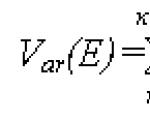Elon Musk on the creation of Space X. What is known about the secret projects of SpaceX and Elon Musk. Falcon and Dragon
February 6, Elon Musk's company. The launch was a test and no payload Falcon Heavy didn’t carry it, the launch vehicle carried the founder’s personal car into outer space Space X - Tesla Roadster red. Now an electric car roams the expanses of space, and the inhabitants of the Earth are shown all this in real time from cameras installed on the vehicle.
Thus, Musk became the first person in the world to launch a car into space.
But this, of course, is not his main achievement in the space sphere.
Firstly, after launch Falcon Heavy two of its three upper stages returned safely to Earth and can be reused. Musk, contrary to the beliefs of NASA, proved that booster blocks from rockets can not be burned in the atmosphere after use, but can be planted back on Earth and then reused, which has significantly reduced the cost of space flights.
Secondly, Falcon Heavy- a launch vehicle that has never existed in the history of space research. Theoretically, it is capable of delivering up to 63 tons of cargo into low Earth orbit. This rocket is capable of sending more than 16 tons of cargo to Mars. The cost of one launch is estimated at 80-120 million dollars, depending on the rocket load.
None of the modern launch vehicles is capable of launching such cargo into orbit. For example, American Delta IV Heavy, the largest rocket in existence, is capable of delivering about 29 tons to low orbit and only 14 tons to geostationary orbit. The cost of launching such a rocket is estimated at $400 million; and she, unlike the development SpaceX, there is no way to return the upper stages to Earth.
Musk certainly owes this success to his own perseverance, ability to go towards a goal and faith in the idea, because he did not give up after several unsuccessful launches of his first rockets, along with which millions of dollars invested in their construction exploded or crashed.
But, no matter how unexpected it may sound, Russia gave him the impetus for this success. In 2001, the entrepreneur held several meetings in Moscow, including with representatives of the Kosmotras company, trying to negotiate the purchase of an intercontinental ballistic missile to send mice to Mars.
This story was told by journalist Ashley Vance in his biography of the entrepreneur, “ Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX and the search for a fantastic future", excerpts from which were published by Bloomberg.
However, the negotiations ended in vain, since the Russians did not take the businessman’s proposals seriously.
In February 2002, Musk decided to convince them of the seriousness of his intentions by returning to Russia with money, then he wanted to purchase three rockets. But Kosmotras set him a price of $8 million for the rocket. He tried to bargain, offering to pay this amount for two missiles. The Russians refused, teasing Musk with the phrase: “Oh, the little boy has no money.”
Musk replied that he could build a rocket himself and left the meeting.
During a flight from Russia to the United States, he sketched out a plan for further action and told his stunned partners that he had decided to build the rockets himself. This is how the story began SpaceX. In September 2008, the rocket Falcon 1 became the first private liquid fuel rocket in history to enter Earth orbit. To the success of the rockets Falcon preceded by three unsuccessful launches. After this, Musk managed to learn how to return the upper stages to Earth, some of them have already been reused.
Well, then there was Falcon Heavy, which impressed the whole world, everyone called its launch a breakthrough, but the Russians perceived it skeptically, perhaps because at one time they lost the chance to be involved in the achievements of the genius Elon Musk.
The head of the Institute of Space Policy of Russia Ivan Moiseev called the launch Falcon Heavy an undoubted success, but urged not to exaggerate the significance of the launch, writes Vzglyad.
"I wouldn't use it in relation to launch Falcon Heavy such big words as “revolution” in the field of space,” Moiseev noted.
According to him, if you weigh history on the scales, this does not reach either the first manned flight into space or the landing of man on the moon.
The expert emphasized that “so far this is only the first test launch, and the start of regular operation of the rocket is still far away.” Secondly, according to him, we should not forget that Musk still did not meet his original schedule - the entrepreneur promised to carry out the first launch Falcon Heavy in the summer of 2017, that is, six months earlier than it actually happened.
SpaceX founder Elon Musk believes that there is a 70% chance that he will be able to fly to Mars. The 47-year-old inventor stated this in an interview with the website.
The investor suggested that such an expedition using new multi-purpose launch vehicles being developed by SpaceX would become possible within seven years, and the cost of a ticket for one space tourist would not exceed “several hundred thousand dollars.”
"We've recently made some discoveries that I'm very excited about," the entrepreneur added.
“I clearly know what needs to be done. I’m talking about the opportunity to move there,” he emphasized.
At the same time, Musk ruled out that such a flight would be a kind of escape for the wealthy segment of the population from the problems that they may encounter on Earth.
“The likelihood that you will die on Mars is much higher than on Earth,” admitted the publication’s interlocutor.
He did not rule out that death could occur during the flight in outer space. If this does not happen, you will still have to “work tirelessly building a base” on the Red Planet, the entrepreneur added.
“And even if you overcome all this, the conditions there are very harsh... The probability of death is very high,” he repeated.
At the same time, Musk expressed confidence that, despite all the difficulties, he would undoubtedly go on such an expedition: “There are climbers. Someone always dies on Everest. For them, this is a kind of challenge.”
Let us remind you that the super-heavy one - now its manned part and upper stages will be called Starship, and the reused lower stage will be called Super Heavy.
What big announcements should we expect in the coming years? And, most importantly, where will Musk get the money for this?
Elon Musk's SpaceX has many ambitious projects, but two stand out among them - entwining the planet with a network of Internet satellites and building a huge rocket that can take people to the Moon and Mars. There is little information about these plans, but we still know something - from the company’s reporting, Elon Musk’s tweets and published ones.
SpaceX's flagship product, the Falcon 9 rocket, recently received NASA certification for its most expensive science missions. Company President Gwynne Shotwell called the event "a major achievement for the Falcon 9 team." The company said at least 22 Falcon 9 launches are planned for 2019, highlighting the reliability of the rocket that will carry astronauts into orbit next year.
But around the world, only $5.5 billion is spent annually on rocket launches, and this money also goes to competitors from Europe, Russia and China. So SpaceX needs to develop new businesses to justify its $27 billion valuation.
Internet from space
The global goal of the Starlink project is to launch several thousand satellites into low Earth orbit and provide Internet access to all users on Earth. The company has been developing these plans for several years. This year the news is mixed. On the one hand, two test satellites have been launched and approval has been received from the US government. On the other hand, there have been changes in the project management, and today SpaceX refuses to say who is now responsible for the design and construction of satellites.
However, the company still plans to launch the service in 2020, with the first batch of satellites expected to be in orbit by the end of next year. Computer scientist Mark Handley from University College London believes that Internet connections will be so fast that high-speed trading (high-frequency trading - trading using special strategies in which computers buy and sell positions within fractions of a second - Ed.) will be able to use it. .).
Recently, the US Federal Communications Commission, led by Ajit Pai, took an initiative to ease regulation of space-related businesses. And this is to SpaceX's advantage, since the Starlink project requires the launch of 4,425 satellites, which will double the number of devices in orbit and increase the risk of collisions and space debris.
On November 7, the SpaceX executive working to obtain satellite licenses met with Pai to show how seriously SpaceX takes this problem, since the company's survival depends on the ability to launch satellites, which means it is the most threatened by space debris. The next day, SpaceX submitted an application to reduce the orbital altitude of future satellites by 560 kilometers relative to the original plans.
A lower orbit reduces the risks associated with debris generation because satellites will deorbit and burn up in the atmosphere within five years, and there will also be 16 fewer satellites needed and faster connection speeds. On the other hand, SpaceX will have to sacrifice some of its service reach and amortize its satellite investment in a shorter time frame, but the company clearly believes that these costs will make it easier for regulators and shareholders to approve.
Matt Desch, CEO of Iridium, which provides satellite communications services and uses SpaceX to launch satellites into orbit, called the move “a very responsible one.”
Financing of rocket launches

Musk says the goal of the Starlink project is to raise money for the company's Mars mission. However, launching the system itself will not be cheap, and SpaceX plans to borrow money. According to Bloomberg, the company hopes to raise $750 million, and Bank of America will act as the organizer of the round.
It is reported that initially they wanted to organize the deal through the bank Goldman Sachs, with which Musk usually cooperates, but investment bankers refused to participate, suggesting that the company would continue to lend more and more. Today, SpaceX doesn't have major debt and even has a profit, but the company does rely on debt to finance future launches and government projects.
The company's first spacecraft, called Falcon 1, was financed mainly from Musk's personal funds. The next major project, the Falcon 9 and Dragon spacecraft, was created with government support. In 2015, Google and Fidelity invested $1 billion in SpaceX, partly for the Starlink project. But raising funds to build the huge, fully reusable BFR rocket capable of taking people to Mars (which the company wants to launch by 2022) is much more difficult.
Another source of profit is space tourism. It is known that Musk accepted a significant deposit of the order of hundreds of millions of dollars from Japanese billionaire Yusaku Maezawa for a future flight around the Moon.

Last Saturday Musk
SpaceX Falcon Heavy was looking forward to the launch of the Space X Falcon Heavy rocket (the rocket was launched from Cape Canaveral in Florida on February 6 - editor's note) the entire space industry.
What's special about this rocket?
It will be the first of its kind, the world's most powerful launch vehicle designed for repeated use. The Space X Falcon launch has been delayed several times since 2013, but if all goes well, we'll be one step closer to Musk's incredibly ambitious goal of a manned mission to Mars within the next decade.
Context
Russia's competition plan with SpaceX has a flaw
Ars Technica 11/16/2017 However, rocket science is a complex thing. Even Elon Musk, as CEO of SpaceX, is reserved in his assessments: “Everything has gone further than originally planned on paper. I hope this doesn't lead to any surprises. I'd like to think this is a victory."We will also have to wait for the launch and see what happens next. Absolutely in the style of Elon Musk, the payload for the rocket will be his Tesla Roadster electric car, which will become the fastest car in the world launched into space.
Rockets capable of carrying a payload weighing more than 20 tons are classified as super-heavy launch vehicles. To enter orbit, the rocket must reach a speed of over 8 thousand meters per second at a distance of 160 kilometers above the Earth's surface.
To illustrate these numbers, imagine that a rocket could carry two fully loaded city buses to an altitude greater than 50 Everests, and at a speed that is 32 times the cruising speed of a Boeing 747.
Falcon Heavy will achieve this goal using three boosters "linked together." The central one will lift the Tesla Roadster into space and enter an elliptical orbit between Earth and Mars. The electric car will remain in this orbit for thousands of years.
Pioneers of the new space
Multimedia
NASA 02/20/2017 Since the launch of the first space missions, space exploration, as a rule, has been a state sphere. Governments created and funded organizations such as NASA, the European Space Agency, the Russian agency Roscosmos, and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency.Along with these agencies, private space companies were created. However, given the enormous costs of space exploration, space innovation has always been driven by governments.
But in the 21st century everything begins to change. SpaceX has figured out how to reduce the cost of launching reusable launch vehicles and increase their efficiency. The new space industry is growing at a tremendous pace, and SpaceX is leading the way.
SpaceX's ambitions don't end with launching space satellites with the Falcon Heavy. The rocket was designed so that it could also be used for manned missions. SpaceX also plans to complete testing of its capsule for astronauts Dragon2 - a contract with two space tourists, whose names have not yet been disclosed, has already been signed. They will embark on a week-long flight around the moon.
Will everything work out?
Unfortunately, quite often the first rocket launches are unsuccessful. Typically, companies conduct test trials over several years. And, for example, in 2016, SpaceX engineers faced numerous problems.
But Falcon Heavy is a very ambitious endeavor for SpaceX, and no matter what, Falcon will leave its mark on the skies, to one degree or another. In addition, it is already absolutely clear that Musk is changing the landscape of the entire space industry, with far-reaching consequences.
Ben Thornber, engineer, space innovation researcher, associate professor at the University of Sydney.
InoSMI materials contain assessments exclusively of foreign media and do not reflect the position of the InoSMI editorial staff.
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) February 7, 2018
The publication also draws attention to the remark of some astronomers regarding the real trajectory of Tesla. The electric car actually flew further than the orbit of Mars, they say, but not far enough to end up in the asteroid belt. Scientists provide some calculations, but they have not become the subject of widespread discussion.
Why did Musk send Tesla into space?
Many experts and columnists called Tesla's launch into space a large-scale advertising campaign.
“Musk, the master marketer of our time, has found the perfect way to make science sexy and memorable for everyone: the Tesla Roadster. Without the human element, even the fiery eruptions of a rocket launch can begin to feel repetitive, especially in this age of instant access to the immersive and otherworldly. So Musk thought, ‘How about a sleek red supercar to spark the imagination?’” Vlad Savov, one of The Verge’s editors, wrote in his column.
The launch turned out to be literally assembled from spectacular details - the inscription Made on Earth by Humans (“Made on Earth by Humans”), which was printed on the car, a sign with the names of six thousand SpaceX employees.
Inside the electric car, the message “Don’t Panic!” glows as a reference to “The Hitchhiker’s Guide to the Galaxy,” a series of science fiction novels by English writer Douglas Adams. A few years ago, in an interview, Musk said that one of his favorite science fiction spaceships was from The Hitchhiker's Guide to the Galaxy. He admitted that he first read the book when he was a teenager and suffered from an existential crisis trying to determine the meaning of life.
 SpaceX
SpaceX
Other memorable parts of the flight included the Starman mannequin from David Bowie's song of the same name wearing a SpaceX spacesuit. And, of course, the continuously repeating song Space Oddity inside the Tesla. All this and much more are called elements of great advertising for Tesla, which is now in a difficult situation.
Musk himself spoke, which considers the usual payload used in such launches - most often concrete and steel blocks - to be "terribly boring". He said he wanted to send “something unusual that would make us feel” into space. However, some experts associated this decision with the fact that the first launch of the new rocket could be unsuccessful.
Since 2016, Musk’s company has been developing Tesla 3. Now Musk is faced with the task of launching the model and beginning its mass production. The company has approximately 400 thousand customers interested in purchasing electric vehicles - a deposit of $1,000 was taken from each of them.
Sales and, accordingly, Tesla's income will increase if the company can quickly set up production, writes The New York Times. If two years ago Musk promised to produce 500 thousand cars of this model by 2018, then in January he planned to produce only about 2.5 thousand - however, promising to increase production volume, the newspaper notes.
However, Tesla has lost money in eight of the last nine quarters. The day before, the company reported a record quarterly loss of $675 million in the fourth quarter of 2017, while losses in the same period last year were $121 million. The New York Times also links the decision to send Tesla into space with Musk's attempt to restore the company, including the production of Tesla 3.
Tesla, after the launch of Falcon Heavy, will be able to confidently say that its electric car was sent into space and is there. According to The Verge's editor, this will help distract attention from some of Tesla's problems, including the release of the Tesla 3. "This is the biggest advertising stunt we've seen in a long time," he wrote.
Tesla is now valued at about $58 billion.
How Musk assessed the first launch of Falcon Heavy
“I imagined the image of a giant explosion on the launch pad, a Tesla wheel bouncing along the road, the Tesla logo falling somewhere. Fortunately, none of this happened,” he said at the first press conference after the launch.
 John Raoux/Associated Press
John Raoux/Associated Press
Even before the launch of Falcon Heavy, Musk said that the likelihood of an accident at launch is very high. However, on the eve of the flight, he told CNN that he usually feels “super stressed” the day before sending a rocket into space. “Right now, though, I feel pretty giddy and happy. And that could be a bad sign,” he added.
Before the press conference, Musk inspected both returned boosters. He noted that they are in good condition, especially the titanium lattice rudders - this is especially important for SpaceX, since their production has proven to be quite expensive and difficult.
According to Musk, SpaceX does not have a forecast regarding the behavior of the electric car after entering orbit. “It might just be in space for millions or billions of years. Maybe some future alien intelligence will discover it and think, “What the hell is this?” What did these guys do? Did they worship this machine? Why is there another small car in this car?’ This whole thing is going to really confuse them,” Musk said.
Musk said that he was convinced that the most incredible things can come true. “I really didn’t think it would work: that I would see a rocket rise, see a thousand things that seem like they couldn’t work—and it was just amazing when they worked.”
How experts assessed the Falcon Heavy launch
Experts greeted the launch mostly positively, congratulating Musk and the SpaceX team.
The Falcon Heavy launch is a reminder of how quickly the private space industry has grown over the past five to ten years, Phil Larson, a former SpaceX employee who now works as an assistant dean at the University of Colorado, told Mashable. Like many experts, he links the flight to creating conditions for US economic competitiveness and national security.
University of Southern California professor and former NASA employee Greg Autry says the Falcon Heavy launch is a case of a private company "simply outperforming every government on earth." “This is bigger than anything Russia or China is doing. Nobody is close to such results yet,” he told Bloomberg.
“You see this so often with space, and even with exploration missions to Mars and Pluto: people feel almost an antidote to the everyday world of social networks, where we persist (to try to attract them to the topic of space - approx.). And now this process is almost literally and metaphorically forcing people from their own devices to look at how space is explored,” Casey Dreyer, co-manager of the US NGO Planetary Society, told The Guardian.
Astronaut Gerald Carr praised Musk for "breaking a new frontier in space." “Mars is the next logical step in space exploration,” he told The Guardian.
With whom and how can SpaceX compete?
Private companies began launching as early as 1980, when the French company Arianespace was created. However, until recently, customers wishing to launch a satellite into orbit primarily relied on rockets owned by the United States or Russia, Forbes notes. Recent developments in competition have led to increased investment in private space ventures around the world. A Forbes columnist asks who will win the new commercial space race that came after the Cold War.
Mashable predicts that Musk will soon face a competitor quite comparable to him in the future - the aerospace company Blue Origin of Jeff Bezos (also the founder of Amazon.com and owner of the publishing house The Washington Post). The company was created back in 2000 (SpaceX - in 2002) to develop space tourism. Bezos is now also working on a new super-heavy space rocket project.
 Gregg Newton/Reuters
Gregg Newton/Reuters
SpaceX's advantage is in creating reusable rockets, which can significantly reduce production costs. Bloomberg, comparing various launches as an example, notes that with the cost of one Falcon Heavy launch being $90 million, SpaceX is now capable of delivering twice as much cargo as the company's main competitors - and this price will still be about a fifth of the average cost of other launches.
One flight of Falcon 9 costs about $62 million, Falcon Heavy - about $90 million. For comparison: the flight of the United Launch Alliance's one-time two-stage Atlas 5 launch vehicle (a joint company between Boeing and Lockheed Martin) costs $109 million. It is expected that the launch of the super-heavy launch vehicle Space Launch System, which is being developed by NASA, will cost at least ten times more than the launch of Falcon Heavy.
But now, new commercial opportunities for private space companies seem to be more intriguing projects, Bloomberg notes. The publication cites tasks that some are already developing or testing - for example, equipment for asteroid mining. If we add to this the fact that super-heavy rockets will become cheaper and more reliable, then obtaining energy from outer space will no longer be science fiction.
How Musk's relationship with the White House affects the development of SpaceX
The success of SpaceX is largely due to the political climate in the United States and almost constant cooperation with NASA throughout almost the entire history of the company, writes The Verge. US President Donald Trump congratulated Elon Musk on Twitter on the launch of Falcon Heavy almost immediately.
Thank you on behalf of SpaceX. An exciting future lies ahead!
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) February 7, 2018
Recently, Trump signed documents for a program related to the US focusing, among other things, on the Moon. The US President instructed NASA to begin preparing a manned flight to the Earth's satellite. The Verge notes that SpaceX clearly expects that nothing will change in the near future in this state interest in space.
However, many of SpaceX's plans could be cut short if the Trump administration ends funding for the International Space Station program after 2024. According to media sources, including The Verge, Trump is considering this option. It is expected that the draft US federal budget for 2019 will be presented in February.
Reducing funding for the ISS, which now amounts to approximately $3-4 billion a year, would be a step backward and would not be in the country's interests, American astronaut Mark Kelly wrote in a column for The New York Times. He noted that NASA programs have been bringing benefits to people since the second half of the 20th century - for example, they helped in the development of solar technologies, microscopic computer chips, and contributed to the emergence of computed tomography and MRI. Kelly calls research funding one of the best uses of taxpayer money. “Not only does it create new jobs, but it also creates industries that would never have come into existence otherwise. It’s quite easy to see how a dollar spent on our space program will come back to the taxpayer many times over,” he said.
Previously, Elon Musk was on the White House council, where he was one of the consultants. However, in June 2017, he announced that he was leaving the board. This was due to Trump's decision to withdraw the United States from the Paris climate agreement. Musk publicly announced his decision, noting that climate change is very real, and stopping work on it is not good for America or the world.
What Musk is most often criticized for and what questions he does not answer
One of the harshest criticisms of Musk can be found in the Opinions column of The Guardian newspaper. In his column, news editor Nathan Robinson criticized SpaceX for its massive spending. He noted that on the day of the Falcon Heavy's launch, another important news was the death of 80 people in Syria as a result of a long civil conflict. “Meanwhile, in Florida, Elon Musk launched his sports car into space. Guess which story dominated the major news sites?”
Robinson even calls Musk’s actions “the tragedy of global inequality of the 21st century.” “There’s probably no better way to appreciate it than to watch a billionaire spend $90 million to launch a $100,000 car into the far reaches of the solar system,” he writes, beginning to list the world’s many social problems—war, poverty, disease, violence. . In his opinion, Musk unreasonably spends money on demonstration flights, without paying attention to spending on social spheres, where the situation of people is often critical.
Analyzing Musk's plans, The Verge notes that there are still questions to which he does not provide concrete answers. For example, one of the main questions from the professional community about Musk is the details of his plan to colonize Mars: how exactly he is going to organize a human habitat there, where people will live for so long and how exactly can one get there, taking into account the serious radiation factor. In addition, it is still not clear how this project is planned to be financed.
Bloomberg also released a list of his questions for Musk - they relate to Tesla. The publication is interested in how many electric cars the company can actually produce, what share of Tesla’s income comes from customer deposits for future cars, how exactly the company plans to enter the Chinese market and whether this can really be considered a success.
Speaking about Musk's weaknesses, The Verge notes frequent postponements of testing or launches of various rockets, and sometimes their absence altogether. However, he adds that the results are often impressive.
Falcon 9, Dragon, Big Falcon Rocket: what you need to know about other SpaceX projects
Falcon 9 was first launched in 2010. It consists of two stages. This type of rocket can be either disposable or reusable. It uses kerosene and liquid oxygen as fuel. The nine in the name indicates the number of liquid rocket engines that are installed on the first stage of the launch vehicle.
Falcon 9 is the rocket that actually allows SpaceX to make money, writes The Verge. In 2017, it completed eighteen successful missions, and in 2018, SpaceX plans to accomplish even more with its help. The Falcon 9 primarily sends satellites into space and delivers cargo to the International Space Station. In addition, Falcon 9 is directly related to the collaboration between SpaceX and NASA - the launch vehicle is an integral part of the Dragon cargo spacecraft.
Reusable unmanned spacecraft Dragon developed by SpaceX for NASA. This is one of SpaceX's longest-running projects - the company began working on it back in 2004. The space agency ordered a model for working with cargo - delivering it into space and returning it. In the future, they also plan to transport people to the International Space Station.
The Dragon has several modifications: a cargo type, manned with a crew of up to seven people, and a mixed type - a combined cargo and passenger type, which is capable of carrying up to four people and several tons of cargo. SpaceX partially connects its Martian plans with one of the Dragon modifications, in particular those related to research on the planet.
One of the most anticipated models right now is the Dragon V2 manned spacecraft. Already in the second half of 2018, Musk plans to send several people on it to the Moon. It is known that they have already been selected - these are two non-astronauts who know each other and are not associated with Hollywood. Musk has so far refused to name them. They are expected to fly around the Moon without landing. In the near future they will begin to actively prepare them for flight. The cost of such a space trip is estimated at $150 million.
Big Falcon Rocket(BFR) is still a project of a reusable launch vehicle and spacecraft, which should replace the existing SpaceX rockets. Musk spoke about its development in September 2017. One of the main goals of the project is human flights to the Moon and Mars. Musk said that the rocket could, in principle, help carry out fast flights around the Earth. He recently said that SpaceX may abandon plans to send people into space using the Falcon Heavy and use the BFR to do so.
BFR is larger than SpaceX's current rockets. It is expected that it will be capable of launching up to 150 tons of cargo into orbit.
The approximate date for the first testing of BFR was previously called 2019. The tests are planned to be carried out at one of the company's facilities in Brownsville (Texas). The Verge suggests that this will be similar to the very first tests of the Falcon 9, which were carried out as normal flights of about a few hundred meters.
If the BFR isn't ready in time, SpaceX could return to plans to send people into space on the Dragon and Falcon Heavy.
When will SpaceX launch Falcon Heavy again?
In the next 3-6 months, SpaceX will not try to launch Falcon Heavy again, Musk said. The duration of the interval between flights, he said, depends on two factors: the speed at which the company produces the core part of the rocket and customer demand. External boosters—that is, upgraded Falcon 9 boosters—are easier to manufacture.
The central core of Falcon Heavy also has parts from the Falcon 9 - the same engines, for example - but the rest of it (i.e. the core) must be completely modeled for each individual flight. Therefore, it can be considered that the frequency of Falcon Heavy flights mainly depends on the production rate of the central booster. However, Musk promises to organize fairly fast production. He states: “Whatever the demand (for launches - approx.), We will be able to meet it halfway.”
It is now quite difficult to analyze and forecast this demand in detail, notes The Verge. In 2018, SpaceX has several large-scale launches planned, including projects related to Saudi Arabia and American military structures.
It is now known that the next launch of Falcon Heavy will not use the blocks or any major parts of the last first flight. The two side boosters are already obsolete, serving on various Falcon 9 missions. The next Falcon Heavy will consist of a new center and side boosters.
At the same time, SpaceX can still use parts of the rockets of the first launch - for example, writes The Verge, the metal of the upper part of each of them, parts of which helped guide the structure safely to the ground. They are made from titanium, and this process is quite long and expensive.
Why did they start talking about a new space age?
CNN columnist Gene Seymour called the launch "the beginning of a new space age." “Although many of the details referred to the old (century), but only in a positive sense,” he added. The main feature of the present time, which distinguishes it from the past space age, is private companies that have decided to organize space travel. Previously, only governments could do this kind of thing. Another feature, no less significant in Seymour's opinion, is that there should be no winner in the new space race. It's about competition, not confrontation.
“Is it worth it? We won't know until we try. Musk will most likely say yes - and NASA will answer the same. This is not the most detailed or satisfying answer. But until something better happens, sit back and enjoy the show."
 SpaceX
SpaceX