Competitive advantages: a review of strategies and methods of development during a crisis. Competitive advantages of business: we search, highlight and correctly present to our client
In the article we will talk about the likely areas of competitive advantages using examples of world-class companies, we will look at the features of creating business advantages in different industries: in the banking sector, in the tourism and hotel markets, we will separately talk about the specifics of creating competitive advantages for wholesale and retail stores, taking into account modern global trends.
- Universal for everyone
- Advantages in the field of trade
Universal for everyone
Let's start our list of examples of competitive advantages with 12 best methods for creating them, which were prepared by analyzing leading industries, global brands and large markets. The point of all the examples outlined below is that there is no single correct formula for creating competitive advantage. You can win in any market. It is important to find that feature of the business that can ensure the highest level of profit for the company.
Research and Innovation
The IT branch is the most technologically equipped area of business. Each player in this market strives to become a leader in innovative solutions and developments. In this industry, those who set the pace for the development of innovations and technologies are in the lead and receive super profits. Apple and Sony are striking examples of two companies that have achieved leadership in the IT market through the use of innovation as a sustainable competitive advantage.
Brand awareness
Global recognition, fame and respect for the brand has allowed companies such as Coca-Cola and Virgin to maintain their market share and dominate the market for many years. Higher brand awareness and a positive brand identity have also reduced the costs for Virgin to capture new parts of the market.
Corporate reputation
The highest level of corporate reputation can also serve as a source of competitive advantage in the market. Price Waterhouse (consulting and auditing) and Berkshire Hathaway (investments, insurance) have used this competitive advantage to give their companies world-class status.
Patents
Proprietary technologies are assets that can provide a company with a competitive advantage in the long term. In world practice, methods of purchasing companies due to the ownership of patents and other protected technologies are widely used. General Electric is known for becoming one of the most powerful companies in the world through its ownership of patented designs.
Economies of scale
Dangote Group has become one of the leading manufacturing conglomerates in Africa due to its ability to create products in greater volume and maintain uniform prices throughout its trading area.
Quick access to reverse capital
In world practice, OJSCs win over private companies due to their ability to attract the highest level of investment in a very short period of time. For example, Oracle attracted investment to purchase more than 50 companies in just 5 years.
Barriers to entry
Country restrictions on rivals; a country's protectionist policies can serve as a competitive advantage for local companies. Example, Telmex (telecommunications company, Mexico) or Chevron (energy, USA).
The highest quality product and level of service
The highest level of service is always a strong competitive advantage of a product. IKEA has gained a strong position in the market by being able to provide superior product performance at low cost and the highest level of after-sales service.
Exclusive
Coscharis Group has seized leadership in the Nigerian market by possessing exclusive rights to distribute BMW vehicles throughout West Africa.
Elasticity
The ability to quickly adapt to market changes has provided Microsoft with a leading position in the global software market.
Speed and time
Concentration of all efforts on achieving the greatest speed and reducing service completion times has given companies such as FedEx and Domino Pizza a growing and sustainable position in the industry.
Low prices
The low-price strategy and the ability to maintain, strengthen and develop it have provided the Wall-Mart retail chain with global leadership and the highest level of company capitalization.
Improved database processing
GTBank, AT&T, Google, Facebook have achieved global leadership thanks to advanced technologies and achievements in the field of processing and managing large volumes of information.
Advantages in the banking services market
In this section, we will offer top tips for developing competitive advantages for companies in the banking sector. The weakening of the economies of European countries in the modern world and the increasing level of instability in the global economy leads to the need to revise the basis of the competitive advantages of the monetary sector. In 2013 - 2015, it will be more profitable and important for the banking sector to concentrate efforts on developing subsequent competitive advantages:
- increase in return on capital
- achieving leading positions in profitability in one or more areas of banking activity (in other words, transition to specialization and provision of the best interest rates for narrow market niches)
- improvement of banking services, speed and convenience of transactions by updating and simplifying business processes
- achieving leadership in safety, reliability and asset protection
- development of mobile Internet banking and increase in the technological level of service provision
- simplification of making purchases and lowering commissions using bank cards (including the creation of payment cancellation guarantees in case of negligent execution of sales contracts - following the example of the PayPal payment system)
Advantages in the hotel services market
In order to choose the right competitive advantage, be sure to conduct a comparative analysis of the criteria for the provision of services by your hotel company and its competitors. More successful examples of competitive advantages for the hotel business:
- leadership in service level
- low cost advantage (subject to the existence of the ability to obtain higher profits compared to competitors)
- provision of free meals or other additional services
- the most profitable loyalty programs that stimulate repeat purchases and more frequent implementation of hotel services
- comfortable location of the hotel for certain groups of clients
- availability of all necessary additional services (conference room, wi-fi, internet, swimming pool, beauty salon, restaurant, etc.)
- a unique style of decoration and hotel service, allowing the consumer to immerse themselves in a completely new environment
Advantages in the tourism services market
In order to choose the right competitive advantage, be sure to conduct a comparative analysis of the criteria for the provision of services by your company and its competitors. More successful examples of competitive advantages for tourism businesses:
- leadership in the level of service provision
- focusing on the quality of service to certain customer groups
- the ability to set low prices (subject to the ability to obtain higher profits compared to competitors)
- ease of use of the service and minimization of client time
- the most profitable loyalty programs that stimulate repeat purchases
- leadership in one of the types of tourism (see example of tourism market segmentation)
- availability of all necessary related services
- the most noteworthy travel programs
- availability of a mobile application and the highest technology of the service
- the most profitable flaming tours
Advantages in trading
More successful examples of competitive advantages for the trade industry (using the example of a retail store): breadth of assortment, exclusivity of sales in a certain area, the ability to set low prices, leadership in warranty period and after-sales service, availability of free prizes for the buyer, leadership in the attractiveness of promotions -offers, leadership in quality, freshness, modernity of products sold; personnel competence; ease of selection, convenience of selection and time saving for the buyer; computerization of business and the presence of web trading; the most profitable loyalty programs; advice from professionals on choosing products for the buyer; Convenient location of the retail outlet.
The world does not stand still, information is constantly updated, and market participants are in search of marketing ideas, ways of doing business, and new views on their product. Any business is tested for strength by its competitors, so when developing a development strategy, it is wise to take into account their influence, market share, positions and behavior.
What is competitive advantage
Competitive advantage is a certain superiority of a company or product over other market participants, which is used to strengthen its position when reaching the planned level of profit. Competitive advantage is achieved by providing the client with more services, higher quality products, relative cheapness of goods and other qualities.
A competitive advantage for a business provides:
– prospects for long-term growth;
– stability of work;
– obtaining a higher rate of profit from the sale of goods;
– creating barriers for new players when entering the market.
Let us note that competitive advantages can always be found for any type of business. To do this, you should conduct a competent analysis of your product and the competitor’s product.
What types of competitive advantages are there?
What allows you to create competitive advantages for a business? There are 2 options for this. First of all, the product itself can provide competitive advantages. One type of competitive advantage is the price of a product. Buyers often prefer to buy a product only because it is cheap relative to other offers with similar properties. Due to its low cost, a product can be purchased even if it does not provide much consumer value to buyers.
The second competitive advantage is differentiation. For example, when a product has distinctive features that make the product more attractive to the consumer. In particular, differentiation can be achieved through characteristics that are not related to consumer properties. For example, due to the trademark.
If a company creates a competitive advantage for its product, it can uniquely differentiate its position in the market. This can be achieved by monopolizing part of the market. True, such a situation contradicts market relations, since the buyer is deprived of the opportunity to choose. However, in practice, many companies not only provide themselves with such a competitive advantage of the product, but also maintain it for quite a long time.
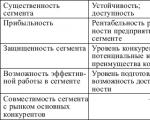
4 criteria for assessing competitive advantages
Utility. The proposed competitive advantage should be beneficial to the company's operations and should also enhance profitability and strategy development.
Uniqueness. A competitive advantage should differentiate a product from its competitors, not replicate them.
Security. It is important to legally protect your competitive advantage and make it as difficult as possible to copy it.
Value for the target audience of the business.
Strategies for Competitive Advantage
1. Cost leadership. Thanks to this strategy, the company receives income above the industry average due to the low cost of its production, despite high competition. When a company receives a higher rate of profit, it can reinvest these funds to support the product, inform about it, or beat competitors due to lower prices. Low costs provide protection from competitors, since income is preserved in conditions that are not available to other market participants. Where can you use a cost leadership strategy? This strategy is used when there are economies of scale or when there is a prospect of achieving lower costs in the long term. This strategy is chosen by companies that cannot compete in the industry at the product level and work with a differentiation approach, providing distinctive characteristics for the product. This strategy will be effective when there is a high proportion of consumers who are price sensitive.
- Information about competitors: 3 rules for its collection and use
This strategy often requires unification and simplification of the product to facilitate production processes and increase production volumes. It may also require a high level of initial investment in equipment and technology to reduce costs. For this strategy to be effective, careful control of labor processes, product design and development, with a clear organizational structure is required.
Cost leadership can be achieved through certain opportunities:
– limited access of the enterprise to obtaining cheap resources;
– the company has the opportunity to reduce production costs due to accumulated experience;
– management of the company’s production capacity is based on the principle that promotes economies of scale;
– the company provides for scrupulous management of its inventory levels;
– strict control of overhead and production costs, abandoning small operations;
– availability of technology for the cheapest production in the industry;
– standardized production of the company;
2 steps to building a competitive advantage
Alexander Maryenko, project manager of the A Dan Dzo group of companies, Moscow
There are no clear instructions for creating a competitive advantage, taking into account the individuality of each market. However, in such a situation, you can be guided by a certain logical algorithm:
Determine the target audience that will buy your product or influence this decision.
Determine the real need of such people related to your services or products, which is not yet satisfied by suppliers.
2. Differentiation. When working with this strategy, the company provides unique properties for its product that are important to the target audience. Consequently, they allow you to set a higher price for the product compared to competitors.
A product leadership strategy requires:
– the product must have unique properties;
– the opportunity to create a reputation for high quality product;
– highly qualified employees;
– the ability to protect competitive advantage.
The advantage is the ability to sell the product at higher prices than the industry average, avoiding direct competition. Thanks to this strategy, it is possible to achieve better commitment and loyalty to the brand, under the conditions of competent construction of the assortment and the presence of competitive advantages.
Risks or disadvantages of using a differentiated marketing strategy:
– a significant difference in prices is possible, due to which even the unique qualities of the product will not attract a sufficient number of buyers;
– a product may lose its uniqueness when its advantages are copied by cheaper products.
This strategy is used for saturated markets by companies that are ready to make high investments in promotion. There is no need to talk about low cost - it will be higher than the market average. However, this is offset by the ability to sell the product at higher prices.
3. Niche leadership or focus. The strategy involves protection from major competitors and substitute products. In this case, it is possible to achieve a high rate of profit by more effectively meeting the needs of a narrow audience of consumers. This strategy can be based on any type of competitive advantage - the breadth of the offered range or the lower price of the product.
In this case, the company is limited in market share, but it does not need significant investments to develop the product, which is a chance for the survival of small enterprises.
Risks and disadvantages of using a focusing strategy:
– there is a high probability of large differences in product prices compared to leading brands on the market, which can scare away its target audience;
– the attention of large market participants switches to niche segments in which the company operates;
– a serious danger of reducing the difference between the needs of the industry and the niche market.
Where to Use a Niche Leadership Strategy? Working with this strategy is recommended for small companies. It is most effective when the market is saturated, there are strong players, when costs are high or when costs are uncompetitive in comparison with market leaders.
Three stages of service strategy
Stage I. Innovation. When one of the market participants introduces something new in terms of customer service. The company stands out during this period, given the presence of a new competitive advantage.
Stage II. Addiction. The proposed service is becoming familiar to consumers, and an analogue is gradually being introduced in the activities of competitors.
Stage III. Requirement. For consumers, this offer becomes an integral element of a service or product, becoming a standard.
How to check the level of service in your company
- Conducting informal surveys. The CEO and other managers need to understand consumers’ opinions about the proposed service.
- Conducting formal surveys (focus groups). It would be rational to involve both consumers and representatives of all departments of your company for these events.
- Hire outside consultants to survey company employees. With external consultants, the value of the answers increases (with more candid answers).
How to improve the service
Tatiana Grigorenko, managing partner of 4B Solutions, Moscow
Let's look at general tips for improving service in companies.
1. Surprise, influence emotions. Typically, visitors to the office are offered packaged tea or instant coffee. We decided to pleasantly surprise our customers - the visitor is offered a choice of 6 types of professionally prepared coffee, 6 excellent varieties of tea with signature chocolate for dessert.
2. Break the rules. In today's market, it is ineffective to be like everyone else; you need to be better than the rest.
3. Listen to your customers. Do you need to ask your clients what would be of interest to them?
How to create a competitive advantage
When developing a competitive advantage, there are nine criteria for a successful option to consider:
1) Uniqueness.
2) Long-term. Competitive advantage must be of interest for at least three years.
3) Uniqueness.
4) Credibility.
5) Attractiveness.
6) Have ReasonstoBelieve (reason for trust). Specific reasons that will make buyers believe.
7) Be better. Buyers must understand why this product is better than others.
8) Have the opposite. There needs to be a complete opposite in the market. Otherwise it will not be a competitive advantage.
9) Brevity. Must fit into a 30 second sentence.
Step #1. We make a list of all the benefits
Product benefits are sought as follows:
– we ask buyers what competitive advantages they hope to gain from your product;
– make a detailed list of all the properties that the product has, based on the characteristics from the “marketing mix” model:
1) Product
What can you say about the product:
– functionality;
– brand symbols: logo, name, corporate identity;
– appearance: packaging, design;
– required product quality: from the position of the target market;
– service and support;
– assortment, variability.
2) Price
What can you say about the price:
– pricing strategy for entering the market;
– retail price: the selling price of a product must necessarily correlate with the desired retail price, only if the company does not become the last link in the overall distribution chain.
– pricing for different sales channels; different prices are assumed, depending on a specific link in the distribution chain, a specific supplier;
– package pricing: with the simultaneous sale of several company products at special prices;
– policy regarding promotional events;
– availability of seasonal promotions or discounts;
– possibility of price discrimination.
3) Place of sale
It is necessary to have the product on the market in the right place so that the buyer can see it and purchase it at the right time.
What can you say about the sales meta:
– sales markets, or in which the sale of goods is planned;
– distribution channels for selling goods;
– type and conditions of distribution;
– conditions and rules for displaying goods;
– issues of logistics and inventory management.
4) Promotion
Promotion in this case involves all marketing communications to attract the attention of the target audience to the product, with the formation of knowledge about the product and key properties, the formation of the need to purchase the product and repeat purchases.
What can you say about promotion:
– promotion strategy: pull or push. The Push strategy involves pushing goods through the trade chain by stimulating intermediaries and sales personnel. Pull – “pulling” products through the distribution chain by stimulating consumers, the final demand of their product;
– target values of knowledge, brand loyalty and consumption among its target audience;
– required marketing budget, SOV in the segment;
– geography of your communication;
– communication channels for contact with consumers;
– participation in specialized shows and events;
– media strategy of your brand;
– PR strategy;
– promotions for the coming year, events aimed at stimulating sales.
5) People
– employees who represent your product and company;
– sales personnel in contact with target consumers of the product;
– consumers who are “opinion leaders” in their category;
– manufacturers on whom the quality and price of the product may depend;
– privileged consumer groups also belong to this group, including VIP clients and loyal customers who generate sales for the company.
What can you say about working with people:
– programs to create motivation, with the development of relevant competencies and skills among employees;
– methods of working with people on whom the opinion of the consumer audience depends;
– education and loyalty programs for its sales staff;
– methods for collecting feedback.
6) Process
This one applies to the services market and the B2B market. “Process” refers to the interaction between the company and consumers. It is this interaction that constitutes the basis for purchasing on the market with the formation of consumer loyalty.
- Unique selling proposition: examples, development tips
You can talk about programs to improve the process of providing services to your target clients. The goal is to provide the most comfortable conditions for customers when purchasing and using the proposed service.
7) Physical environment
This also applies to the services and B2B markets. This term describes what surrounds the buyer during the purchase of a service.
Step #2: Rank all the benefits
To evaluate the list, a three-point scale of the importance of characteristics is best suited:
1 point - the benefit of this characteristic for target consumers is not valuable;
2 points - the benefit is not primary, which stimulates the purchase of the product in the first place;
3 points - the benefit received is one of the most significant properties of the proposed service.
Step #3. Compare the list of benefits with competitors
The resulting list of characteristics should be compared with your competitors according to two principles: the presence of this property in the competitor, whether the competitor’s condition is better or yours.
Step #4. Seek Absolute Competitive Advantages
Among the sources of absolute competitive advantages, the following should be noted:
– the product is unique due to one or several properties;
– uniqueness in combination of properties;
– special components of the product composition, a unique combination of ingredients;
– certain actions are performed better, more efficiently and quickly;
– features of appearance, shape, packaging, method of sales or delivery;
– creation and implementation of innovations;
– unique technologies, methods for creating a product, patents;
– qualification of personnel and uniqueness of its human capital;
– the ability to provide the minimum cost in your industry, while assuming higher profits;
– special conditions of sales and after-sales service for consumers;
– availability of access to limited raw materials and resources.
Step #5. Look for “false” competitive advantages
First mover. Be the first to announce the properties of competitors’ products, before they have yet communicated them to their target audience;
Performance indicator. Creating your own performance measurement indicator;
Curiosity and interest. You can stand out thanks to a factor that is not considered decisive when purchasing, but will allow you to attract the attention of the target audience.
Step #6. Make a development and control plan
After identifying a competitive advantage, you need to formulate two further plans for marketing actions - a plan for developing your competitive advantage over the next few years and a plan for maintaining the relevance of the presented advantage.
How to Analyze Current Competitive Advantages
Stage 1. Make a list of evaluation parameters
Create a list of key competitive advantages of your product and competitors.
For assessment, a three-point scale is best suited, on which the following are rated:
1 point = the parameter is not fully reflected in the competitive advantages of the product;
2 points = the parameter is not fully reflected in the competitive advantage;
3 points = the parameter is fully reflected.
Stage 3. Make a development plan
Form your action plan aimed at improving the company's competitive advantage. It is necessary to plan improvements on assessment items that received less than three points.
How to develop competitive advantages
Competitive behavior in the market can be of three types:
Creative. Implementation of measures to create new components of market relations to gain a competitive advantage in the market;
Adaptive. Taking into account innovative changes in production, ahead of competitors in terms of modernization of production;
Providing and guaranteeing. The basis is the desire to maintain and stabilize the obtained competitive advantages and market positions in the long term by adding to the range, improving quality, and additional services to consumers.
The duration of maintaining competitive advantages depends on:
Source of competitive advantage. Can be a high and low order competitive advantage. The low-order advantage is represented by the possibility of using cheap raw materials, labor, components, materials, fuel and energy resources. At the same time, competitors can easily achieve low-order advantages by copying and searching for their sources of these advantages. The advantage of cheap labor can also lead to negative consequences for the enterprise. With low salaries for repairmen and drivers, they can be lured away by competitors. The advantages of a high order are the excellent reputation of the company, specially trained personnel, and production and technical base.
The number of obvious sources of competitive advantage in the enterprise. The greater number of competitive advantages an enterprise has will more seriously complicate the tasks of its pursuers and competitors;
Constant modernization of production.
How to survive a crisis and maintain a competitive advantage
Alexander Idrisov, managing partner of StrategyPartners, Moscow
1. Keep your finger on the pulse of events. One of the employees should collect and analyze information about the state and trends of the market, how these trends can affect the business, taking into account the study of consumer preferences, demand dynamics, data on investors and competitors.
2. Develop the most pessimistic forecast for your company.
3. Focus on paying customers.
4. Focus on a narrow range of tasks. You need to carefully examine your company's business model. This does not mean that you need to abolish all areas of your activity. But it is worth focusing on a narrow range of tasks, abandoning non-core tasks or areas that can be outsourced.
- Reframing, or How to deal with customer objections
5. Consider merging with competitors. Many companies are now ready for alliances with competitors on mutually beneficial terms.
6. Maintain relationships with potential investors. A particularly important condition during a crisis is that you must not lose contact with investors; it is better to activate them whenever possible.
Information about the author and company
Alexander Maryenko, project manager of the A Dan Dzo group of companies, Moscow. Graduated from the Faculty of Finance of Nizhny Novgorod State University. Participated in projects (more than 10, six of them as a manager) aimed at increasing the profitability of companies' businesses and solving their systemic problems.
John Shoal President of ServiceQualityInstitute, Minneapolis (Minnesota, USA). Considered the founder of service strategy. At the age of 25, he founded a firm specializing in teaching companies about service culture. Author of five best-selling books on the topic of service, translated into 11 languages and sold in more than 40 countries.
ServiceQualityInstitute formed by John Schole in 1972. Specializes in the development and implementation of service strategies in companies. ServiceQualityInstitute specialists have trained more than 2 million people. The main office is located in Minneapolis, branches are located all over the world (in 47 countries), their share is 70% of the total number of representative offices of the company. In Russia, ServiceQualityInstitute and John Shoal are represented by ServiceFirst.
Tatiana Grigorenko, managing partner of 4B Solutions, Moscow.
4B Solutions Company founded in 2004. Provides outsourcing and consulting services. Areas of specialization: improving customer service systems, crisis management, professional legal and accounting support for business. The company's staff is over 20 people. Clients include the Business Aviation Association, Triol Corporation, Rafamet machine tool plant (Poland), ANCS Group, IFR Monitoring, MediaArtsGroup, and the Gaastra boutique chain.
Alexander Idrisov, managing partner of StrategyPartners, Moscow.
StrategyPartners. Field of activity: strategic consulting. Form of organization: LLC. Location: Moscow. Number of personnel: about 100 people. Main clients (completed projects): companies Atlant-M, Atlant Telecom, Vostok, GAZ, MTS, Press House, Razgulay, Rosenergoatom, Russian Machines, Talosto, "Tractor Plants", "Uralsvyazinform", "Tsaritsyno", publishing houses "Prosveshchenie", "Eksmo", Ministry of Information Technologies and Communications of the Russian Federation, Ministry of Regional Development of the Russian Federation, Murmansk Port, Rosprirodnadzor, administrations of the Arkhangelsk, Nizhny Novgorod, Tomsk regions and Krasnoyarsk Territory, Avantix company.
Honestly, competitive advantages- This is a topic to which I have an ambivalent attitude. On the one hand, rebuilding a company from competitors in the market is a very interesting task. Especially when the company, at first glance, is like everyone else and does not stand out in anything special. On this issue I have a principled position. I am convinced that any business can be rebuilt, even if it is one of a thousand and trades at prices above the market average.
Types of competitive advantages
Conventionally, all competitive advantages of any organization can be divided into two large groups.
- Natural (price, terms, delivery conditions, authority, clients, etc.)
- Artificial (personal approach, guarantees, promotions, etc.)
Natural benefits carry more weight because they represent factual information. Artificial advantages are more of a manipulation, which, if used correctly, can greatly strengthen the first group. We will return to both groups below.
Now comes the fun part. Even if a company considers itself to be the same as everyone else, inferior to competitors in terms of prices and believes that it does not stand out in any way, it still has natural advantages, plus, it can be made artificial. You just need to spend a little time finding them and formulating them correctly. And this is where it all starts with competitive analysis.
Competitive analysis that doesn't exist
Do you know what is the most amazing thing about Runet? 80-90% of businesses do not conduct competitive analysis and do not highlight the company’s advantages based on its results. That’s all, but what you have enough time and energy in most cases to do is look at your competitors and tear off some elements from them. That's the whole setup. And it is here that clichés grow by leaps and bounds. Who do you think was the first to coin the phrase “Young and dynamically developing company”? It doesn't matter. Many took it and... Quietly adopted it. On the quiet. In the same way, clichés appeared:
- Individual approach
- Highly qualified professionalism
- High quality
- First class service
- Competitive prices
And many others, which in fact are not competitive advantages. If only because no company in its right mind would say that its employees are amateurs, and the quality is a little worse than none.
I am generally surprised by the attitude of some businessmen. If you talk to them, everything “somehow” works for them, orders “somehow” go through, there is a profit - and okay. Why invent, describe and count something? But as soon as things start to get tough, that’s when everyone remembers marketing, differentiation from competitors, and the company’s advantages. It is noteworthy that no one is counting the money that was lost due to such a frivolous approach. But this is also profit. Could be...
In 80-90% of cases, Runet businesses do not conduct competitive analysis and do not show the company’s advantages to their clients.
However, there is a positive side to all this. When no one shows their advantages, it’s easier to rebuild. This means it’s easier to attract new customers who are searching and comparing.
Competitive advantages of products (products)
There is another serious mistake that many businesses make when formulating benefits. But here it is worth mentioning right away that this does not apply to monopolists. The essence of the mistake is that the client is shown the advantages of the product or service, but not the company. In practice it looks like this.
That is why it is very important to correctly place emphasis and bring to the fore the benefits and emotions that a person receives and experiences when working with the organization, and not from purchasing the product itself. I repeat, this does not apply to monopolists who produce a product that is inextricably linked with them.
Main competitive advantages: natural and artificial
It's time to return to the varieties of benefits. As I already said, they can be divided into two large groups. Here they are.
Group No. 1: natural (actual) benefits
Representatives of this group exist on their own, as a fact. Only many people don’t write about them. Some think it’s obvious, others because they hide behind corporate clichés. The group includes:
Price- one of the strongest competitive advantages (especially when there are no others). If your prices are lower than those of your competitors, write how much. Those. not “low prices”, but “prices 20% below market prices”. Or “Wholesale prices at retail”. Numbers play a key role, especially when you work in the corporate segment (B2B).
Timing (time). If you are delivering goods from today to today, say so. If you deliver to remote regions of the country in 2-3 days, tell us about it. Very often the issue of delivery times is very acute, and if you have thoroughly worked out logistics, then write specifically where and for how much you can deliver the goods. Again, avoid abstract clichés like “fast/prompt delivery.”
Experience. If your employees are keen on what you sell and know all the ins and outs of your business, write about it. Buyers love working with professionals they can consult with. In addition, when purchasing a product or service from an experienced seller, customers feel more secure, which brings them closer to purchasing from you.
Special conditions. If you have any special delivery conditions (deferred payment, postpayment, discounts, presence of a showroom, geographic location, wide warehouse program or assortment, etc.). Anything that competitors don’t have will do.
Authority. Certificates, diplomas, diplomas, major clients or suppliers, participation in exhibitions and other evidence that increase the significance of your company. The status of a recognized expert is a great help. This is when company employees speak at conferences, have a well-promoted YouTube channel, or give interviews in specialized media.
Narrow specialization. Imagine that you have a Mercedes car. And in front of you are two workshops: a specialized service that deals only with Mercs, and a multidisciplinary one that repairs everything: from UAZs to tractors. Which service will you contact? I bet the first one, even if it has higher prices. This is one of the types of unique selling proposition (USP) - see below.
Other actual benefits. For example, you may have a wider range of products than your competitors. Or a special technology that others do not have (or that everyone has, but which competitors do not write about). Anything can happen here. The main thing is that you have something that others don’t have. As a fact. This also constitutes your USP.
Group No. 2: artificial advantages
I especially love this group because it helps a lot in situations where the customer’s company does not have any advantages as such. This is especially true in the following cases:
- A young company, just entering the market, has no clients, no cases, no reviews. As an option, specialists leave a larger company and organize their own.
- The company occupies a niche somewhere in the middle: it does not have a wide range, like large retail chains, and does not have a narrow specialization. Those. sells goods, like everyone else, at prices slightly above the market average.
- The company has some adjustments, but it is the same as its competitors. Those. everyone in the niche uses the same actual advantages: discounts, experience, etc.
In all three cases, introducing artificial advantages helps. These include:
Added value. For example, you sell laptops. But you can't compete on price with a larger seller. Then you use a trick: install an operating system and a basic set of programs on your laptop, selling it a little more. In other words, you create added value. This also includes various promotions a la “Buy and Win...”, “When buying an apartment - a T-shirt as a gift”, etc.
Personal adjustment. It works great when everyone around is hiding behind corporate clichés. Its essence is that you show the face of the company (for example, the director) and involve. It works great in almost any niche: from selling children's toys to armored doors.
Responsibility. A very strong advantage that I actively use on my laboratory’s website. Combines perfectly with the previous point. People love to work with people who are not afraid to take responsibility for the products and/or services they sell.
Reviews. Provided they are real. The more authoritative the person who gives you feedback, the stronger the impact on the audience (see trigger “”). Reviews on letterhead with a stamp and signature work better.
Demonstration. The best presentation is a demonstration. Let's say you have no other advantages. Or there are, but implicit. Make a clear presentation of what you are selling. If these are services, show how you provide them, make a video. At the same time, it is important to place the accents correctly. For example, if you check each product for functionality, tell us about it. And this will be an advantage for your company.
Cases. This is a kind of visual demonstration of solved problems (completed projects). I always recommend describing them because they work great for sales. But there are situations when there are no cases. This is especially true for young companies. Then you can make so-called artificial cases. The idea is simple: do yourself or a hypothetical client a favor. As an option - to a real client on a mutual basis (depending on the type of services, if possible). This way you will have a case that you can show and demonstrate your expertise.
Unique selling proposition. We have already talked about it a little higher. Its essence is that you enter some detail or disclose information that sets you apart from your competitors. Take me, for example. I provide copywriting services. But many specialists provide a wide range of copywriting services. And my USP is that I guarantee results expressed in numbers. Those. I work with numbers as an objective indicator of performance. And it's catchy. You can find out more about the USP in.
How to find and correctly describe the company's advantages
As I already said, I firmly believe that every company has its own advantages (and disadvantages, but that doesn’t matter now :)). Even if she is a strong middle peasant and sells everything like everyone else. And even if it seems to you that your company does not stand out in any way, the easiest way to understand the situation is to ask directly the clients who are already working with you. Be prepared that the answers may surprise you.
The easiest way to find out the strengths of your company is to ask your clients why they chose you.
Someone will say that they work with you because you are closer (geographically). Some will say that you inspire confidence, while others simply liked you. Collect and analyze this information and it will increase your profits.
But that is not all. Take a piece of paper and write down the strengths and weaknesses of your company. Objectively. Like in spirit. In other words, what you have and what you don’t have (or don’t have yet). At the same time, try to avoid abstractions, replacing them with specifics. Check out the examples.
Not all advantages can and should be written about on the same website. However, at this stage the task is to write down as many strengths and weaknesses of the enterprise as possible. This is an important starting point.

Take a pen and paper. Divide the sheet into two columns and write down the advantages of the company in one and the disadvantages of the company in the second. Maybe with a cup of coffee. Don’t look at the rowan tree, it’s just there for the ambiance.
Yes, we have, but this
Look at the examples:
| Flaw | Turning into an advantage |
|---|---|
| Office on the outskirts | Yes, but the office and warehouse are in one place. You can see the product right away. Free parking even for trucks. |
| Price higher than competitors | Yes, but it comes with a rich package: a computer + an installed operating system + a set of basic programs + a gift. |
| Long delivery on order | Yes, but there are not only standard components, but also rare spare parts for individual orders. |
| Young and inexperienced company | Yes, but there is mobility, high efficiency, flexibility and the absence of bureaucratic delays (these points need to be discussed in detail). |
| Small assortment | Yes, but there is a specialization on the brand. Deeper knowledge of it. The ability to advise better than competitors. |
You get the idea. This gives you several types of competitive advantages:
- Natural (factual information that you have that sets you apart from your competitors)
- Artificial (amplifiers that also set you apart from competitors - guarantees, personal approach, etc.)
- “Shifters” are disadvantages that are turned into advantages. They complement the first two points.
Little trick
I use this trick from time to time, when it is not possible to fully show off my strengths, as well as in a number of other cases when I need something more “weighty”. Then I don’t just write the company’s advantages, but combine them with the benefits that the client receives from the product or service. It turns out to be a kind of “explosive mixture”.
See what this looks like in practice.
- Was: Experience 10 years
- Became: Budget savings of up to 80% due to 10 years of experience
Or another example.
- Was: Low prices
- Became: The price is 15% lower, plus a reduction in transport costs by 10% due to our own fleet of vehicles.
You can learn in detail about how to correctly form benefits from.
Summary
Today we looked at the types of main competitive advantages of a company and, using examples, we looked at how to formulate them correctly. At the same time, it is important to understand that everything that we did today should by default be part of the competitive strategy (if it is being developed). In other words, everything will work better when linked into a single system.
I really hope that the information in this article will expand your capabilities and allow you to conduct competitive analysis more effectively. In turn, if you have any questions, ask them in the comments.
I'm sure you will succeed!
Honestly, competitive advantages- This is a topic to which I have an ambivalent attitude. On the one hand, rebuilding a company from competitors in the market is a very interesting task. Especially when the company, at first glance, is like everyone else and does not stand out in anything special. On this issue I have a principled position. I am convinced that any business can be rebuilt, even if it is one of a thousand and trades at prices above the market average.
Types of competitive advantages
Conventionally, all competitive advantages of any organization can be divided into two large groups.
- Natural (price, terms, delivery conditions, authority, clients, etc.)
- Artificial (personal approach, guarantees, promotions, etc.)
Natural benefits carry more weight because they represent factual information. Artificial advantages are more of a manipulation, which, if used correctly, can greatly strengthen the first group. We will return to both groups below.
Now comes the fun part. Even if a company considers itself to be the same as everyone else, inferior to competitors in terms of prices and believes that it does not stand out in any way, it still has natural advantages, plus, it can be made artificial. You just need to spend a little time finding them and formulating them correctly. And this is where it all starts with competitive analysis.
Competitive analysis that doesn't exist
Do you know what is the most amazing thing about Runet? 80-90% of businesses do not conduct competitive analysis and do not highlight the company’s advantages based on its results. That’s all, but what you have enough time and energy in most cases to do is look at your competitors and tear off some elements from them. That's the whole setup. And it is here that clichés grow by leaps and bounds. Who do you think was the first to coin the phrase “Young and dynamically developing company”? It doesn't matter. Many took it and... Quietly adopted it. On the quiet. In the same way, clichés appeared:
- Individual approach
- Highly qualified professionalism
- High quality
- First class service
- Competitive prices
And many others, which in fact are not competitive advantages. If only because no company in its right mind would say that its employees are amateurs, and the quality is a little worse than none.
I am generally surprised by the attitude of some businessmen. If you talk to them, everything “somehow” works for them, orders “somehow” go through, there is a profit - and okay. Why invent, describe and count something? But as soon as things start to get tough, that’s when everyone remembers marketing, differentiation from competitors, and the company’s advantages. It is noteworthy that no one is counting the money that was lost due to such a frivolous approach. But this is also profit. Could be...
In 80-90% of cases, Runet businesses do not conduct competitive analysis and do not show the company’s advantages to their clients.
However, there is a positive side to all this. When no one shows their advantages, it’s easier to rebuild. This means it’s easier to attract new customers who are searching and comparing.
Competitive advantages of products (products)
There is another serious mistake that many businesses make when formulating benefits. But here it is worth mentioning right away that this does not apply to monopolists. The essence of the mistake is that the client is shown the advantages of the product or service, but not the company. In practice it looks like this.
That is why it is very important to correctly place emphasis and bring to the fore the benefits and emotions that a person receives and experiences when working with the organization, and not from purchasing the product itself. I repeat, this does not apply to monopolists who produce a product that is inextricably linked with them.
Main competitive advantages: natural and artificial
It's time to return to the varieties of benefits. As I already said, they can be divided into two large groups. Here they are.
Group No. 1: natural (actual) benefits
Representatives of this group exist on their own, as a fact. Only many people don’t write about them. Some think it’s obvious, others because they hide behind corporate clichés. The group includes:
Price- one of the strongest competitive advantages (especially when there are no others). If your prices are lower than those of your competitors, write how much. Those. not “low prices”, but “prices 20% below market prices”. Or “Wholesale prices at retail”. Numbers play a key role, especially when you work in the corporate segment (B2B).
Timing (time). If you are delivering goods from today to today, say so. If you deliver to remote regions of the country in 2-3 days, tell us about it. Very often the issue of delivery times is very acute, and if you have thoroughly worked out logistics, then write specifically where and for how much you can deliver the goods. Again, avoid abstract clichés like “fast/prompt delivery.”
Experience. If your employees are keen on what you sell and know all the ins and outs of your business, write about it. Buyers love working with professionals they can consult with. In addition, when purchasing a product or service from an experienced seller, customers feel more secure, which brings them closer to purchasing from you.
Special conditions. If you have any special delivery conditions (deferred payment, postpayment, discounts, presence of a showroom, geographic location, wide warehouse program or assortment, etc.). Anything that competitors don’t have will do.
Authority. Certificates, diplomas, diplomas, major clients or suppliers, participation in exhibitions and other evidence that increase the significance of your company. The status of a recognized expert is a great help. This is when company employees speak at conferences, have a well-promoted YouTube channel, or give interviews in specialized media.
Narrow specialization. Imagine that you have a Mercedes car. And in front of you are two workshops: a specialized service that deals only with Mercs, and a multidisciplinary one that repairs everything: from UAZs to tractors. Which service will you contact? I bet the first one, even if it has higher prices. This is one of the types of unique selling proposition (USP) - see below.
Other actual benefits. For example, you may have a wider range of products than your competitors. Or a special technology that others do not have (or that everyone has, but which competitors do not write about). Anything can happen here. The main thing is that you have something that others don’t have. As a fact. This also constitutes your USP.
Group No. 2: artificial advantages
I especially love this group because it helps a lot in situations where the customer’s company does not have any advantages as such. This is especially true in the following cases:
- A young company, just entering the market, has no clients, no cases, no reviews. As an option, specialists leave a larger company and organize their own.
- The company occupies a niche somewhere in the middle: it does not have a wide range, like large retail chains, and does not have a narrow specialization. Those. sells goods, like everyone else, at prices slightly above the market average.
- The company has some adjustments, but it is the same as its competitors. Those. everyone in the niche uses the same actual advantages: discounts, experience, etc.
In all three cases, introducing artificial advantages helps. These include:
Added value. For example, you sell laptops. But you can't compete on price with a larger seller. Then you use a trick: install an operating system and a basic set of programs on your laptop, selling it a little more. In other words, you create added value. This also includes various promotions a la “Buy and Win...”, “When buying an apartment - a T-shirt as a gift”, etc.
Personal adjustment. It works great when everyone around is hiding behind corporate clichés. Its essence is that you show the face of the company (for example, the director) and involve. It works great in almost any niche: from selling children's toys to armored doors.
Responsibility. A very strong advantage that I actively use on my laboratory’s website. Combines perfectly with the previous point. People love to work with people who are not afraid to take responsibility for the products and/or services they sell.
Reviews. Provided they are real. The more authoritative the person who gives you feedback, the stronger the impact on the audience (see trigger “”). Reviews on letterhead with a stamp and signature work better.
Demonstration. The best presentation is a demonstration. Let's say you have no other advantages. Or there are, but implicit. Make a clear presentation of what you are selling. If these are services, show how you provide them, make a video. At the same time, it is important to place the accents correctly. For example, if you check each product for functionality, tell us about it. And this will be an advantage for your company.
Cases. This is a kind of visual demonstration of solved problems (completed projects). I always recommend describing them because they work great for sales. But there are situations when there are no cases. This is especially true for young companies. Then you can make so-called artificial cases. The idea is simple: do yourself or a hypothetical client a favor. As an option - to a real client on a mutual basis (depending on the type of services, if possible). This way you will have a case that you can show and demonstrate your expertise.
Unique selling proposition. We have already talked about it a little higher. Its essence is that you enter some detail or disclose information that sets you apart from your competitors. Take me, for example. I provide copywriting services. But many specialists provide a wide range of copywriting services. And my USP is that I guarantee results expressed in numbers. Those. I work with numbers as an objective indicator of performance. And it's catchy. You can find out more about the USP in.
How to find and correctly describe the company's advantages
As I already said, I firmly believe that every company has its own advantages (and disadvantages, but that doesn’t matter now :)). Even if she is a strong middle peasant and sells everything like everyone else. And even if it seems to you that your company does not stand out in any way, the easiest way to understand the situation is to ask directly the clients who are already working with you. Be prepared that the answers may surprise you.
The easiest way to find out the strengths of your company is to ask your clients why they chose you.
Someone will say that they work with you because you are closer (geographically). Some will say that you inspire confidence, while others simply liked you. Collect and analyze this information and it will increase your profits.
But that is not all. Take a piece of paper and write down the strengths and weaknesses of your company. Objectively. Like in spirit. In other words, what you have and what you don’t have (or don’t have yet). At the same time, try to avoid abstractions, replacing them with specifics. Check out the examples.
Not all advantages can and should be written about on the same website. However, at this stage the task is to write down as many strengths and weaknesses of the enterprise as possible. This is an important starting point.

Take a pen and paper. Divide the sheet into two columns and write down the advantages of the company in one and the disadvantages of the company in the second. Maybe with a cup of coffee. Don’t look at the rowan tree, it’s just there for the ambiance.
Yes, we have, but this
Look at the examples:
| Flaw | Turning into an advantage |
|---|---|
| Office on the outskirts | Yes, but the office and warehouse are in one place. You can see the product right away. Free parking even for trucks. |
| Price higher than competitors | Yes, but it comes with a rich package: a computer + an installed operating system + a set of basic programs + a gift. |
| Long delivery on order | Yes, but there are not only standard components, but also rare spare parts for individual orders. |
| Young and inexperienced company | Yes, but there is mobility, high efficiency, flexibility and the absence of bureaucratic delays (these points need to be discussed in detail). |
| Small assortment | Yes, but there is a specialization on the brand. Deeper knowledge of it. The ability to advise better than competitors. |
You get the idea. This gives you several types of competitive advantages:
- Natural (factual information that you have that sets you apart from your competitors)
- Artificial (amplifiers that also set you apart from competitors - guarantees, personal approach, etc.)
- “Shifters” are disadvantages that are turned into advantages. They complement the first two points.
Little trick
I use this trick from time to time, when it is not possible to fully show off my strengths, as well as in a number of other cases when I need something more “weighty”. Then I don’t just write the company’s advantages, but combine them with the benefits that the client receives from the product or service. It turns out to be a kind of “explosive mixture”.
See what this looks like in practice.
- Was: Experience 10 years
- Became: Budget savings of up to 80% due to 10 years of experience
Or another example.
- Was: Low prices
- Became: The price is 15% lower, plus a reduction in transport costs by 10% due to our own fleet of vehicles.
You can learn in detail about how to correctly form benefits from.
Summary
Today we looked at the types of main competitive advantages of a company and, using examples, we looked at how to formulate them correctly. At the same time, it is important to understand that everything that we did today should by default be part of the competitive strategy (if it is being developed). In other words, everything will work better when linked into a single system.
I really hope that the information in this article will expand your capabilities and allow you to conduct competitive analysis more effectively. In turn, if you have any questions, ask them in the comments.
I'm sure you will succeed!
Talk about the number of completed projects, the volume of products produced, publish successful cases. It is very important not to slip into self-praise, but to show how much real benefit your products or services brought.
Are your services useful? Tell us about it!
Post reviews from real customers with links to their social media profiles/company websites so that potential clients can get confirmation. 90% of people will not check the authenticity of these reviews, but such openness on your part will earn their trust.
High level of quality/service
And the standard continuation: “Our company employs highly qualified specialists who have undergone special training.”
At all The qualifications of specialists do not indicate the level of service, unless your employees took courses on “How to lick a client.”
Take the example of hotels for which international service standards have been developed. A person entering a three-star hotel already has a rough idea of what awaits him: a room with an area of at least 12 square meters. m, free bottled water, bathroom with towels, soap and toilet paper.
What can a client expect in your company?
Write to him how quickly the repair will be carried out or the goods will be delivered. Explain how the personal manager will work to solve his problem - step by step, from receiving the application to the result. Convince him that even after completing the order you are always ready to help.
Imagine calling a company about a large contract, and the sales representative replies, “We’re having lunch, call us later.” And hangs up. Will you call him back or find another supplier?
If the company's employees are not polite and friendly, your “high level of service” is worthless.
 What can your employees do?
What can your employees do? And if you want to boast about the professionalism of your employees, tell us about them separately: where they received their qualifications, how long they have been working in their specialty and what they can do.
Individual approach
This expression has not convinced potential customers for a long time, it is so hackneyed. Most often, they simply don’t notice him, and if they do, they grin skeptically, mentally saying “well, well, of course.”
Don't believe me? Look through the websites of your competitors - in 99 cases out of 100 you will find this phrase, if not on the “About the Company” page, then on some other page.
Replace general phrases with specific information.
List point by point everything you rely on when developing a project or completing an order. Explain what you mean by the concept of “individual approach”.
Surely put fulfilling the customer’s wishes first. But you understand that others are doing the same thing. Agree, it’s hard to imagine a designer who makes a red kitchen for clients who dream of a green one.
 Show HOW you fulfill customer desires
Show HOW you fulfill customer desires Write, what is included in your system of relationships with customers →
- How do you satisfy the needs of each client depending on the specifics of the tasks assigned to them. What exactly do you take into account when developing a project or completing an order?
- What additional terms of cooperation can you include in a standard contract at the client’s discretion: different payment schemes, individual discounts, delivery, assembly.
- How broad are the powers of the client who wishes to participate in the process or observe it with the possibility of adjustment. At what point are wishes no longer accepted?
Low prices and/or great deals
Another “nothing” stamp. And if you consider that not only low, but also high prices can drive sales with equal success, then this advantage becomes completely useless.
 Are you trying to attract customers with low prices? Do not do it this way!
Are you trying to attract customers with low prices? Do not do it this way! Instead of empty words use honest numbers.
For example: we offer Scandinavian-style kitchens at prices starting from 20,000 rubles per square meter; the basic package includes standard sections, a countertop, a sink, and a dish dryer.
Or: in January we are reducing the cost of the “Chicardos” collection by 30% - when ordering a kitchen 3 meters long, you save 25,000 rubles.
Most often, companies that have nothing else to attract a client say about low prices. Don't deny the buyer minimum math skills. Believe me, he will do a great job of comparing prices on his own.
When choosing a product, the buyer compares several alternative (not identical!) options:
- wooden houses - with brick and aerated concrete
- white gold jewelry - with silver and platinum
- facial mesotherapy - with sculptural massage and plasma lifting.
Make a comparison table, based on the results of which your proposal wins as the safest, fastest to achieve, durable (warm, prestigious, comfortable - select the advantages of your product or service). And then the price will fade into the background.
A wide range of
These 18 characters without spaces will only become an advantage when the client sees them as a solution to their problems →
 Decipher what gives a wide range
Decipher what gives a wide range - Possibility to choose from a specific product range. You can offer dozens or even hundreds of gold rings, but the buyer is interested in a specific size. And if it is not on the display of the online store, for the client the slogan about the richness of the assortment will remain zilch. An initially loyal visitor will go to competitors next time, so as not to be disappointed again.
- Opportunity to purchase related products- a lid for the frying pan, a brush for collecting animal hair - for the vacuum cleaner, wipes for cleaning the screen - for the monitor. This is beneficial for both parties. The client buys everything in one place and saves on delivery, the seller increases profits by 5-15%.
- Possibility to order a turnkey service. When you talk about a company's wide range of services, list them. Indicate which of them you provide separately and which ones only as a package. For example, a consulting company performs naming exclusively as part of a multi-stage company registration service, while assistance in preparing documents may be outside its scope.
Often a list of useless benefits is posted in the “About Us” section. Already fixed it? Great! Now check whether you have used all the ways to persuade customers on the “About” page. Look into the arguments that hit the mark.
And admit in the comments, do you often have professional professionals with an individual approach working in your companies? 😉
 About the author.
About the author.