ideological activity
leadership within the organization and actualization of selfless enthusiasm
workers. This approach often prevails in emerging
organizations due to their lack of material resources as a basis
stimulation.
Stimulating influence and motivational management are the most
optimal approach. This policy is being implemented by developed countries in all
relations between organizations in which a corporate structure has already been formed
culture and mechanism for distribution of material benefits of the organization.
Types of incentive payments to employees
24stimulus
stimulus
stimulus
Additional payments
Allowances
Compensation
Awards
Bonuses
Commission
Participation in
profits and
income
Participation in
joint stock
capital
Incentive pay – pay that targets the employee
to achieve indicators that expand and exceed the circle
his duties provided for by the basic norm.
Audit of the motivation system
Audit levelsSocioeconomic assessment of socioeconomic
efficiency
motivation management
Socio-psychological assessment of motivational
workers' potential
Organizational and technological assessment used in
document organization
and procedures
25
Methods for conducting a motivational audit
Introductory, expert interviews;Analysis of current documentation;
Supervising the work of managers;
Questioning and testing of personnel;
Formalized description of procedures;
Statistical processing methods
needs study results
workers.
26
Classification of personality needs (according to A. Maslow)
Two-factor model of F. Herzberg
F. Herzberg's theory of motivation
Motivation theoryTo dissatisfaction
influence hygienic
factors:
Control method
Company policy and
administration
Working conditions
Interpersonal
relationship
Earnings
Uncertainty about
stability of work
Impact of work on
personal life
F. Herzberg
For satisfaction
influence motivational
factors:
Achievements
(qualification) and
recognition of success
The work itself
Responsibility
Promotion by
service
Opportunity
professional
growth
Motivation and stimulation
Motivation is the inner drive of a person to do something.conditioned by his existing needs and the presence of real
possibilities to satisfy them
Stimulation is external encouragement of human activity, his
encouragement to perform actions necessary to achieve goals
goals
Hierarchy of needs according to A. Maslow
Physiological needs - necessary for survivalSecurity needs - protection from mental and
physiological dangers from the environment
Social needs – a sense of belonging to something or someone, feelings of social interaction, affection and support
Esteem needs – self-esteem, respect for personal
achievements, competence, recognition
The need for self-expression - the realization of one’s potential
opportunities and growth as a person
McClelland's concept of needs
1. The need for powerExpressed as a desire to influence other people
Characteristic of frank and energetic people who are not afraid
confrontation
Realized through managing other people
2. The need for success
Satisfied with the process of bringing work to successful completion
Characterized by moderate risk, a tendency to situations in which it is possible
take personal responsibility for finding a solution to the problem
3. Need for belonging
Manifests itself in the possibility of social communication and establishing
contacts
Characterized by interest in the company of acquaintances, establishing
friendships, helping others
Intrinsic motivation concept
Hackman and Oldham formulated a model of work motivation based onon key performance characteristics:
Skill variety - the extent to which a job requires
various types of activities involving the use of a number of
various skills and abilities of the individual
Job identifiability - the extent to which the job requires
completion of a specific task or its stage from beginning to end with
visible result
Task significance - the degree to which the task is significant
influence on the lives or work of others
Autonomy is the degree to which a job provides real
freedom and independence
Feedback - the extent to which performance of work tasks
accompanied by receiving direct and clear relativity information
work efficiency
Concept of I. Adizes
Each stage of a company's life cycle determines when andwhat ways to motivate employees
The same employee's motivators can change from
over time
Changes in motivators can change both spontaneously and
as a result of purposeful actions of the leader
Any motivational need has its own period of growth, peak and
recession period
Herzberg's two-factor concept
Hygiene factors:Related to the environment in which work is carried out
By themselves, they do not cause job satisfaction and cannot
motivate a person to do something
In the absence or insufficient degree of presence, call
job dissatisfaction
Motivations:
Related to the nature and nature of the work
The absence or inadequacy of motivation does not lead to
job dissatisfaction
If available, they fully cause satisfaction and motivate
employees to improve performance
Porter-Lawler concept
There are 5 variables in the Lyman Porter and Edward Lawler model:Effort Expended
Perception
Results obtained
Reward
Degree of satisfaction
According to the Porter-Lawler model:
The results achieved depend on the efforts made by the employee, his
abilities and characteristics, as well as his awareness of his
roles
The level of effort put in will be determined by the value
rewards
A person satisfies his needs through rewards for
results achieved
V. Vroom's concept of expectations
Expectancy theory emphasizes the importance of three relationships:Expectations regarding labor inputs - results (L-R) - ratio
between the effort expended and the results obtained
Expectations regarding results - rewards (RP) - expectations
certain reward or encouragement in response to achievements
level of results
Value - the perceived degree of relative satisfaction or
dissatisfaction arising from receiving a certain
rewards
Motivation = 3-R * R-V * C
K. Alderfer's concept of needs
K. Alderfer identified three classes of needs:Existence needs are fundamental physiological
needs and security needs
Social needs – communication needs, group needs
belonging and respect from others
Personal growth needs - needs for self-realization, in
including participation in management
Unlike Maslow, who assumed motivating influence
needs only during the transition from lower to higher needs,
Alderfer argues that such an effect can occur in both
directions
Human relations concept
Motivation to work is determined primarily by existingorganizations by social norms rather than physiological ones
needs and material incentives
The most important motive for high performance efficiency is
job satisfaction, which involves good pay,
opportunity for professional growth, interesting content and
diversity
Social security and care are important for motivation
about each person, informing employees about the life of the organization,
development of communication between hierarchical levels of the organization
Concept by William Ouchi
5 Key Control Features That Helpemployee motivation:
Emphasis on the movement of information and initiative from the bottom up
Transformation of senior management from a body issuing orders into a body
decision-making
Using middle management as the initiator and
driving force behind problem solving
Decision making based on consensus
Increased attention to employee well-being
P. Drucker's concept
The level of employee motivation in the company is most affected byinfluences:
Compliance of employee values with company values
Personal responsibility
Focus on employee strengths
Working style
Myth
Reality
1. “Motivation system – Motivation system – a powerful application
just a fashionable toy" is a personnel management tool capable of
help the company and its employees achieve
set goals. However, the system effectively
only works when it takes into account
interests of both the employer and employees
Myths that hinder the development and implementation of personnel motivation systems
MythReality
Openness of incentive schemes is essential
2. “Motivate –
means to manipulate” the condition of motivation. If the employee knows the system
in general, if he understands how others are motivated,
It’s easier for him to understand the company’s policy and evaluate it
justice. However, in this case, it is
It's about schemes. Reveal real earnings
employees are unethical
Myths that hinder the development and implementation of personnel motivation systems
Myth3. “Motivate –
means to force"
Reality
In certain corporate cultures this
the situation is a fact of life, but companies with
they live in such a corporate culture
powder keg", they always have the opportunity
"armed uprising". Hard authoritarian
management style requires managers
constant tough “counterintelligence” for
identifying employees who, behind the scenes
expressing dissatisfaction with the attitude of management,
will “rock” the rest of the staff
Myths that hinder the development and implementation of personnel motivation systems
Myth4. “Motivate -
means to raise
salary"
Reality
Company hiring as employees
newcomers and young professionals and training them
at your own expense, is not at all obliged to pay them the same
the salary paid by the hiring company
position with the same title people with
extensive experience, MBA and knowledge of three
foreign languages
Myths that hinder the development and implementation of personnel motivation systems
Myth5. "System
stimulation is possible
write off"
Reality
The motivation system only works if
if it is internally balanced and takes into account
all the unique features of the company and
functional responsibilities of the motivated
personnel
Myths that hinder the development and implementation of personnel motivation systems
Myth6. “Loyalty is possible
buy for money"
Reality
The salary level is far from
the only factor of job satisfaction, and
this should not be neglected. Whatever it is
employee's salary, after some time
time will be short. Moreover, there is always
a company that is ready to offer employees more
Active, constructive work behavior
ІІ
І
Avoidance motivation
Achievement motivation
ІІІ
IV
Passive, destructive work behavior
Typological concept of work motivation V.I. Gerchikova
I quadrantThe efficiency of work activity is proportional
degree of satisfaction of motivational expectations
employee
II quadrant
Employee productivity is fundamentally limited
the task and the opportunity of the manager to prove guilt
employee in case of failure to complete the task
Quadrant III The level of destructive reactions of the employee most often
comes down to passive labor behavior and “work according to
rules"
Quadrant III If organizational working conditions and system
incentives run counter to motivational expectations
employee, the likelihood of him being destructive increases
labor behavior
Behavior of employees with different degrees of motivation
A motivated employee leads to almost identicalplanned growth in labor productivity, which remains unchanged
over a period of time
Unmotivated employee – has a short-term impact on
increase in labor productivity, or has no effect at all
Demotivated employee – employee provides
short-term positive effect, and then its effects
become protests
The nature of human motivation
The basis for employee motivation is hisneeds
Each employee has an individual set of needs,
Accordingly, motivation is individual for everyone
employee
The employee demonstrates a high level of motivation to work in
if he sees real opportunities in this work
meet your needs and achieve your goals
Motivating the same employee may, over time,
change as his needs do
Types of needs
Primary needs universal necessary conditionsfor human survival
Water requirement
Food requirement
Need for security
Need for housing
Need for rest
Secondary needs needs based on
individual preferences and
human aspirations
Need for achievement
Need for recognition
Need for self-expression
Need for implementation
Need to belong
Need for creation
Need for patronage
Need for dominance
Need for autonomy
Need for support
Need for cognition
Need for impressions
Manifestation of human needs
Needs are expressed in...Typical behavioral tendencies or reactions
Typical modes of action
Seeking favorable opportunities and avoiding unfavorable ones
Characteristic emotions and feelings
Satisfaction upon achieving a certain result
Dissatisfaction with failure to achieve a certain result
Three levels of development of internal motivation
Situational. The emergence of internal motivation is determinedSituational-value. The emergence of internal motivation on this
Subjective-value. Intrinsic motivation becomes
the ability of the activity to satisfy the needs for
self-determination, competence and meaningful relationships
level is possible even when the activity does not satisfy
all named psychological needs. It is only necessary that
the activity was meaningful to the person
personal property. Self-determination needs
competence and meaningful relationships acquire the status of values Ensure a successful experience
Ensure that rewards match the difficulty of the task completed
Use not only material, but also verbal encouragement
Involve staff in a variety of activities
Involve staff in the decision-making process
Set realistic goals for staff that are commensurate with capabilities
Help a person discover their strengths and weaknesses
Together with your subordinate, outline a step-by-step strategy for achieving goals
Indicators of high employee motivation
Amount of time devoted to work (How much workemployees?)
Effort (How engaged are employees at work?)
Focus (How hard do employees work?)
Job satisfaction (How satisfied are employees with their
work?)
Future plans (Are employees going to stay with the company?)
Striving to achieve better results (Do employees work at
level of your abilities?)
Voluntary contribution to work (Do employees take it upon themselves to
additional responsibilities?)
Employees have difficulty motivating themselves if...
You have to monitor your subordinates to make sure thatthey really work
Your people don't care about improving their skills and rarely do
conclusions from your mistakes
You are the only one who takes serious problems seriously
Do you get the feeling that your employees think that
deserve more pay and promotion just for what they do
show up for work and perform the bare minimum of their duties
Your employees are cynical about most incentives your company uses.
Your subordinates seem to “support” the new
initiatives just to “please the bosses”
Factors of demotivation according to A. Maslow
PhysiologicalLack of good working conditions
Lack of stable salary
Inconvenient operating mode
Safety
High stress loads
Unpaid benefits package
Employment policy involves staff reductions
Relationship
accessories
Conflict relationships between colleagues at work
Presence of obstacles to informal activities in
within the company
Lack of corporate traditions
Self-esteem
The lack of prestige of the work
Lack of career advancement
Lack of recognition of achievements and results from
management and colleagues
use of any employee skills,
Self-actualization Not
which he himself values
Ignoring employee initiative and ideas
Lack of professional and personal growth
Stages of decreased motivation
Confusion - the employee ceases to understand what he needs to do andwhy isn't his work going well?
Irritation – the employee begins to feel irritated due to
feeling of powerlessness
Dual role (subconscious hopes) - employee
establishes the manager as the culprit for the difficulties encountered
Frustration - the employee believes that if he skimps on his
duties, the manager will pay attention to him and try to
help in any difficulties that arise
Loss of readiness to cooperate - what is happening is no longer a struggle for
maintaining interest in work while trying to maintain self-respect
Final – the employee either moves to another place or
begins to treat work as hard labor
Signs of employee loyalty to the company
Helping other colleagues during their absenceVoluntary agreement to perform activities outside the circle
job responsibilities
Help other employees if their workload increases
Providing personal resources for use by colleagues (contacts,
acquaintances, connections, resources, etc.)
Making rationalization proposals to improve quality
work of the entire department
Punctuality, high quality work
Showing concern for the company's image
Respect for the rights of others
The employee does not abuse his rights and privileges
Types of loyalty
Loyalty to your work group. Desire to work here and now withthis team
Loyalty to your management and senior managers.
Trust, unconditional support of the leader
Loyalty to your functional activities. Clear
motivation to perform the chosen professional function
Dedication to the profession. Psychological ability to identify
yourself with your profession
Loyalty to the company as a whole. Absolute identification of oneself with
company, its brand, participation in its work
Loyalty to investment. Employees invest in the company
labor and knowledge
Loyalty to values or goals. Employees feel complete
the alignment of their personal goals or values with those of
companies
Myths and facts of loyalty
MythFact
Employee behavior can be
be interpreted unambiguously - for example, if
there is a high criticality,
cynicism and negativism towards
colleagues, we can talk about
demotivation
No signs of demotivation and
detachment does not indicate
loyalty, as well as the lack of those
or other criteria of devotion are not
indicates disloyalty
The longer an employee works in
company, the higher its level
loyalty
In companies on a long-term basis
employees can work, just
making money
Young employees are the most loyal
linking their future with the company
Senior employees are more loyal
age
Myths and facts of loyalty
MythFact
Company loyalty and “internal
marketing" for employees is on
last place in terms of influence on
employee loyalty
How employees perceive
dedication to the organization
attitude towards them, directly affects
to their satisfaction and
company commitment
It is necessary to support only
adaptation stage, after the employee does not
needs some kind of care
The more support they feel
employees from management and
colleagues, the greater their devotion
show
Myths and facts of loyalty
MythFact
Than versatile activities,
the more interesting it is for an employee to work,
therefore, he is more loyal to
companies
The more diverse and
perform different types of tasks
employees, the lower their loyalty
In matters of loyalty, gender
differences don't matter
The more women enter
team, the lower the level
devotion among men than
The more men are in the group, the more
higher level of women's devotion
Loyalty forms
Emotional loyaltyCognitive loyalty
Comes from the heart and is connected with such
instincts like devotion to family,
old friends or religious
traditions
An employee evaluates not only
what will he have to do in the company,
but also pays attention to how he
will do it
It usually occurs quite
early, at the selection stage, and also in
during the first few months
work
Comes with time, experience and
ability to make a logical assessment
events
The employee evaluates how
the company satisfies his basic
needs and contributes
professional growth and development
Occurs when an employee
it becomes possible to apply
your personal skills and talents
Classification of employees according to their motivational level
EmployeeMotivated
Experienced
Personally
mature
Personally
immature
Stimulated
Inexperienced
Personally
mature
Personally
immature
Experienced
Personally
mature
Personally
immature
Inexperienced
Personally
mature
Personally
immature
Behavior of motivated
employees
Behavior of stimulated
employees
Proactive, eager to take
take the situation into your own hands, rather than wait,
until they are asked to do so
Reactive, allows other people
and situations to decide for themselves
Aimed at obtaining outstanding
results and have a reputation
people who know how to achieve goals
They strive to maintain the status quo and do not
interested in doing
more than is required of them
Can work with any style
leadership, in different atmospheres and
conditions, in many and different
companies, thanks to which
achieve success at any
positions
Can be successful in some
divisions of the company, but it is unlikely
can be successful if
different leadership styles
Behavior of motivated and stimulated employees
Behavior of motivatedemployees
Work successfully in a team, can
be interested in success
team more than in your own
Behavior of stimulated
employees
Not team players because
focused primarily on
to myself
Constantly developing and
Do not carry out targeted
improve themselves with the goal
actions for your own development and
provide yourself with more opportunities for self-improvement
Constantly strive
improve products or
processes
Perform actions that
beneficial to their own careers
and are consistent with their personal
requirements
They strive to develop other people and
bring out the best in them
Show no interest in
about developing other people
Experienced
Inexperienced
Achieve goals independently
Need constant support
on the way to achieving the goal
Use effective methods
achieving results
Experiment with methods and
methods for achieving results, for
determining the most effective
of which
Make minimal mistakes
standard processes are reliable
May make mistakes even when
performing standard processes
Behavior of experienced and inexperienced employees
ExperiencedInexperienced
Have a large volume
practical skills in your field
activities through which
can form their own
theoretical knowledge
At best, they only have
theoretical knowledge, on
on the basis of which they are trying
build practical actions
Able to advise and train
other employees
Need counseling and
training by other employees
Strive to improve
processes as they progress
They strive to improve their
skills for quality performance
processes
Mature
Immature
Strive to have great
degrees of freedom in order to
personally responsible for what they do
Fear of a large degree of freedom
and too much responsibility
Ready to take full responsibility
for your successes and mistakes, reasons
they look for failures, first of all, in
to myself
Tend to shift or
“blur” responsibility, look for
reasons for your failures in other people
or circumstances
They know exactly what is best for them and what
unnecessary, where should you direct your
efforts, and what is better to let go of
gravity
Chaotic in their choice of interests and
priorities are not fully understood
your zone of influence and opportunities
Behavior of mature and immature employees
MatureImmature
Confident in your abilities and
they know exactly their limitations,
adequate in self-esteem
Often display distorted
idea of one's strengths and
weaknesses, have inadequate
self-esteem
Strive to get feedback
connections from other people
development tool, mostly
degree interested in obtaining
criticism than praise
Critics are afraid, not always
react to it adequately,
need constant praise and
support
Make decisions and evaluate
themselves based on their own
criteria
Evaluate themselves and accept
decisions based on criteria and
other people's opinions
Behavior of mature and immature employees
MatureImmature
Able to express directly and openly
your opinion, confident and convincing
when defending your position
Tend to remain silent
veiledness and vagueness
when expressing thoughts, in controversial
may be aggressive in situations
or, conversely, passivity
Clearly separate interpersonal
relationships from work results
Quality of work results of colleagues
influences attitudes towards them and vice versa
Know their goals and live in harmony with them
own values
Don't have long term goals
prone to double standards
Working with incentivized employees
Mature / Experiencedrewards
Mature/Inexperienced
The most expressed need is interest,
safety
Immature / Experienced
The most expressed need is
recognition, respect, status
Immature/Inexperienced
The most expressed need is
belonging, establishing contacts
Working with motivated employees
Mature / ExperiencedThe most expressed need is
self-realization and self-expression
Mature/Inexperienced
The most expressed need is
achievements
Immature / Experienced
The most expressed need is
recognition and respect
Immature/Inexperienced
The most expressed need is
belonging, establishing contacts,
recognition and support
"Motivational cards"
“Motivational map” is a certain set of factors thatincreases the efficiency of a person’s work, promotes his growth
job satisfaction due to the fact that the organization of work
activity corresponds to his internal needs or motives,
who are currently not satisfied or require
satisfaction
Advantages of “motivational cards”
Help assess employee compliance with job requirements andcompany policy
Optimize the use of human resources
Create a competitive advantage
Increases the efficiency of staff and the company as a whole
Helps increase employee loyalty to the company
The motivational sphere is quite dynamic:
the meaning and influence of individual motives changes over time and age
(depending on circumstances and people's influence)
Activity is stimulated not by one, but by several motives:
the more motives determine activity, the higher the overall
level of motivation
Much depends on the driving force of each motive: sometimes
the strength of one motive prevails over the influence of several
motives. In most cases, however, the more motives
updated, the stronger the motivation
The dynamism of the hierarchy of motives
The overall level of motivation depends on...Number of motives
which encourage
activities
Updates
situational
factors
motivating force
each of these
motives
Methods for identifying employee motivators
Psychodiagnostics - tests that determine work motivationS.T.A.R. technique (Situation, Task, Action, Result) – building open
questions that provide the following information: what is the situation or
the task the employee faced, what actions were taken, what
received as a result of these actions
Projective questions are questions constructed in such a way that
offer the employee to evaluate not himself, but some character or people
at all
Cases – construction of certain situations, after which the employee
are asked to describe a model of their behavior or solution to a situation
Questionnaire – candidate’s self-assessment of his leading motivators
Type of motivation
Description
The work is being reviewed
only as a source
Instrumental earnings and other benefits
Payment Features
Piecework, according to achieved
results, taking into account
quality of work performed
work
Employee values at work
Time-based, based
its contents,
on an accurate account of differences in
Professional opportunity to demonstrate your skill level
workers or
features of the performed
jobs (positions)
Formation of systems of material incentives for employees with various types of motivation
Type of motivationDescription
Payment Features
Patriotic
Based on belief
employee in his
needs for the company
Accounting based
labor contribution
employee in general
work results
divisions and companies in
in general
Master's
Employee acceptance
take responsibility
for the work performed
Piecework or time-based
payment based on results
individual or
permanent teams
composition
Formation of systems of material incentives for employees with various types of motivation
Type of motivationDescription
Based on belief
employee in his
needs for the company
Patriotic
Payment Features
Time-based with
salary dependence
from labor costs, but better
from overall results
department work
or the whole company
Three facts about financial incentives for employees
Material incentives do not always “work”: for example,young employees who do not have their own family and are not professionally
those who have decided can value the opportunity more than high earnings
have free time
Salary satisfaction depends not on size, but
from social justice: equalization of pay is an obstacle
maintaining and strengthening work motivation
Salary is not a significant factor influencing
complex attitude of the employee to the company: the majority
people prefer the company they work for
numerous benefits than companies that pay more
Methods of non-material incentives
Benefits related to work scheduleMaterial non-financial rewards
Corporate events
Appreciation
Change of status
Movement of information in the company
Special functions of the benefit system as an incentive mechanism
Determination of employee statuses: each status is “assigned”certain benefits
Maintaining expectations: benefits and privileges act as
expected personal goals of the employee. But satisfied expectations
lead to loss of social activity, therefore an important tool
is to maintain expectations
Maintaining a Dependency State: Dependency stems from
expectations. The stronger the expectation of a team member who can
satisfy the manager, the higher his dependence, and therefore
leader's authority
When using psychological stimuli, one should proceed from
goals and objectives of the company: selecting certain methods
stimulation, attention should be focused on those that
will stimulate the required behavior of the employee
It is necessary to understand that the lack of psychological
incentives from the manager in most cases
is perceived negatively by subordinates, because after several times
receiving psychological stimuli, they begin to be perceived as
due
The manager must be clearly aware that the use
psychological stimulation largely consumes it
personal resource, therefore, it is necessary to understand in what
situation can be allowed to use it and what not
Principles of using psychological stimuli
When using psychological stimulation, it is necessary to take into accountthe employee’s readiness to adequately perceive the proposed
manager incentive
It is important to be aware that if a manager uses
psychological stimulation in the presence of other employees,
comparison situations are possible in which one employee can
experience discomfort, for example, from the fact that his work does not deserve
leader's praise
A manager should not project his own thoughts onto his subordinates.
needs regarding psychological stimulation
Algorithm for creating positive motivation
Imagine situations that you want to make motivating,sensory obvious: that which is clearly visible, audible, felt and
tangibly
Use more pictures and illustrations in your speech: thesis - illustration
Describe the problem with convincing pictures and intelligible
Slide 2
3 laws of motivation:
The behavior of all people is motivated. You cannot motivate other people. A person is guided by his own motives, not yours.
Slide 3
WORK MOTIVATION
Work motivation is the main component of an employee’s self-awareness, which determines his attitude and behavior at work, his reaction to specific working conditions. Knowing the structure of motivation, we can more accurately predict which forms of incentives will be most effective for a particular category of workers
Slide 4
STIMULATION
STIMULUS is an object or phenomenon that in a given situation has a certain meaning for the control object, activating its behavior due to the positively assessed chance and profitability of possessing them (or avoiding them) and contributing to the achievement of the goal set by the control subject
Slide 5
Typological concept of work motivation (V.I. Gerchikov)
Active, constructive work behavior Avoidance motivation Achievement motivation Passive, destructive work behavior
Slide 6
Typological concept of work motivation
Active, constructive work behavior Avoidant motivation Achievement motivation Passive, destructive work behavior Quadrant I. The growth of organizational efficiency of work activity is proportional to the degree of satisfaction of the employee’s motivational expectations and is limited only by “natural” limits (the maximum possible efficiency for given organizational and technological conditions)
Slide 7
Active, constructive work behavior Avoidant motivation Achievement motivation Passive, destructive work behavior Quadrant II. The growth of labor efficiency of an employee with avoidant motivation is fundamentally limited by: 1) the task (normative value); 2) the manager’s ability to prove the employee’s guilt in case of failure to complete the task.
Slide 8
Active, constructive work behavior Avoidant motivation Achievement motivation Passive, destructive work behavior III quadrant. The level of an employee’s destructive reactions is usually limited and most often comes down to passive labor behavior and “working according to the rules” (solid line). However, if a strong leader appears in the group and comes into conflict with the management of the organization (and this can only be a dissatisfied employee from the IV quadrant), he is able to captivate employees with an avoidant type of motivation and “ignite” them to extreme forms of destructive behavior, even until the organization is completely destroyed (dashed line).
Slide 9
Active, constructive work behavior Avoidant motivation Achievement motivation Passive, destructive work behavior IV quadrant. If organizational working conditions and the incentive system run counter to the employee’s motivational expectations, there is a high probability of receiving destructive work behavior from him, and in quite severe forms. However, things most likely will not come to the point of destroying the organization.
Slide 10
Achievement types of work motivation:
Instrumental: Price (amount of earnings and other benefits) received as a reward for work. Earnings of money received. Developed social dignity.
Slide 11
Professional: Diversity, interestingness, creative nature of the work. An opportunity to prove himself and prove that he can cope with a difficult task that not everyone can do. Opportunity for professional development. Independence at work. Developed professional dignity.
Slide 12
Patriotic: Conviction of one’s need for the organization. Participation in the implementation of a common cause that is very important for the organization. Public recognition of participation in common achievements.
Slide 13
Master: Voluntarily accepting full personal responsibility for the work performed. The desire for maximum independence in work (sovereignty). Aversion to control.
Slide 14
Avoidant type of work motivation (lumpen employee):
Basic characteristics: The desire to minimize your labor efforts. Low labor price (qualification, responsibility, activity). Relying on “freebies” and the favor of the manager.
Description of the presentation by individual slides:
1 slide
Slide description:
2 slide
Slide description:
Motivation is an internal property of a person, an integral part of his character, associated with his interests and determining his behavior in the organization. An incentive is some influence on a person, the purpose of which is to direct his activities and correct behavior in the organization. There are several motivational types, each of which describes the characteristic behavior of a person in an organization. Motivational types can be divided into two classes: 1) the class of avoidant motivation (avoidant motivation - a person seeks to avoid the undesirable consequences of his behavior); 2) the class of achievement motivation (achievement motivation - a person behaves in such a way as to achieve certain milestones that he strives for).
3 slide
Slide description:
No. Need is a state of need for certain living conditions, activities, material objects, people or certain social factors, without which a given individual experiences a state of discomfort.
4 slide
Slide description:
Need is a state of need for certain living conditions, activities, material objects, people or certain social factors, without which a given individual experiences a state of discomfort.
5 slide
Slide description:
Level of needs Contents Physiological (biological) needs Human needs for food, drink, oxygen, optimal temperature and air humidity, rest. The need for security and stability The need for stability in the existence of the current order of things. Confidence in the future, the feeling that nothing threatens you, and that your old age will be secure. The need for acquisition, accumulation and capture The need for the not always motivated acquisition of material assets. Excessive manifestation of this need leads to greed, avarice, stinginess. The need for love and belonging to a group. The need to love and be loved. The need to communicate with other people, to be involved in some group. The need for respect and recognition a) the desire for freedom and independence; the desire to be strong, competent and confident. b) the desire to have a high reputation, the desire for prestige, high social status and power. The need for overcoming difficulties The need for risk, adventure and overcoming difficulties. Need for self-realization The desire to realize your uniqueness, the need to do what you like, what you have abilities and talents for.
6 slide
Slide description:
Stimulation as the basis of motivation Labor stimulation is, first of all, an external motivation, an element of the work situation that influences human behavior in the world of work, the material shell of personnel motivation. At the same time, it also carries an intangible load that allows the employee to realize himself as a person and an employee at the same time. It performs a number of functions: The economic function is expressed primarily in the fact that labor stimulation helps to increase production efficiency, which is expressed in increased labor productivity and product quality. The moral function is determined by the fact that incentives to work form an active life position and a highly moral social climate in society. At the same time, it is important to ensure a correct and justified system of incentives, taking into account tradition and historical experience. The social function is ensured by the formation of the social structure of society through different levels of income, which largely depends on the impact of incentives on different people. In addition, the formation of needs, and ultimately the development of personality, are also predetermined by the organization and stimulation of labor in society.
7 slide
Slide description:
The main forms of incentives for company personnel: Material reward: Salary; Bonuses; Profit sharing; Additional payments; Payment of transportation costs; Additional incentives: Food subsidies; Discounts on the purchase of company goods; Help with educational expenses; Assistance in training; Club memberships; Country trips and picnics; Life insurance; Dependents' life insurance; Accident insurance; Medical and dental care.
8 slide
Slide description:
Slide 9
Slide description:
Theories of motivation The theory of the hierarchy of needs by A. Maslow Its essence comes down to the study of human needs. This is an earlier theory. Its supporters, including Abraham Maslow, believed that the subject of psychology is behavior, not human consciousness. Behavior is based on human needs, which can be divided into five groups: * physiological needs necessary for human survival: food, water, rest, etc.; * needs for security and confidence in the future - protection from physical and other dangers from the environment and confidence that physiological needs will be met in the future; * social needs - the need for a social environment, communication with people, a sense of “elbow” and support; * needs for respect, recognition of others and the desire for personal achievements; * the need for self-expression, i.e. the need for one’s own growth and the realization of one’s potential. The first two groups of needs are primary, and the next three are secondary.
10 slide
Slide description:
McClelland's theory of acquired needs A widely accepted concept of needs that determines a person's motivation for activity is McClelland's concept, which is associated with the study and description of the influence of the needs for achievement, participation and power. These needs are acquired throughout life and if they are present strongly enough in a person, they have a noticeable impact on his behavior, forcing him to make efforts to carry out actions that should lead to the satisfaction of these needs. Achievement needs are manifested in a person’s desire to achieve his goals more effectively than before. Needs for participation - manifest themselves in the form of a desire for friendly relations with others. People with a high need for complicity try to establish and maintain good relationships; approval and support from others are important to them; they worry about what others think of them. The need for power is the desire to control people’s actions, influence their behavior, and take responsibility for the actions and behavior of other people. People with a high need for power can be divided into 2 groups: Group 1 - those who strive for power for the sake of power. They are attracted to the possibility of commanding others. The interests of the organization in this case fade into the background, because they focus only on their position in the organization. Group 2 - those who strive for power in order to solve group problems; these people satisfy their needs for power by defining goals, setting tasks for the team and participating in the process of solving these problems.

Theories of motivation place the main emphasis on determining the list and structure of people's needs. Need is an awareness of the absence of something that causes an urge to action. A need can be satisfied with a reward - something that a person considers valuable to himself.






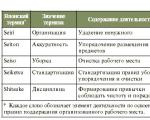
Herzberg's two-factor theory Hygiene factors Company policy and administration Working conditions Salary Interpersonal relationships with superiors, subordinates, colleagues Degree of direct control over work Motivation Success Promotion Recognition and approval of work results High degree of responsibility Opportunities for creative and business growth

Expectancy Theory A person directs his efforts to achieve a goal only when he is confident in the greater likelihood of satisfying his needs or achieving the goal. Motivation Labor costs - Results Results - Reward Valence = xx